Graeme Ritchie
Department of Artificial Intelligence, University of Edinburgh
An implemented model of punning riddles
Jun 13, 1994



Abstract:In this paper, we discuss a model of simple question-answer punning, implemented in a program, JAPE, which generates riddles from humour-independent lexical entries. The model uses two main types of structure: schemata, which determine the relationships between key words in a joke, and templates, which produce the surface form of the joke. JAPE succeeds in generating pieces of text that are recognizably jokes, but some of them are not very good jokes. We mention some potential improvements and extensions, including post-production heuristics for ordering the jokes according to quality.
* 6 pages, using aaai.sty and aaai.bst (in cmp-lg style list). Figs and bib in separate file. Also available by email (kimb@aisb.ed.ac.uk) and www (http://www.dai.ed.ac.uk/students/kimb)
A symbolic description of punning riddles and its computer implementation
Jun 13, 1994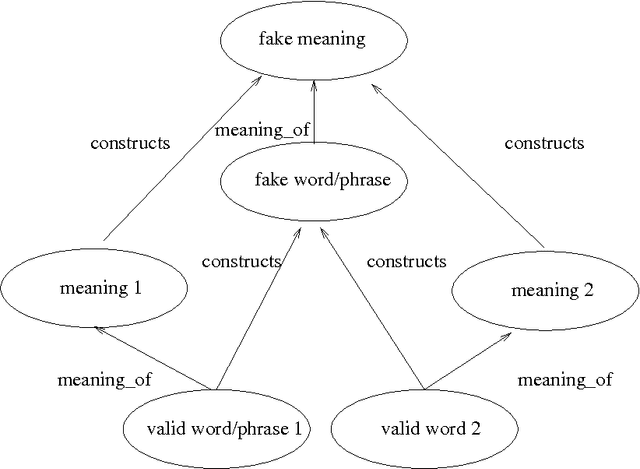
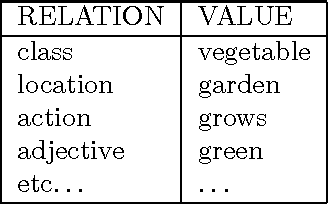
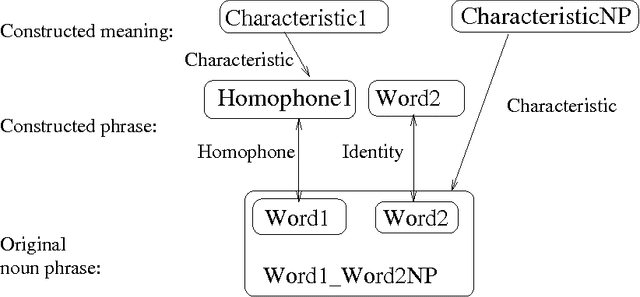
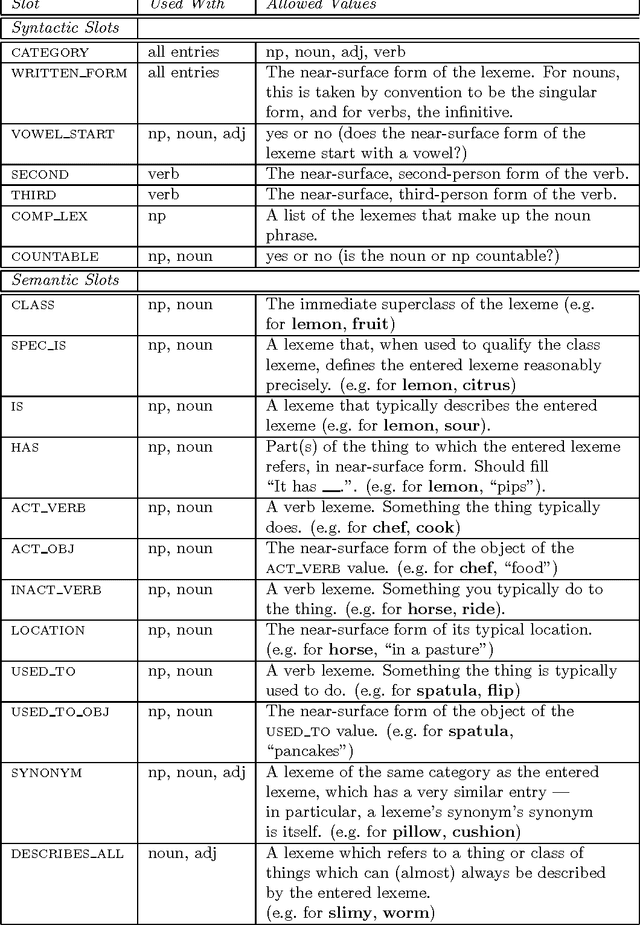
Abstract:Riddles based on simple puns can be classified according to the patterns of word, syllable or phrase similarity they depend upon. We have devised a formal model of the semantic and syntactic regularities underlying some of the simpler types of punning riddle. We have also implemented this preliminary theory in a computer program which can generate riddles from a lexicon containing general data about words and phrases; that is, the lexicon content is not customised to produce jokes. Informal evaluation of the program's results by a set of human judges suggest that the riddles produced by this program are of comparable quality to those in general circulation among school children.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge