Hanuman Verma
An Intuitionistic Fuzzy Logic Driven UNet architecture: Application to Brain Image segmentation
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Accurate segmentation of MRI brain images is essential for image analysis, diagnosis of neuro-logical disorders and medical image computing. In the deep learning approach, the convolutional neural networks (CNNs), especially UNet, are widely applied in medical image segmentation. However, it is difficult to deal with uncertainty due to the partial volume effect in brain images. To overcome this limitation, we propose an enhanced framework, named UNet with intuitionistic fuzzy logic (IF-UNet), which incorporates intuitionistic fuzzy logic into UNet. The model processes input data in terms of membership, nonmembership, and hesitation degrees, allowing it to better address tissue ambiguity resulting from partial volume effects and boundary uncertainties. The proposed architecture is evaluated on the Internet Brain Segmentation Repository (IBSR) dataset, and its performance is computed using accuracy, Dice coefficient, and intersection over union (IoU). Experimental results confirm that IF-UNet improves segmentation quality with handling uncertainty in brain images.
Temporal Deep Learning Architecture for Prediction of COVID-19 Cases in India
Aug 31, 2021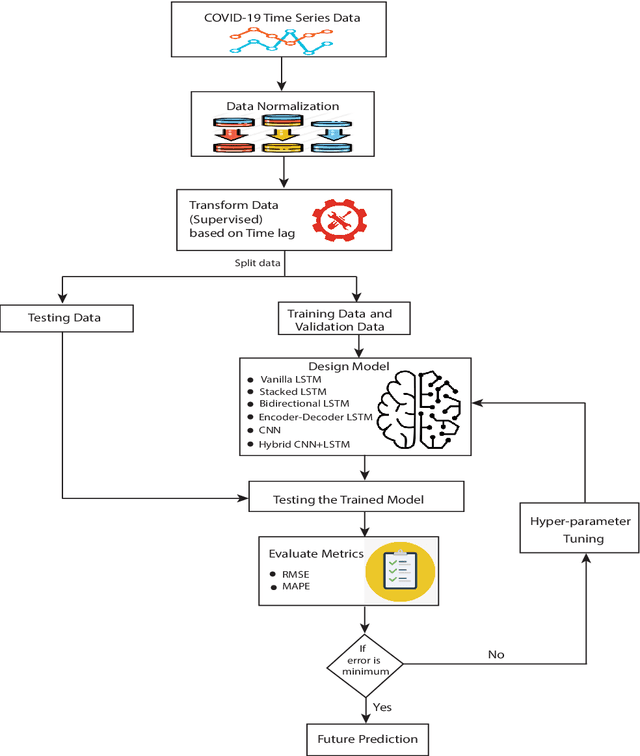
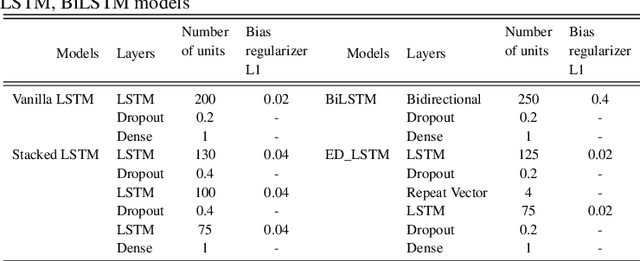
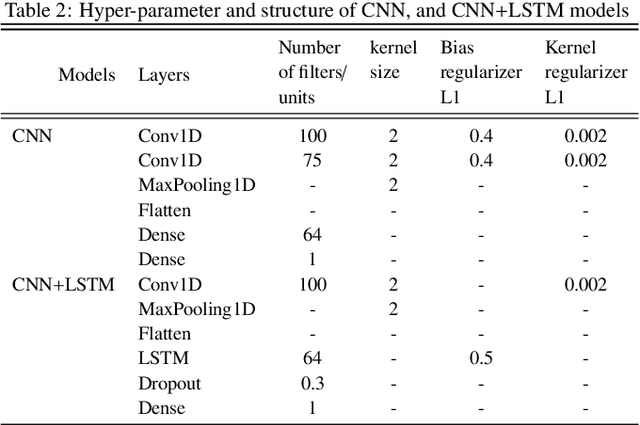
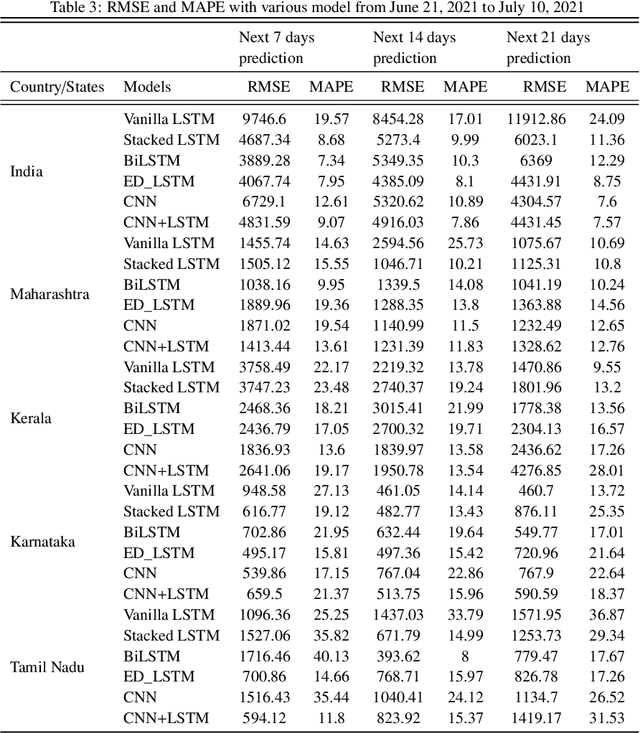
Abstract:To combat the recent coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), academician and clinician are in search of new approaches to predict the COVID-19 outbreak dynamic trends that may slow down or stop the pandemic. Epidemiological models like Susceptible-Infected-Recovered (SIR) and its variants are helpful to understand the dynamics trend of pandemic that may be used in decision making to optimize possible controls from the infectious disease. But these epidemiological models based on mathematical assumptions may not predict the real pandemic situation. Recently the new machine learning approaches are being used to understand the dynamic trend of COVID-19 spread. In this paper, we designed the recurrent and convolutional neural network models: vanilla LSTM, stacked LSTM, ED-LSTM, Bi-LSTM, CNN, and hybrid CNN+LSTM model to capture the complex trend of COVID-19 outbreak and perform the forecasting of COVID-19 daily confirmed cases of 7, 14, 21 days for India and its four most affected states (Maharashtra, Kerala, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu). The root mean square error (RMSE) and mean absolute percentage error (MAPE) evaluation metric are computed on the testing data to demonstrate the relative performance of these models. The results show that the stacked LSTM and hybrid CNN+LSTM models perform best relative to other models.
Analysis of COVID-19 cases in India through Machine Learning: A Study of Intervention
Aug 17, 2020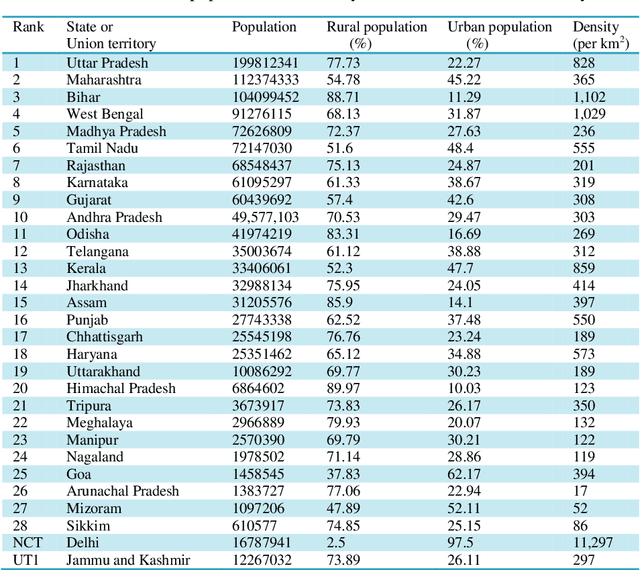
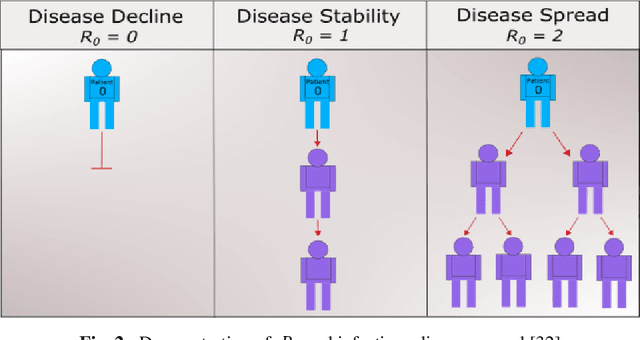
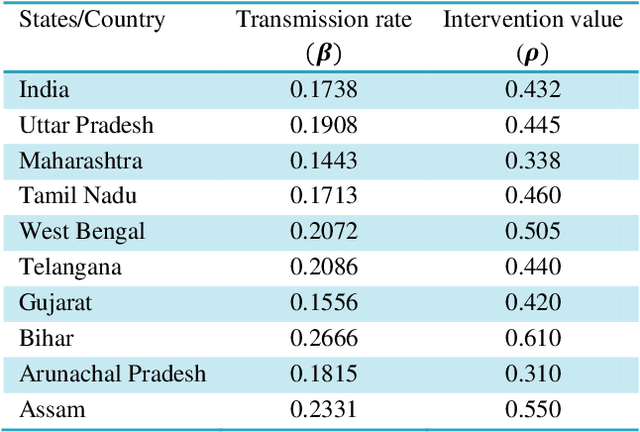
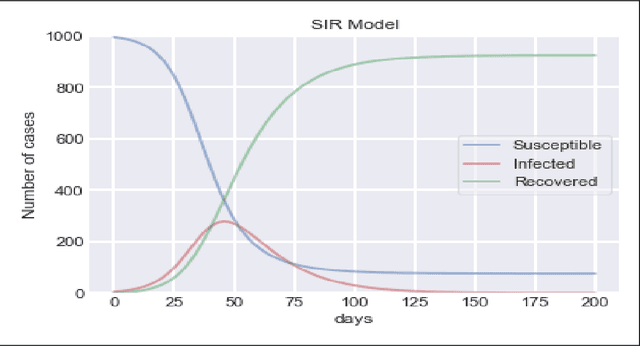
Abstract:To combat the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, the world has vaccination, plasma therapy, herd immunity, and epidemiological interventions as few possible options. The COVID-19 vaccine development is underway and it may take a significant amount of time to develop the vaccine and after development, it will take time to vaccinate the entire population, and plasma therapy has some limitations. Herd immunity can be a plausible option to fight COVID-19 for small countries. But for a country with huge population like India, herd immunity is not a plausible option, because to acquire herd immunity approximately 67% of the population has to be recovered from COVID-19 infection, which will put an extra burden on medical system of the country and will result in a huge loss of human life. Thus epidemiological interventions (complete lockdown, partial lockdown, quarantine, isolation, social distancing, etc.) are some suitable strategies in India to slow down the COVID-19 spread until the vaccine development. In this work, we have suggested the SIR model with intervention, which incorporates the epidemiological interventions in the classical SIR model. To model the effect of the interventions, we have introduced \r{ho} as the intervention parameter. \r{ho} is a cumulative quantity which covers all type of intervention. We have also discussed the supervised machine learning approach to estimate the transmission rate (\b{eta}) for the SIR model with intervention from the prevalence of COVID-19 data in India and some states of India. To validate our model, we present a comparison between the actual and model-predicted number of COVID-19 cases. Using our model, we also present predicted numbers of active and recovered COVID-19 cases till Sept 30, 2020, for entire India and some states of India and also estimate the 95% and 99% confidence interval for the predicted cases.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge