Gregor Hartmann
Inverse Surrogate Model of a Soft X-Ray Spectrometer using Domain Adaptation
Feb 21, 2025Abstract:In this study, we present a method to create a robust inverse surrogate model for a soft X-ray spectrometer. During a beamtime at an electron storage ring, such as BESSY II, instrumentation and beamlines are required to be correctly aligned and calibrated for optimal experimental conditions. In order to automate these processes, machine learning methods can be developed and implemented, but in many cases these methods require the use of an inverse model which maps the output of the experiment, such as a detector image, to the parameters of the device. Due to limited experimental data, such models are often trained with simulated data, which creates the challenge of compensating for the inherent differences between simulation and experiment. In order to close this gap, we demonstrate the application of data augmentation and adversarial domain adaptation techniques, with which we can predict absolute coordinates for the automated alignment of our spectrometer. Bridging the simulation-experiment gap with minimal real-world data opens new avenues for automated experimentation using machine learning in scientific instrumentation.
Toward AI-enhanced online-characterization and shaping of ultrashort X-ray free-electron laser pulses
Aug 31, 2021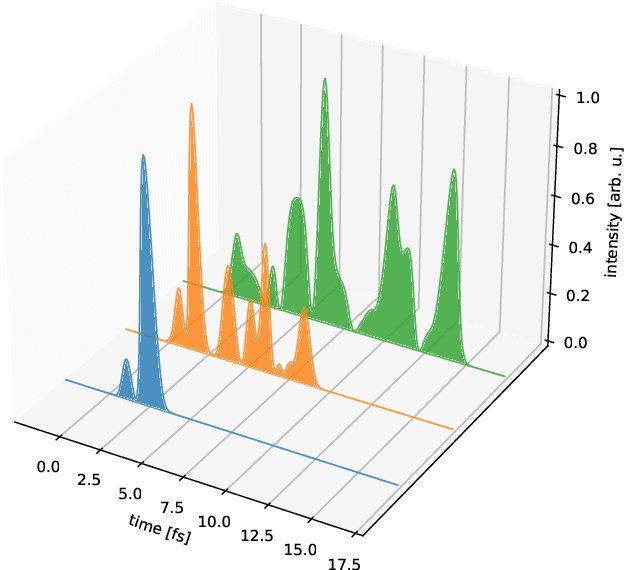
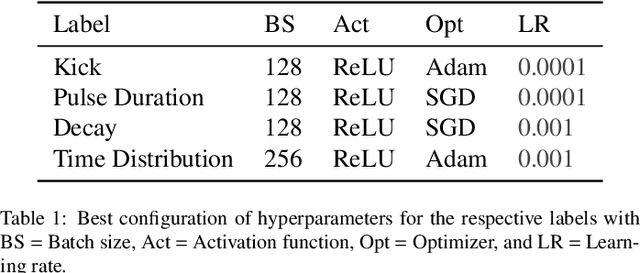
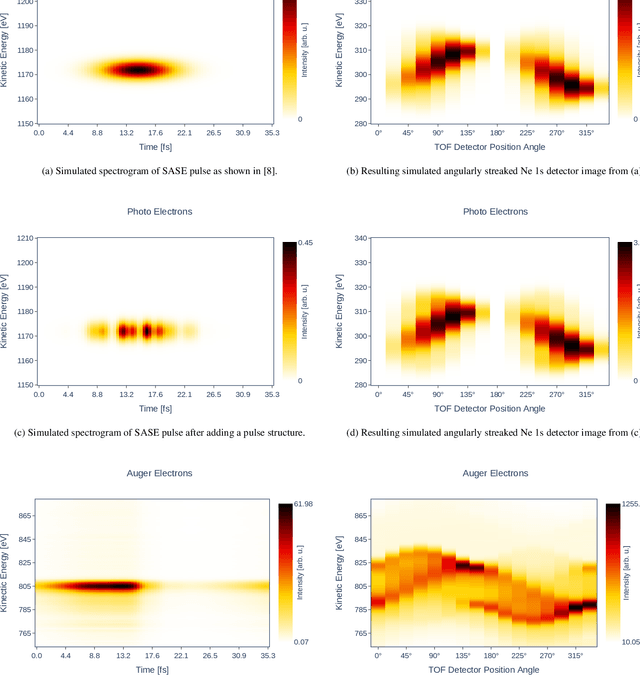
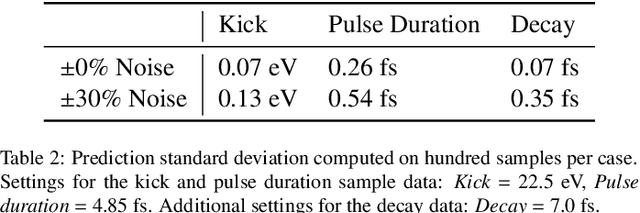
Abstract:X-ray free-electron lasers (XFELs) as the world`s most brilliant light sources provide ultrashort X-ray pulses with durations typically on the order of femtoseconds. Recently, they have approached and entered the attosecond regime, which holds new promises for single-molecule imaging and studying nonlinear and ultrafast phenomena like localized electron dynamics. The technological evolution of XFELs toward well-controllable light sources for precise metrology of ultrafast processes was, however, hampered by the diagnostic capabilities for characterizing X-ray pulses at the attosecond frontier. In this regard, the spectroscopic technique of photoelectron angular streaking has successfully proven how to non-destructively retrieve the exact time-energy structure of XFEL pulses on a single-shot basis. By using artificial intelligence algorithms, in particular convolutional neural networks, we here show how this technique can be leveraged from its proof-of-principle stage toward routine diagnostics at XFELs, thus enhancing and refining their scientific access in all related disciplines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge