Guoxiang Grayson Tong
Conditional Normalizing Flows for Forward and Backward Joint State and Parameter Estimation
Jan 11, 2026Abstract:Traditional filtering algorithms for state estimation -- such as classical Kalman filtering, unscented Kalman filtering, and particle filters - show performance degradation when applied to nonlinear systems whose uncertainty follows arbitrary non-Gaussian, and potentially multi-modal distributions. This study reviews recent approaches to state estimation via nonlinear filtering based on conditional normalizing flows, where the conditional embedding is generated by standard MLP architectures, transformers or selective state-space models (like Mamba-SSM). In addition, we test the effectiveness of an optimal-transport-inspired kinetic loss term in mitigating overparameterization in flows consisting of a large collection of transformations. We investigate the performance of these approaches on applications relevant to autonomous driving and patient population dynamics, paying special attention to how they handle time inversion and chained predictions. Finally, we assess the performance of various conditioning strategies for an application to real-world COVID-19 joint SIR system forecasting and parameter estimation.
InVAErt networks for amortized inference and identifiability analysis of lumped parameter hemodynamic models
Aug 15, 2024



Abstract:Estimation of cardiovascular model parameters from electronic health records (EHR) poses a significant challenge primarily due to lack of identifiability. Structural non-identifiability arises when a manifold in the space of parameters is mapped to a common output, while practical non-identifiability can result due to limited data, model misspecification, or noise corruption. To address the resulting ill-posed inverse problem, optimization-based or Bayesian inference approaches typically use regularization, thereby limiting the possibility of discovering multiple solutions. In this study, we use inVAErt networks, a neural network-based, data-driven framework for enhanced digital twin analysis of stiff dynamical systems. We demonstrate the flexibility and effectiveness of inVAErt networks in the context of physiological inversion of a six-compartment lumped parameter hemodynamic model from synthetic data to real data with missing components.
InVAErt networks: a data-driven framework for emulation, inference and identifiability analysis
Jul 24, 2023Abstract:Use of generative models and deep learning for physics-based systems is currently dominated by the task of emulation. However, the remarkable flexibility offered by data-driven architectures would suggest to extend this representation to other aspects of system synthesis including model inversion and identifiability. We introduce inVAErt (pronounced \emph{invert}) networks, a comprehensive framework for data-driven analysis and synthesis of parametric physical systems which uses a deterministic encoder and decoder to represent the forward and inverse solution maps, normalizing flow to capture the probabilistic distribution of system outputs, and a variational encoder designed to learn a compact latent representation for the lack of bijectivity between inputs and outputs. We formally investigate the selection of penalty coefficients in the loss function and strategies for latent space sampling, since we find that these significantly affect both training and testing performance. We validate our framework through extensive numerical examples, including simple linear, nonlinear, and periodic maps, dynamical systems, and spatio-temporal PDEs.
Data-driven synchronization-avoiding algorithms in the explicit distributed structural analysis of soft tissue
Jul 08, 2022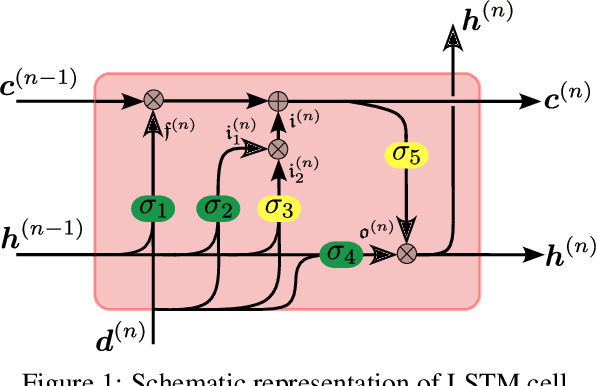
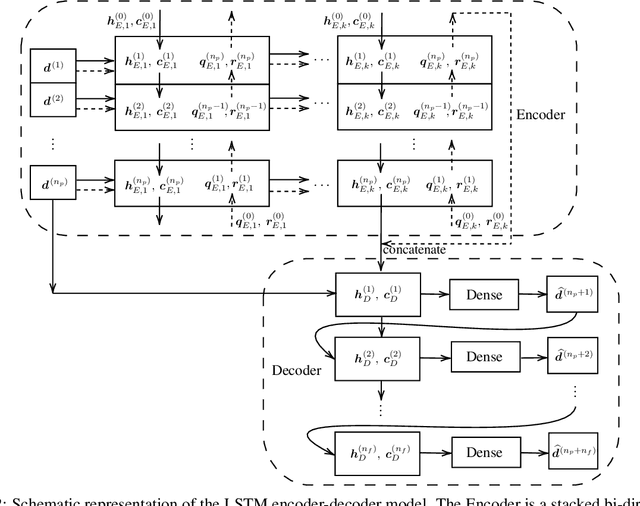
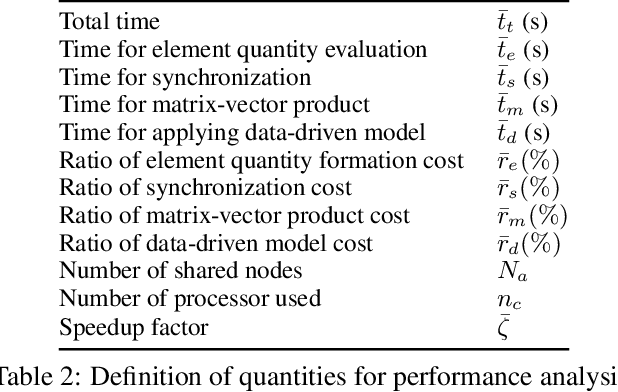
Abstract:We propose a data-driven framework to increase the computational efficiency of the explicit finite element method in the structural analysis of soft tissue. An encoder-decoder long short-term memory deep neural network is trained based on the data produced by an explicit, distributed finite element solver. We leverage this network to predict synchronized displacements at shared nodes, minimizing the amount of communication between processors. We perform extensive numerical experiments to quantify the accuracy and stability of the proposed synchronization-avoiding algorithm.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge