Francesc X. Prenafeta-Boldu
Transfer of Manure as Fertilizer from Livestock Farms to Crop Fields: The Case of Catalonia
Jun 14, 2020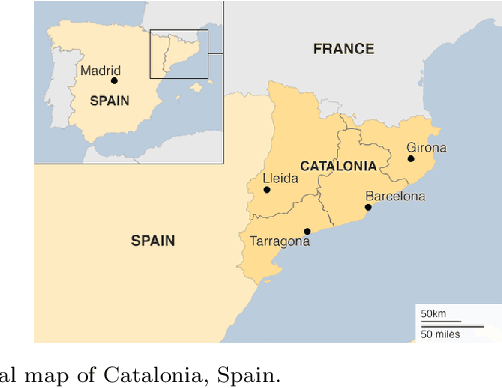
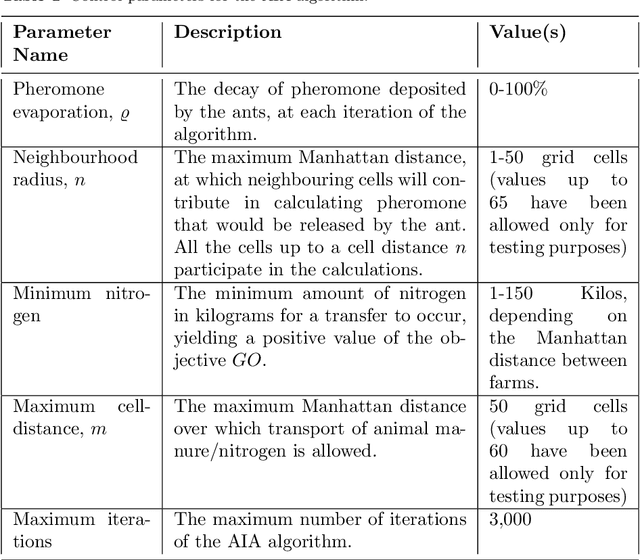
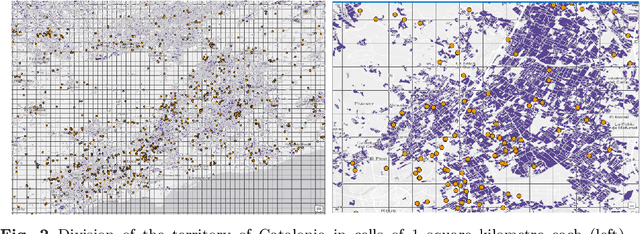

Abstract:Intensive livestock production might have a negative environmental impact, by producing large amounts of animal manure, which, if not properly managed, can contaminate nearby water bodies with nutrient excess. However, if animal manure is exported to nearby crop fields, to be used as organic fertilizer, pollution can be mitigated. It is a single-objective optimization problem, in regards to finding the best solution for the logistics process of satisfying nutrient needs of crops by means of livestock manure. This paper proposes three different approaches to solve the problem: a centralized optimal algorithm (COA), a decentralized nature-inspired cooperative technique, based on the foraging behaviour of ants (AIA), as well as a naive neighbour-based method (NBS), which constitutes the existing practice used today in an ad hoc, uncoordinated manner in Catalonia. Results show that the COA approach is 8.5% more efficient than the AIA. However, the AIA approach is fairer to the farmers and more balanced in terms of average transportation distances that need to be covered by each livestock farmer, while it is 1.07 times more eefficient than the NBS. Our work constitutes the first application of a decentralized AIA to this interesting real-world problem, in a domain where swarm intelligence methods are still under-exploited.
Transfer of Manure from Livestock Farms to Crop Fields as Fertilizer using an Ant Inspired Approach
Jun 05, 2020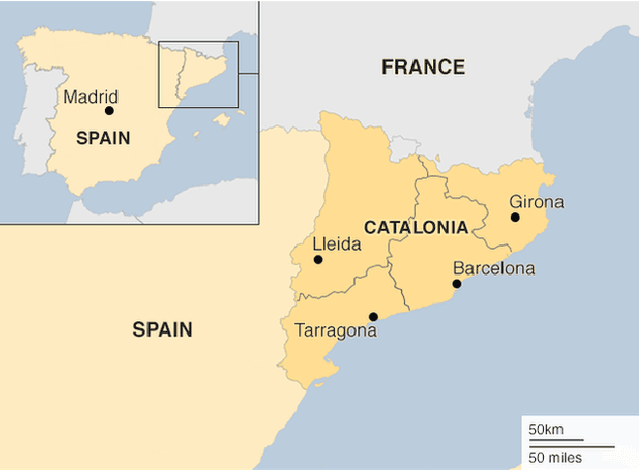


Abstract:Intensive livestock production might have a negative environmental impact, by producing large amounts of animal excrements, which, if not properly managed, can contaminate nearby water bodies with nutrient excess. However, if animal manure is exported to distant crop fields, to be used as organic fertilizer, pollution can be mitigated. It is a single-objective optimization problem, in regards to finding the best solution for the logistics process of satisfying nutrient crops needs by means of livestock manure. This paper proposes a dynamic approach to solve the problem, based on a decentralized nature-inspired cooperative technique, inspired by the foraging behavior of ants (AIA). Results provide important insights for policy-makers over the potential of using animal manure as fertilizer for crop fields, while AIA solves the problem effectively, in a fair way to the farmers and well balanced in terms of average transportation distances that need to be covered by each livestock farmer. Our work constitutes the first application of a decentralized AIA to this interesting real-world problem, in a domain where swarm intelligence methods are still under-exploited.
Deep learning in agriculture: A survey
Jul 31, 2018



Abstract:Deep learning constitutes a recent, modern technique for image processing and data analysis, with promising results and large potential. As deep learning has been successfully applied in various domains, it has recently entered also the domain of agriculture. In this paper, we perform a survey of 40 research efforts that employ deep learning techniques, applied to various agricultural and food production challenges. We examine the particular agricultural problems under study, the specific models and frameworks employed, the sources, nature and pre-processing of data used, and the overall performance achieved according to the metrics used at each work under study. Moreover, we study comparisons of deep learning with other existing popular techniques, in respect to differences in classification or regression performance. Our findings indicate that deep learning provides high accuracy, outperforming existing commonly used image processing techniques.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge