Hendri Murfi
BERT-Based Combination of Convolutional and Recurrent Neural Network for Indonesian Sentiment Analysis
Nov 10, 2022Abstract:Sentiment analysis is the computational study of opinions and emotions ex-pressed in text. Deep learning is a model that is currently producing state-of-the-art in various application domains, including sentiment analysis. Many researchers are using a hybrid approach that combines different deep learning models and has been shown to improve model performance. In sentiment analysis, input in text data is first converted into a numerical representation. The standard method used to obtain a text representation is the fine-tuned embedding method. However, this method does not pay attention to each word's context in the sentence. Therefore, the Bidirectional Encoder Representation from Transformer (BERT) model is used to obtain text representations based on the context and position of words in sentences. This research extends the previous hybrid deep learning using BERT representation for Indonesian sentiment analysis. Our simulation shows that the BERT representation improves the accuracies of all hybrid architectures. The BERT-based LSTM-CNN also reaches slightly better accuracies than other BERT-based hybrid architectures.
Deep Autoencoder-based Fuzzy C-Means for Topic Detection
Feb 02, 2021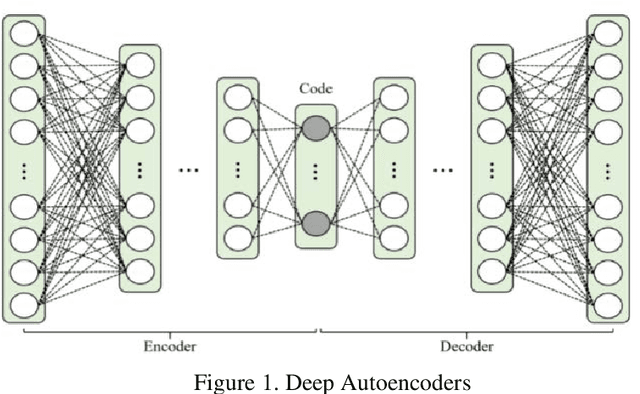
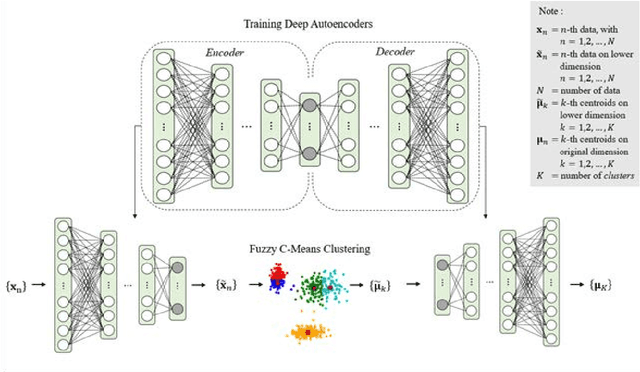
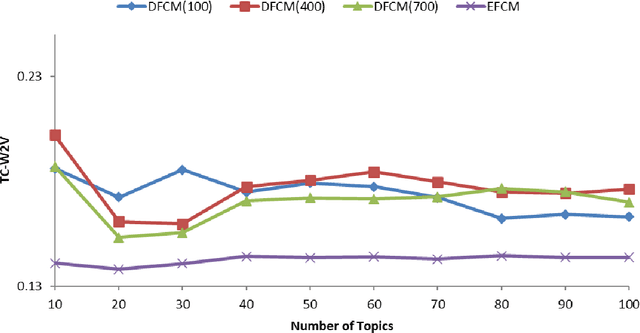
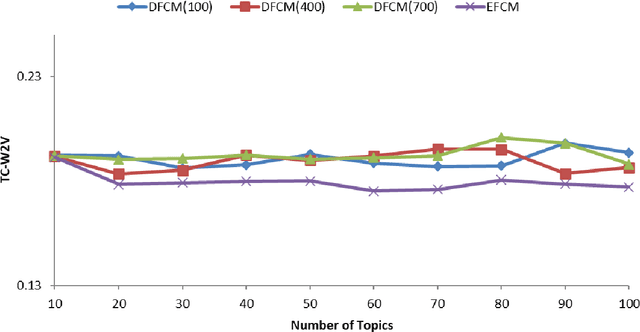
Abstract:Topic detection is a process for determining topics from a collection of textual data. One of the topic detection methods is a clustering-based method, which assumes that the centroids are topics. The clustering method has the advantage that it can process data with negative representations. Therefore, the clustering method allows a combination with a broader representation learning method. In this paper, we adopt deep learning for topic detection by using a deep autoencoder and fuzzy c-means called deep autoencoder-based fuzzy c-means (DFCM). The encoder of the autoencoder performs a lower-dimensional representation learning. Fuzzy c-means groups the lower-dimensional representation to identify the centroids. The autoencoder's decoder transforms back the centroids into the original representation to be interpreted as the topics. Our simulation shows that DFCM improves the coherence score of eigenspace-based fuzzy c-means (EFCM) and is comparable to the leading standard methods, i.e., nonnegative matrix factorization (NMF) or latent Dirichlet allocation (LDA).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge