Habib Asseiss Neto
NASirt: AutoML based learning with instance-level complexity information
Aug 26, 2020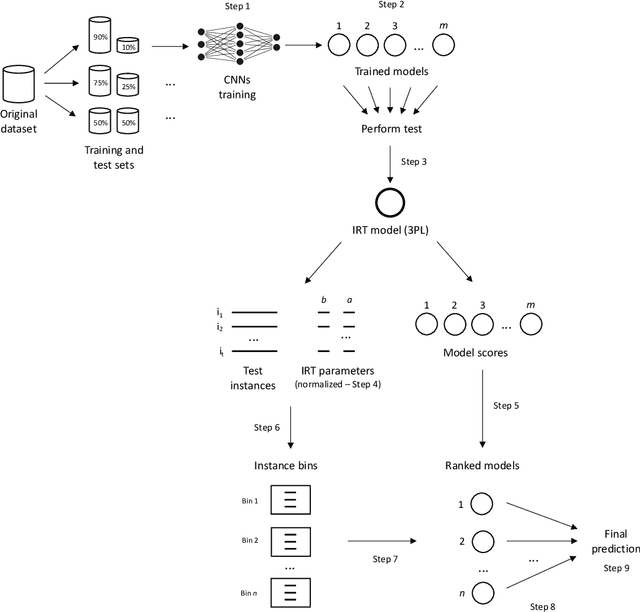
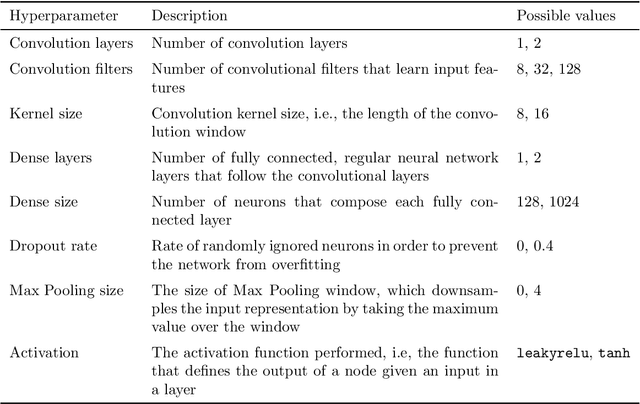
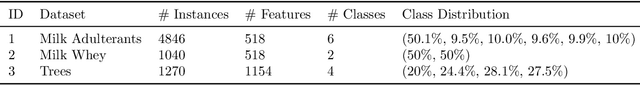
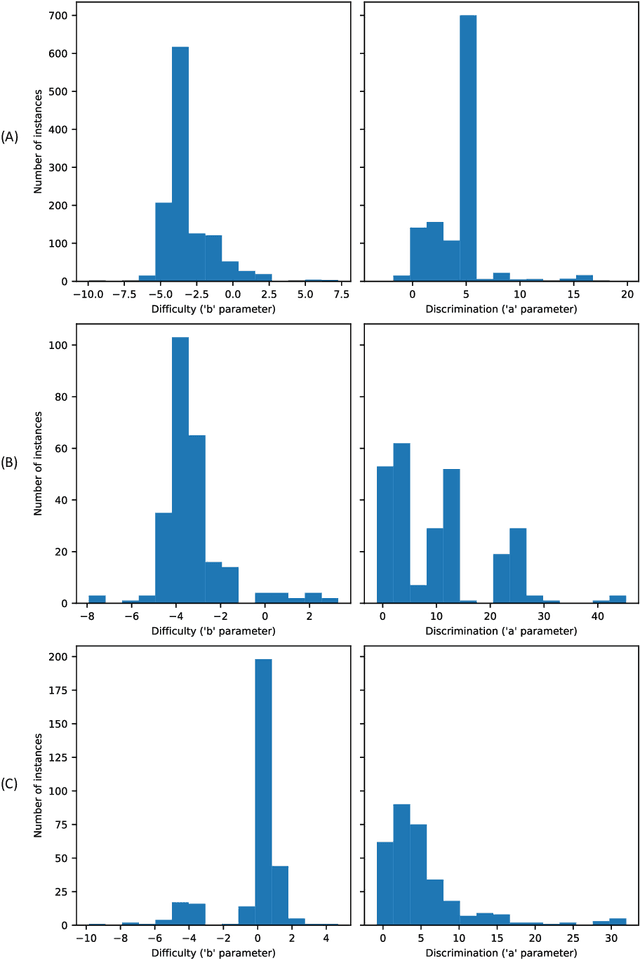
Abstract:Designing adequate and precise neural architectures is a challenging task, often done by highly specialized personnel. AutoML is a machine learning field that aims to generate good performing models in an automated way. Spectral data such as those obtained from biological analysis have generally a lot of important information, and these data are specifically well suited to Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) due to their image-like shape. In this work we present NASirt, an AutoML methodology based on Neural Architecture Search (NAS) that finds high accuracy CNN architectures for spectral datasets. The proposed methodology relies on the Item Response Theory (IRT) for obtaining characteristics from an instance level, such as discrimination and difficulty, and it is able to define a rank of top performing submodels. Several experiments are performed in order to demonstrate the methodology's performance with different spectral datasets. Accuracy results are compared to other benchmarks methods, such as a high performing, manually crafted CNN and the Auto-Keras AutoML tool. The results show that our method performs, in most cases, better than the benchmarks, achieving average accuracy as high as 96.96%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge