Grégoire Francisco
Generative Simulations of The Solar Corona Evolution With Denoising Diffusion : Proof of Concept
Oct 28, 2024
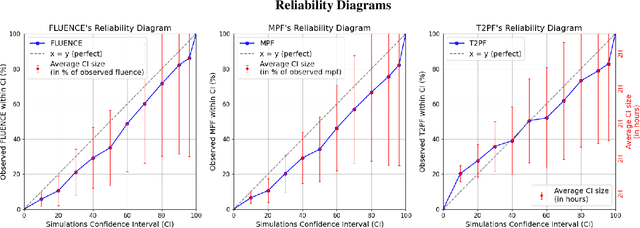
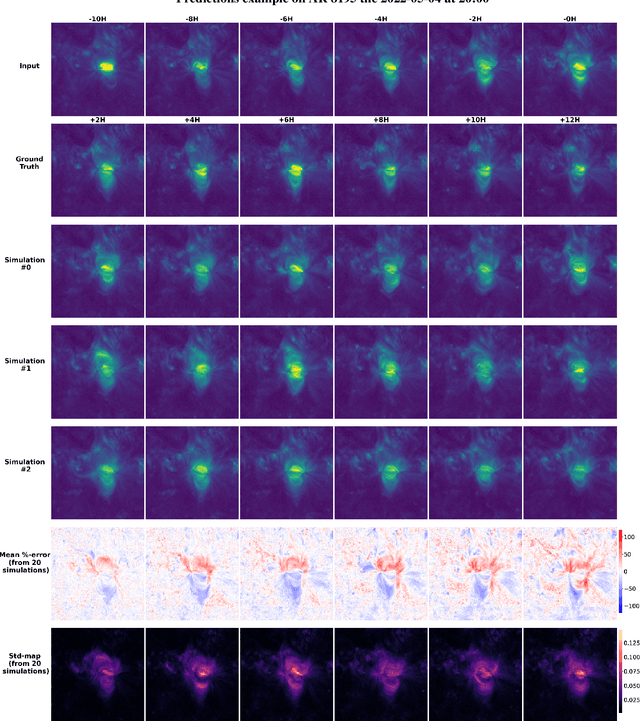
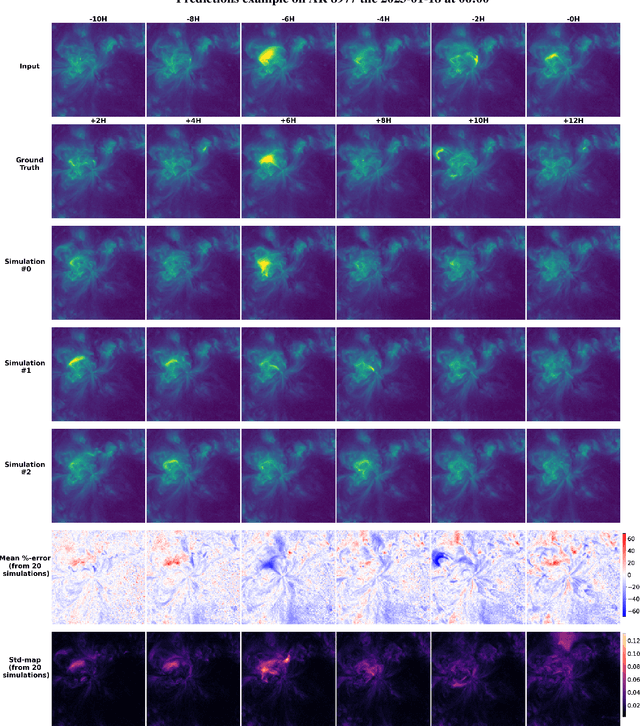
Abstract:The solar magnetized corona is responsible for various manifestations with a space weather impact, such as flares, coronal mass ejections (CMEs) and, naturally, the solar wind. Modeling the corona's dynamics and evolution is therefore critical for improving our ability to predict space weather In this work, we demonstrate that generative deep learning methods, such as Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models (DDPM), can be successfully applied to simulate future evolutions of the corona as observed in Extreme Ultraviolet (EUV) wavelengths. Our model takes a 12-hour video of an Active Region (AR) as input and simulate the potential evolution of the AR over the subsequent 12 hours, with a time-resolution of two hours. We propose a light UNet backbone architecture adapted to our problem by adding 1D temporal convolutions after each classical 2D spatial ones, and spatio-temporal attention in the bottleneck part. The model not only produce visually realistic outputs but also captures the inherent stochasticity of the system's evolution. Notably, the simulations enable the generation of reliable confidence intervals for key predictive metrics such as the EUV peak flux and fluence of the ARs, paving the way for probabilistic and interpretable space weather forecasting. Future studies will focus on shorter forecasting horizons with increased spatial and temporal resolution, aiming at reducing the uncertainty of the simulations and providing practical applications for space weather forecasting. The code used for this study is available at the following link: https://github.com/gfrancisco20/video_diffusion
Multimodal Flare Forecasting with Deep Learning
Oct 21, 2024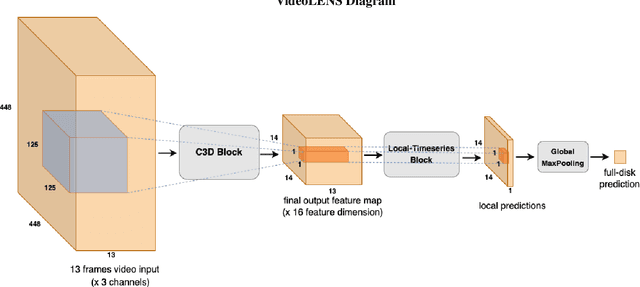
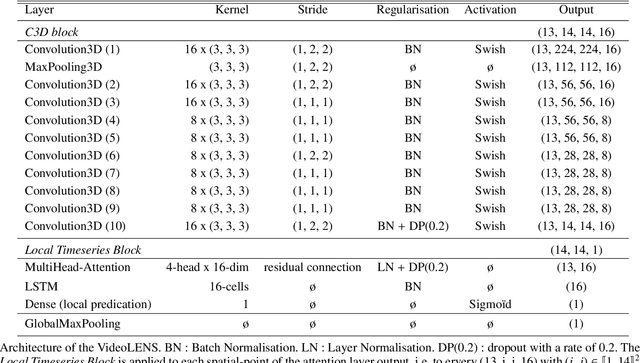
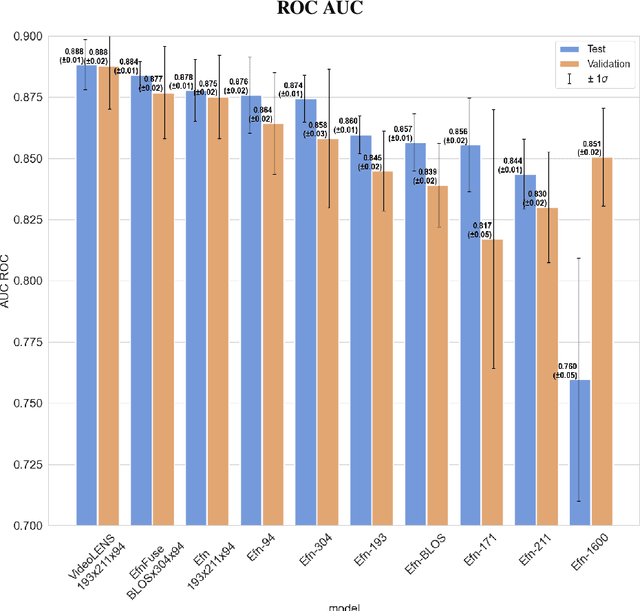
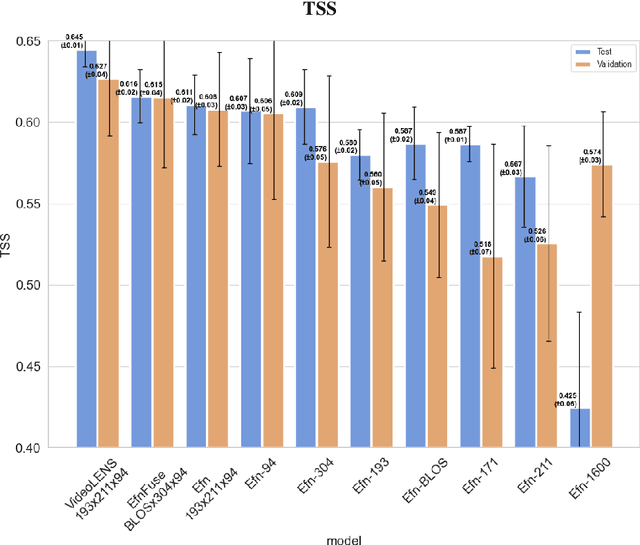
Abstract:Solar flare forecasting mainly relies on photospheric magnetograms and associated physical features to predict forthcoming flares. However, it is believed that flare initiation mechanisms often originate in the chromosphere and the lower corona. In this study, we employ deep learning as a purely data-driven approach to compare the predictive capabilities of chromospheric and coronal UV and EUV emissions across different wavelengths with those of photospheric line-of-sight magnetograms. Our findings indicate that individual EUV wavelengths can provide discriminatory power comparable or better to that of line-of-sight magnetograms. Moreover, we identify simple multimodal neural network architectures that consistently outperform single-input models, showing complementarity between the flare precursors that can be extracted from the distinct layers of the solar atmosphere. To mitigate potential biases from known misattributions in Active Region flare catalogs, our models are trained and evaluated using full-disk images and a comprehensive flare event catalog at the full-disk level. We introduce a deep-learning architecture suited for extracting temporal features from full-disk videos.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge