Farshad Tajeripour
Developing a Novel Approach for Periapical Dental Radiographs Segmentation
Nov 13, 2021



Abstract:Image processing techniques has been widely used in dental researches such as human identification and forensic dentistry, teeth numbering, dental carries detection and periodontal disease analysis. One of the most challenging parts in dental imaging is teeth segmentation and how to separate them from each other. In this paper, an automated method for teeth segmentation of Periapical dental x-ray images which contain at least one root-canalled tooth is proposed. The result of this approach can be used as an initial step in bone lesion detection. The proposed algorithm is made of two stages. The first stage is pre-processing. The second and main part of this algorithm calculated rotation degree and uses the integral projection method for tooth isolation. Experimental results show that this algorithm is robust and achieves high accuracy.
Color Texture Classification Based on Proposed Impulse-Noise Resistant Color Local Binary Patterns and Significant Points Selection Algorithm
Jun 26, 2019



Abstract:The main aim of this paper is to propose a color texture classification approach which uses color sensor information and texture features jointly. High accuracy, low noise sensitivity and low computational complexity are specified aims for our proposed approach. One of the efficient texture analysis operations is local binary patterns. The proposed approach includes two steps. First, a noise resistant version of color local binary patterns is proposed to decrease sensitivity to noise of LBP. This step is evaluated based on combination of color sensor information using AND operation. In second step, a significant points selection algorithm is proposed to select significant LBP. This phase decreases final computational complexity along with increasing accuracy rate. The Proposed approach is evaluated using Vistex, Outex, and KTH TIPS2a data sets. Our approach has been compared with some state of the art methods. It is experimentally demonstrated that the proposed approach achieves highest accuracy. In two other experiments, result show low noise sensitivity and low computational complexity of the proposed approach in comparison with previous versions of LBP. Rotation invariant, multi resolution, general usability are other advantages of our proposed approach. In the present paper, a new version of LBP is proposed originally, which is called Hybrid color local binary patterns. It can be used in many image processing applications to extract color and texture features jointly. Also, a significant point selection algorithm is proposed for the first time to select key points of images.
Full Object Boundary Detection by Applying Scale Invariant Features in a Region Merging Segmentation Algorithm
Oct 26, 2012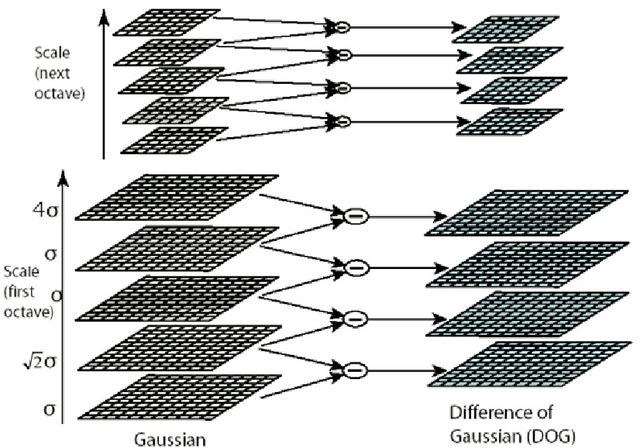

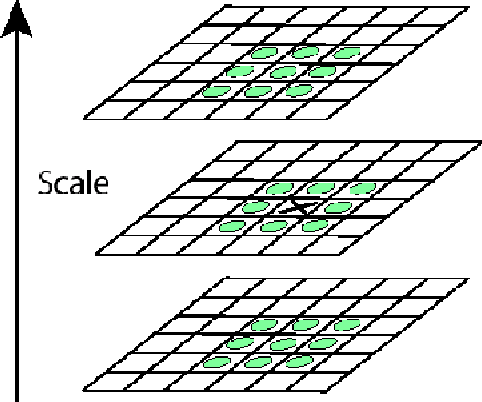
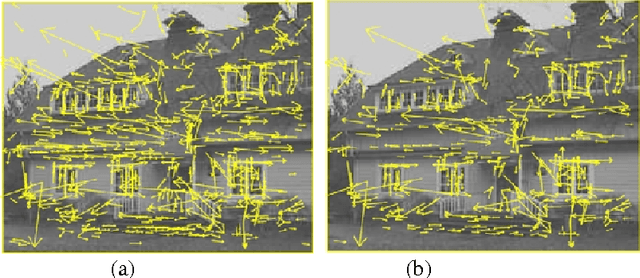
Abstract:Object detection is a fundamental task in computer vision and has many applications in image processing. This paper proposes a new approach for object detection by applying scale invariant feature transform (SIFT) in an automatic segmentation algorithm. SIFT is an invariant algorithm respect to scale, translation and rotation. The features are very distinct and provide stable keypoints that can be used for matching an object in different images. At first, an object is trained with different aspects for finding best keypoints. The object can be recognized in the other images by using achieved keypoints. Then, a robust segmentation algorithm is used to detect the object with full boundary based on SIFT keypoints. In segmentation algorithm, a merging role is defined to merge the regions in image with the assistance of keypoints. The results show that the proposed approach is reliable for object detection and can extract object boundary well.
* 10 pages - 7 figures
An Innovative Skin Detection Approach Using Color Based Image Retrieval Technique
Jul 06, 2012Abstract:From The late 90th, "Skin Detection" becomes one of the major problems in image processing. If "Skin Detection" will be done in high accuracy, it can be used in many cases as face recognition, Human Tracking and etc. Until now so many methods were presented for solving this problem. In most of these methods, color space was used to extract feature vector for classifying pixels, but the most of them have not good accuracy in detecting types of skin. The proposed approach in this paper is based on "Color based image retrieval" (CBIR) technique. In this method, first by means of CBIR method and image tiling and considering the relation between pixel and its neighbors, a feature vector would be defined and then with using a training step, detecting the skin in the test stage. The result shows that the presenting approach, in addition to its high accuracy in detecting type of skin, has no sensitivity to illumination intensity and moving face orientation.
* 9 Pages, 4 Figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge