Eric Goles
Automata networks model for alignment and least effort on vocabulary formation
Apr 07, 2016



Abstract:Can artificial communities of agents develop language with scaling relations close to the Zipf law? As a preliminary answer to this question, we propose an Automata Networks model of the formation of a vocabulary on a population of individuals, under two in principle opposite strategies: the alignment and the least effort principle. Within the previous account to the emergence of linguistic conventions (specially, the Naming Game), we focus on modeling speaker and hearer efforts as actions over their vocabularies and we study the impact of these actions on the formation of a shared language. The numerical simulations are essentially based on an energy function, that measures the amount of local agreement between the vocabularies. The results suggests that on one dimensional lattices the best strategy to the formation of shared languages is the one that minimizes the efforts of speakers on communicative tasks.
Automata networks for multi-party communication in the Naming Game
Apr 07, 2016



Abstract:The Naming Game has been studied to explore the role of self-organization in the development and negotiation of linguistic conventions. In this paper, we define an automata networks approach to the Naming Game. Two problems are faced: (1) the definition of an automata networks for multi-party communicative interactions; and (2) the proof of convergence for three different orders in which the individuals are updated (updating schemes). Finally, computer simulations are explored in two-dimensional lattices with the purpose to recover the main features of the Naming Game and to describe the dynamics under different updating schemes.
Automata networks for memory loss effects in the formation of linguistic conventions
Oct 08, 2015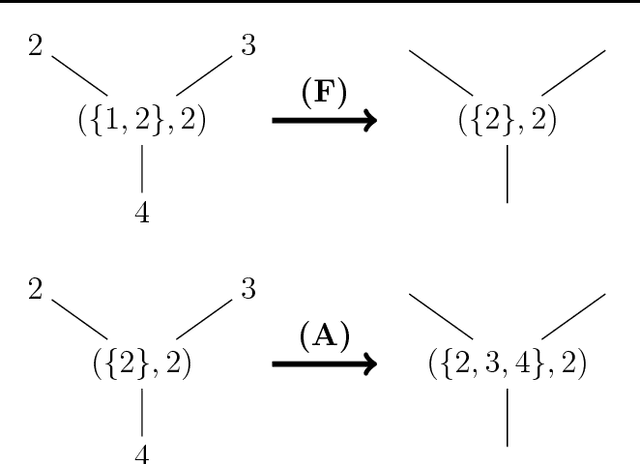
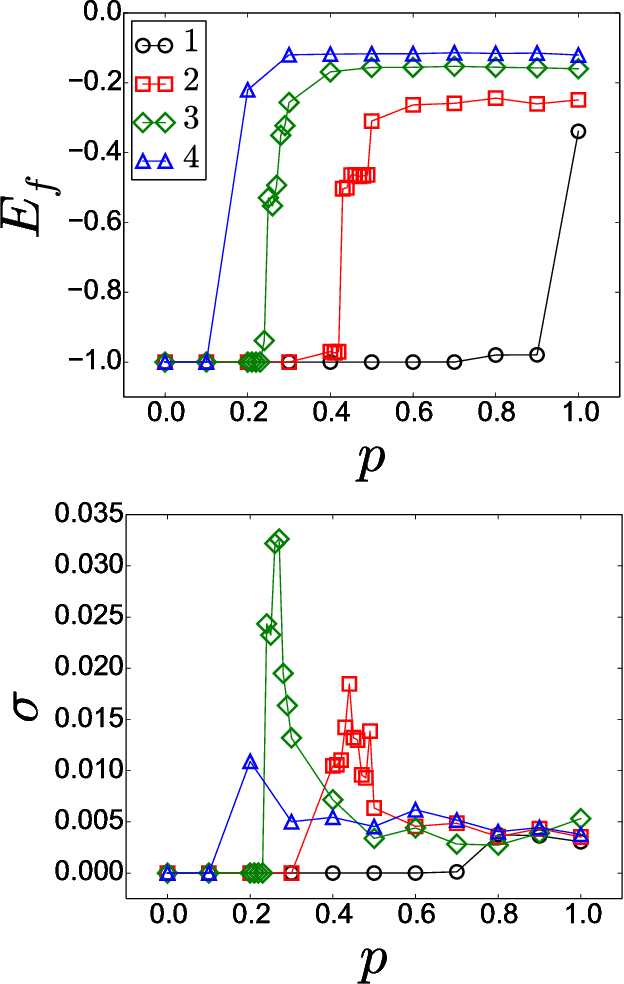
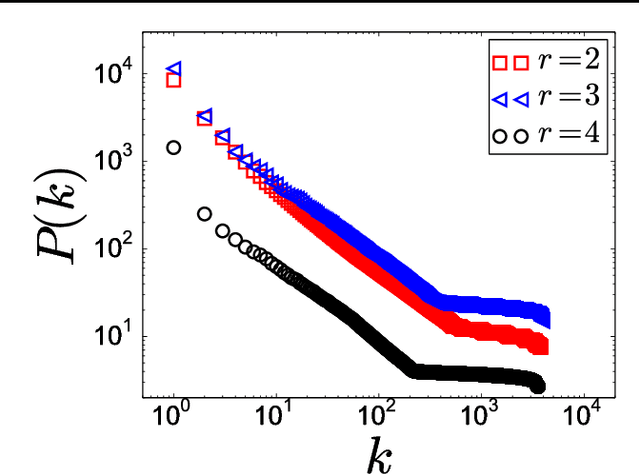
Abstract:This work attempts to give new theoretical insights to the absence of intermediate stages in the evolution of language. In particular, it is developed an automata networks approach to a crucial question: how a population of language users can reach agreement on a linguistic convention? To describe the appearance of sharp transitions in the self-organization of language, it is adopted an extremely simple model of (working) memory. At each time step, language users simply loss part of their word-memories. Through computer simulations of low-dimensional lattices, it appear sharp transitions at critical values that depend on the size of the vicinities of the individuals.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge