Get our free extension to see links to code for papers anywhere online!Free add-on: code for papers everywhere!Free add-on: See code for papers anywhere!
G. Sakkis
Stacking classifiers for anti-spam filtering of e-mail
Jun 19, 2001Authors:G. Sakkis, I. Androutsopoulos, G. Paliouras, V. Karkaletsis, C. D. Spyropoulos, P. Stamatopoulos
Figures and Tables: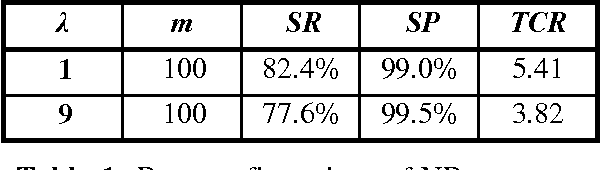

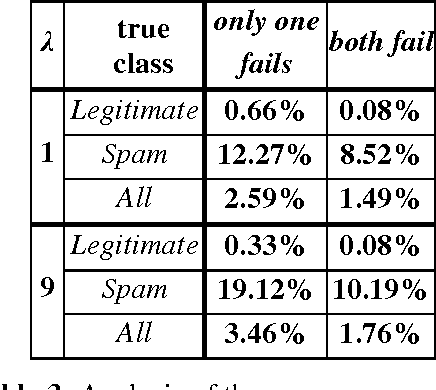
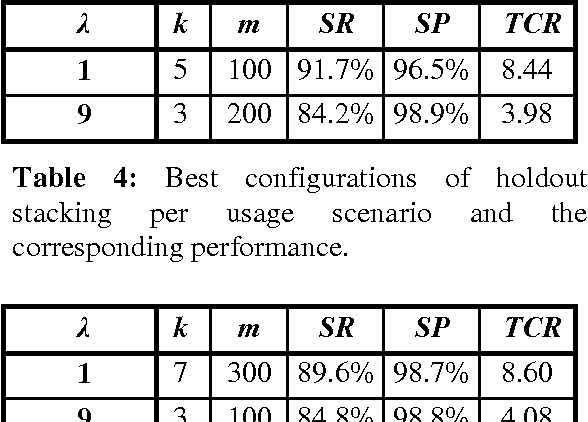




Abstract:We evaluate empirically a scheme for combining classifiers, known as stacked generalization, in the context of anti-spam filtering, a novel cost-sensitive application of text categorization. Unsolicited commercial e-mail, or "spam", floods mailboxes, causing frustration, wasting bandwidth, and exposing minors to unsuitable content. Using a public corpus, we show that stacking can improve the efficiency of automatically induced anti-spam filters, and that such filters can be used in real-life applications.
* Proceedings of "Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing"
(EMNLP 2001), L. Lee and D. Harman (Eds.), pp. 44-50, Carnegie Mellon
University, Pittsburgh, PA, 2001
Via
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge