Gaurish Lakhanpal
LaneSegNet Design Study
Jun 22, 2024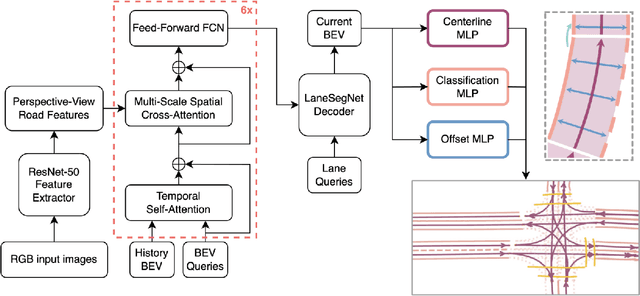
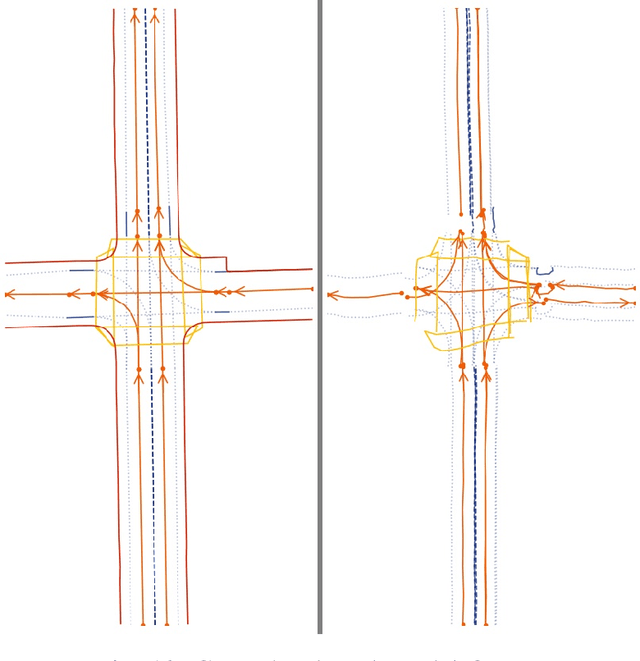
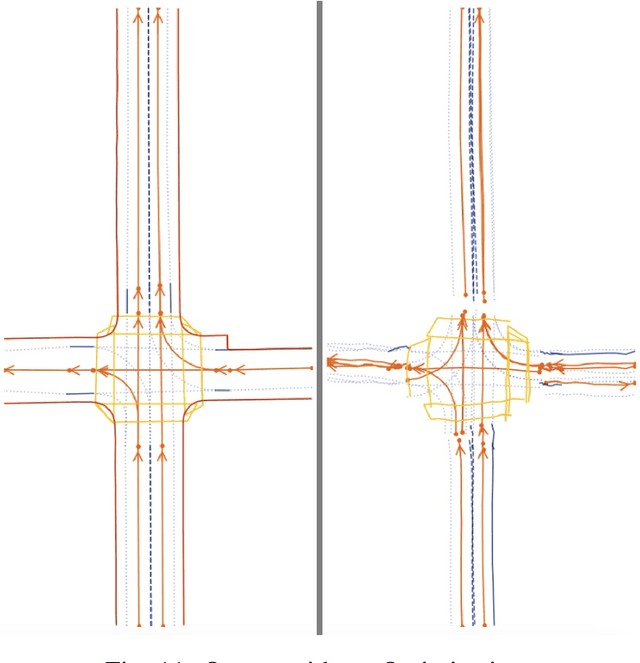
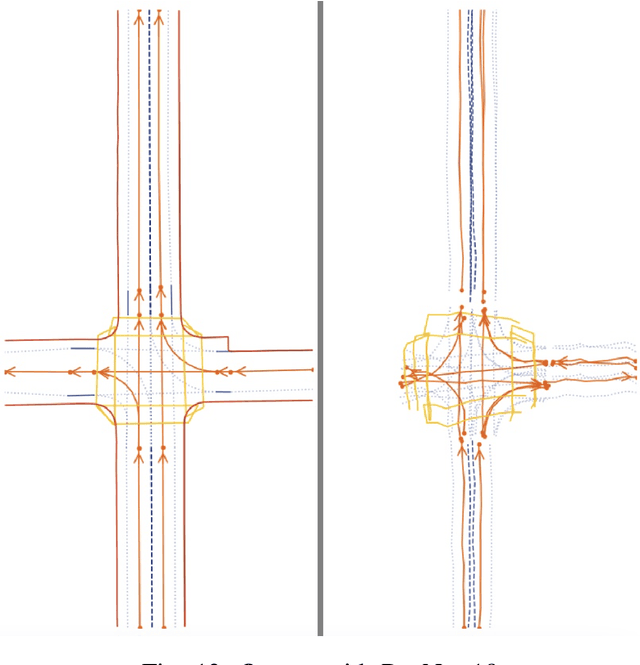
Abstract:With the increasing prevalence of autonomous vehicles, it is essential for computer vision algorithms to accurately assess road features in real-time. This study explores the LaneSegNet architecture, a new approach to lane topology prediction which integrates topological information with lane-line data to provide a more contextual understanding of road environments. The LaneSegNet architecture includes a feature extractor, lane encoder, lane decoder, and prediction head, leveraging components from ResNet-50, BEVFormer, and various attention mechanisms. We experimented with optimizations to the LaneSegNet architecture through feature extractor modification and transformer encoder-decoder stack modification. We found that modifying the encoder and decoder stacks offered an interesting tradeoff between training time and prediction accuracy, with certain combinations showing promising results. Our implementation, trained on a single NVIDIA Tesla A100 GPU, found that a 2:4 ratio reduced training time by 22.3% with only a 7.1% drop in mean average precision, while a 4:8 ratio increased training time by only 11.1% but improved mean average precision by a significant 23.7%. These results indicate that strategic hyperparameter tuning can yield substantial improvements depending on the resources of the user. This study provides valuable insights for optimizing LaneSegNet according to available computation power, making it more accessible for users with limited resources and increasing the capabilities for users with more powerful resources.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge