Golnaz Amiri
A Comprehensive Review of Myoelectric Prosthesis Control
Dec 25, 2021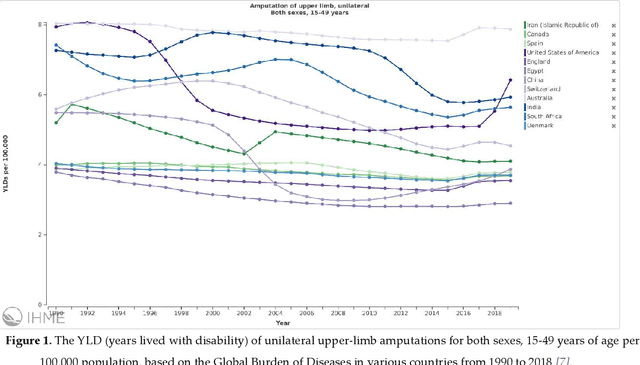
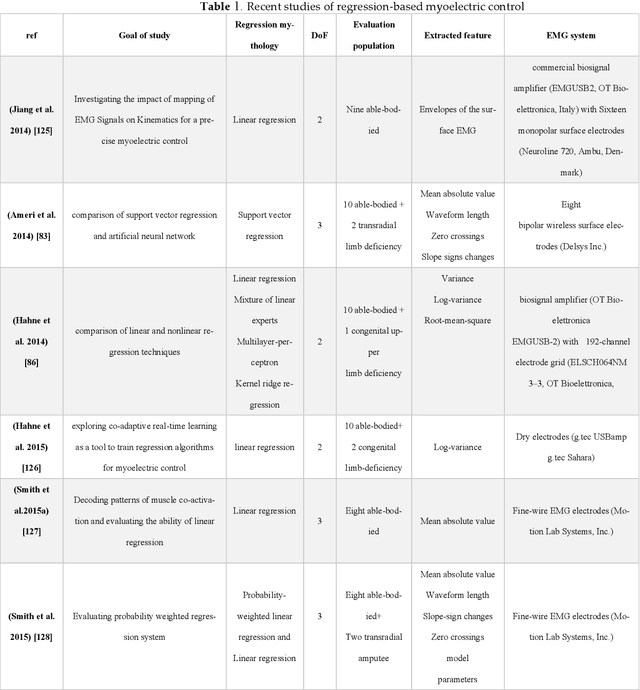
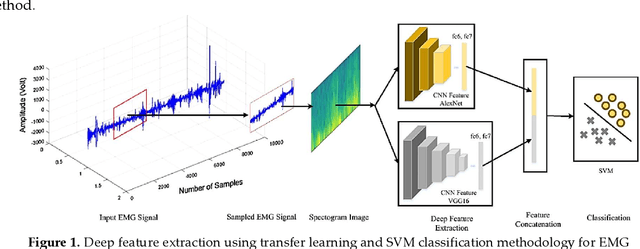

Abstract:Prosthetic hands can be used to support upper-body amputees. Myoelectric prosthesis, one of the externally-powered active prosthesis categories, requires proper processing units in addition to recording electrodes and instrumentation amplifiers. In this paper, the following myoelectric prosthesis control methods were discussed in detail: On-off and finite-state, proportional, direct, and posture, simultaneous, classification and regression-based control, and deep learning methods. Myoelectric control performance indices, such as completion time and rate, throughput, lag, and path length, were reviewed. The advantages and disadvantages of the control methods were also discussed. Some of myoelectric prosthesis control's significant challenges are comfort, durability, cost, the application of under-sampled signals, and electrode shift. Moreover, the proposed algorithms must be usually tuned after each don and doff, which is not comfortable for the users. Real-time simultaneous and proportional myoelectric control, resampling human's arm, has brought much attention. However, increasing the degree of freedom reduces the overall performance. Applying a 3D printed prosthesis arm and under-sampled electromyographic signals could reduce the fabrication cost and improve the application of such methods in practice. There are many technological and clinical challenges in this area to reduce the prosthesis rejection rate.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge