Eric Keller
General Domain Adaptation Through Proportional Progressive Pseudo Labeling
Dec 23, 2020



Abstract:Domain adaptation helps transfer the knowledge gained from a labeled source domain to an unlabeled target domain. During the past few years, different domain adaptation techniques have been published. One common flaw of these approaches is that while they might work well on one input type, such as images, their performance drops when applied to others, such as text or time-series. In this paper, we introduce Proportional Progressive Pseudo Labeling (PPPL), a simple, yet effective technique that can be implemented in a few lines of code to build a more general domain adaptation technique that can be applied on several different input types. At the beginning of the training phase, PPPL progressively reduces target domain classification error, by training the model directly with pseudo-labeled target domain samples, while excluding samples with more likely wrong pseudo-labels from the training set and also postponing training on such samples. Experiments on 6 different datasets that include tasks such as anomaly detection, text sentiment analysis and image classification demonstrate that PPPL can beat other baselines and generalize better.
Enhancing Robustness Against Adversarial Examples in Network Intrusion Detection Systems
Aug 09, 2020



Abstract:The increase of cyber attacks in both the numbers and varieties in recent years demands to build a more sophisticated network intrusion detection system (NIDS). These NIDS perform better when they can monitor all the traffic traversing through the network like when being deployed on a Software-Defined Network (SDN). Because of the inability to detect zero-day attacks, signature-based NIDS which were traditionally used for detecting malicious traffic are beginning to get replaced by anomaly-based NIDS built on neural networks. However, recently it has been shown that such NIDS have their own drawback namely being vulnerable to the adversarial example attack. Moreover, they were mostly evaluated on the old datasets which don't represent the variety of attacks network systems might face these days. In this paper, we present Reconstruction from Partial Observation (RePO) as a new mechanism to build an NIDS with the help of denoising autoencoders capable of detecting different types of network attacks in a low false alert setting with an enhanced robustness against adversarial example attack. Our evaluation conducted on a dataset with a variety of network attacks shows denoising autoencoders can improve detection of malicious traffic by up to 29% in a normal setting and by up to 45% in an adversarial setting compared to other recently proposed anomaly detectors.
Stochastic Substitute Training: A Gray-box Approach to Craft Adversarial Examples Against Gradient Obfuscation Defenses
Oct 23, 2018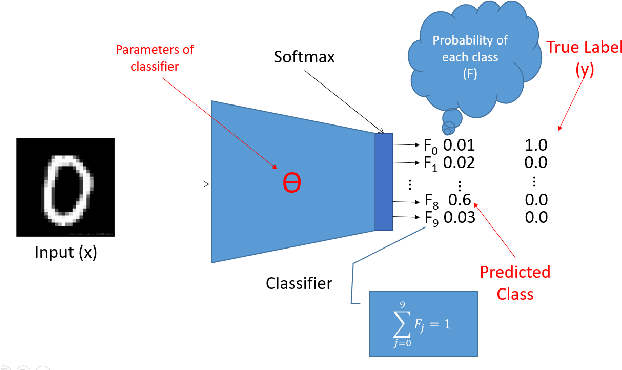

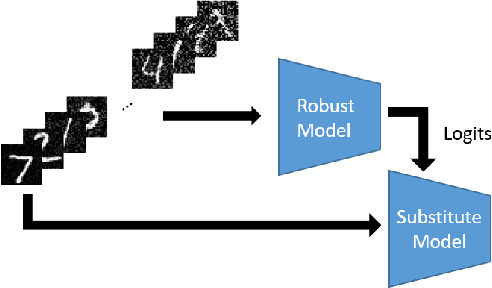
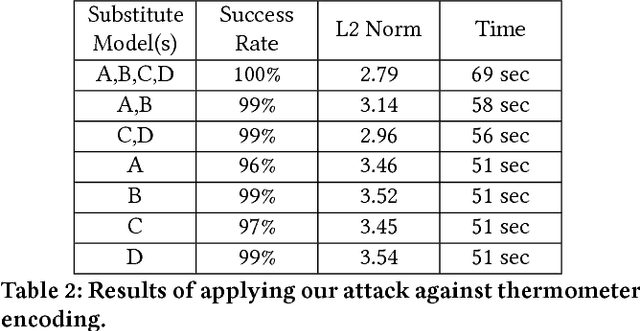
Abstract:It has been shown that adversaries can craft example inputs to neural networks which are similar to legitimate inputs but have been created to purposely cause the neural network to misclassify the input. These adversarial examples are crafted, for example, by calculating gradients of a carefully defined loss function with respect to the input. As a countermeasure, some researchers have tried to design robust models by blocking or obfuscating gradients, even in white-box settings. Another line of research proposes introducing a separate detector to attempt to detect adversarial examples. This approach also makes use of gradient obfuscation techniques, for example, to prevent the adversary from trying to fool the detector. In this paper, we introduce stochastic substitute training, a gray-box approach that can craft adversarial examples for defenses which obfuscate gradients. For those defenses that have tried to make models more robust, with our technique, an adversary can craft adversarial examples with no knowledge of the defense. For defenses that attempt to detect the adversarial examples, with our technique, an adversary only needs very limited information about the defense to craft adversarial examples. We demonstrate our technique by applying it against two defenses which make models more robust and two defenses which detect adversarial examples.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge