G. F. Snyder
DeepMerge II: Building Robust Deep Learning Algorithms for Merging Galaxy Identification Across Domains
Mar 02, 2021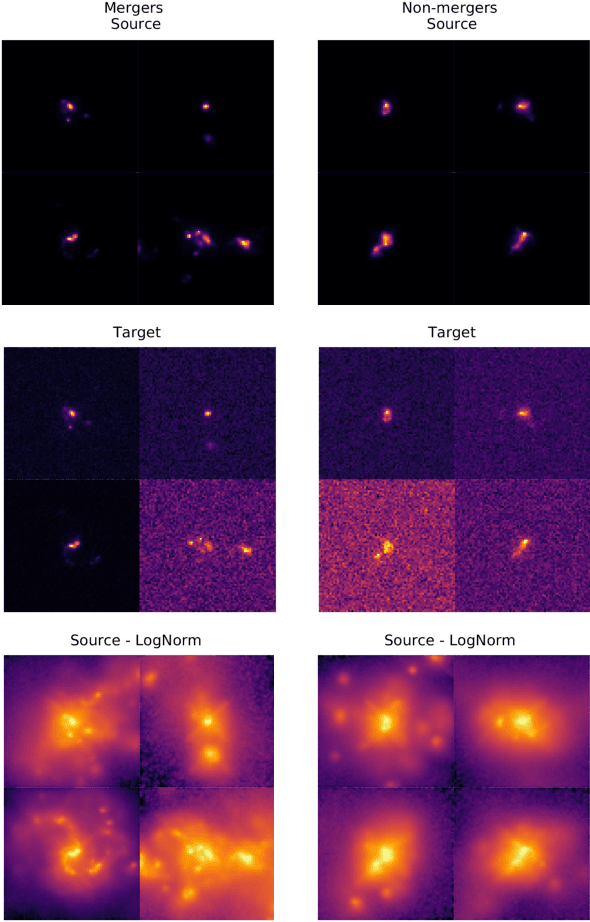
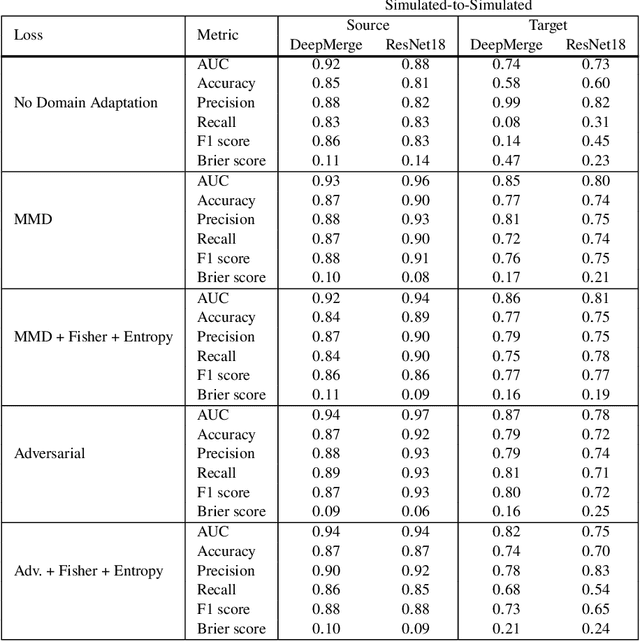
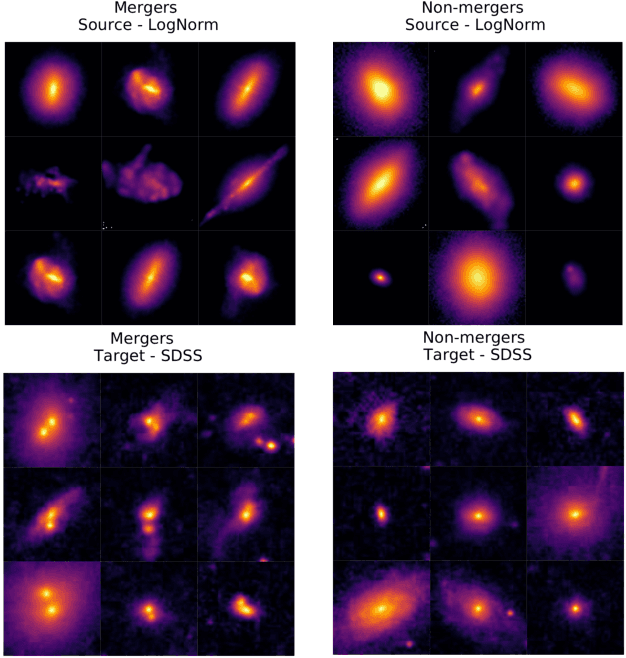
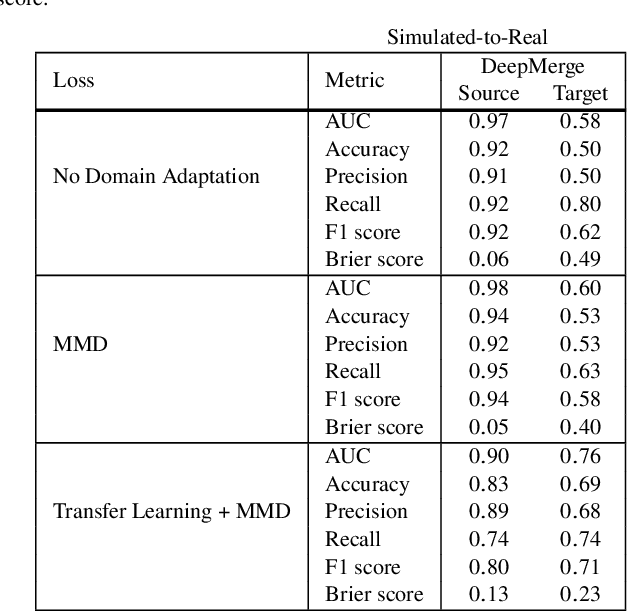
Abstract:In astronomy, neural networks are often trained on simulation data with the prospect of being used on telescope observations. Unfortunately, training a model on simulation data and then applying it to instrument data leads to a substantial and potentially even detrimental decrease in model accuracy on the new target dataset. Simulated and instrument data represent different data domains, and for an algorithm to work in both, domain-invariant learning is necessary. Here we employ domain adaptation techniques$-$ Maximum Mean Discrepancy (MMD) as an additional transfer loss and Domain Adversarial Neural Networks (DANNs)$-$ and demonstrate their viability to extract domain-invariant features within the astronomical context of classifying merging and non-merging galaxies. Additionally, we explore the use of Fisher loss and entropy minimization to enforce better in-domain class discriminability. We show that the addition of each domain adaptation technique improves the performance of a classifier when compared to conventional deep learning algorithms. We demonstrate this on two examples: between two Illustris-1 simulated datasets of distant merging galaxies, and between Illustris-1 simulated data of nearby merging galaxies and observed data from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey. The use of domain adaptation techniques in our experiments leads to an increase of target domain classification accuracy of up to ${\sim}20\%$. With further development, these techniques will allow astronomers to successfully implement neural network models trained on simulation data to efficiently detect and study astrophysical objects in current and future large-scale astronomical surveys.
DeepMerge: Classifying High-redshift Merging Galaxies with Deep Neural Networks
Apr 24, 2020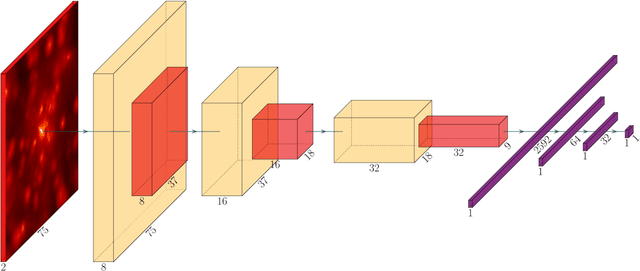
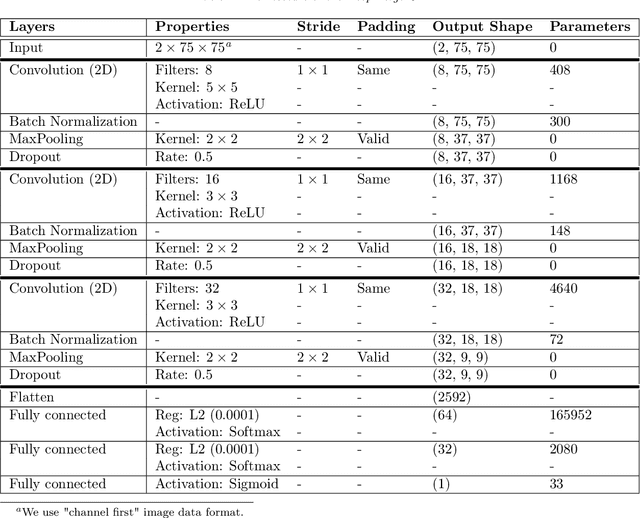
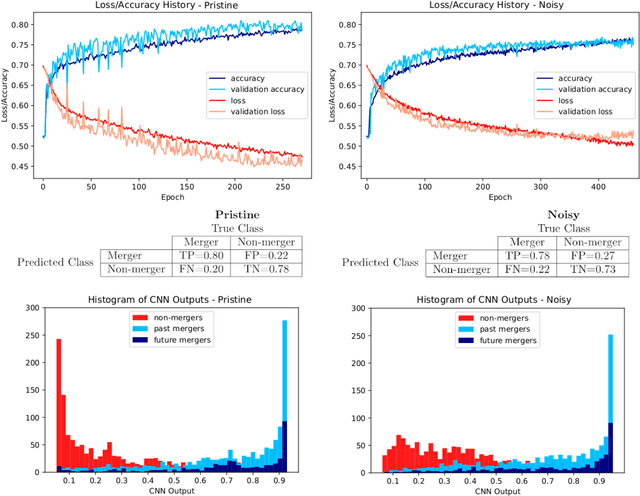
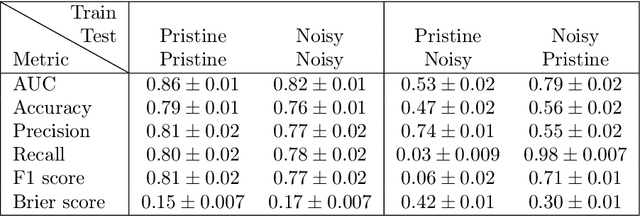
Abstract:We investigate and demonstrate the use of convolutional neural networks (CNNs) for the task of distinguishing between merging and non-merging galaxies in simulated images, and for the first time at high redshifts (i.e. $z=2$). We extract images of merging and non-merging galaxies from the Illustris-1 cosmological simulation and apply observational and experimental noise that mimics that from the Hubble Space Telescope; the data without noise form a "pristine" data set and that with noise form a "noisy" data set. The test set classification accuracy of the CNN is $79\%$ for pristine and $76\%$ for noisy. The CNN outperforms a Random Forest classifier, which was shown to be superior to conventional one- or two-dimensional statistical methods (Concentration, Asymmetry, the Gini, $M_{20}$ statistics etc.), which are commonly used when classifying merging galaxies. We also investigate the selection effects of the classifier with respect to merger state and star formation rate, finding no bias. Finally, we extract Grad-CAMs (Gradient-weighted Class Activation Mapping) from the results to further assess and interrogate the fidelity of the classification model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge