Emmanuel Dadzie
Machine Learning-Based Classification Algorithms for the Prediction of Coronary Heart Diseases
Dec 02, 2021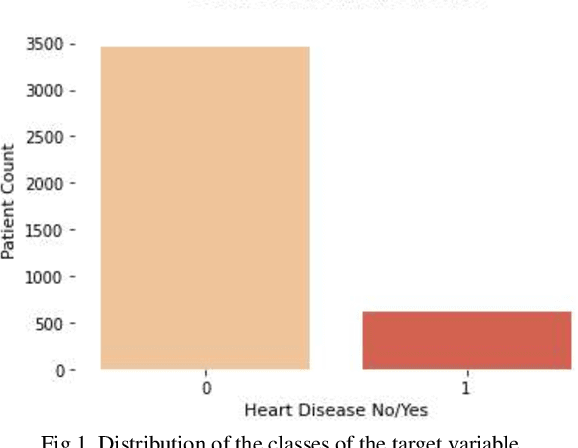
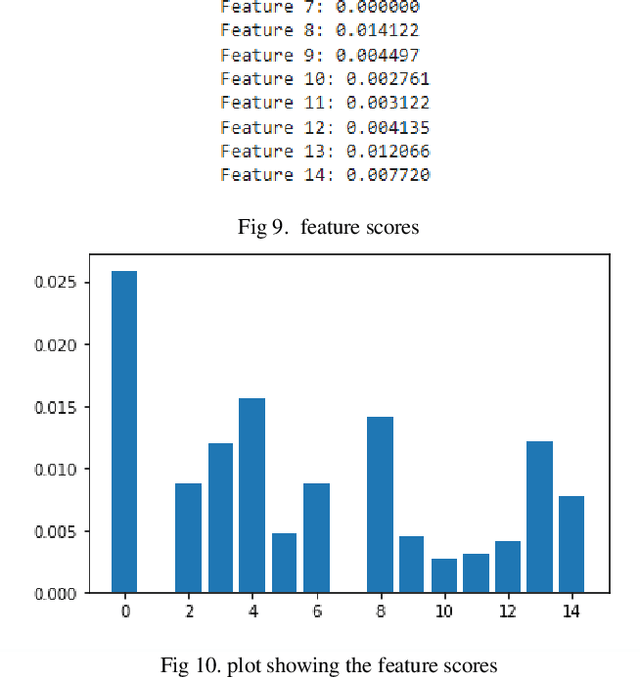
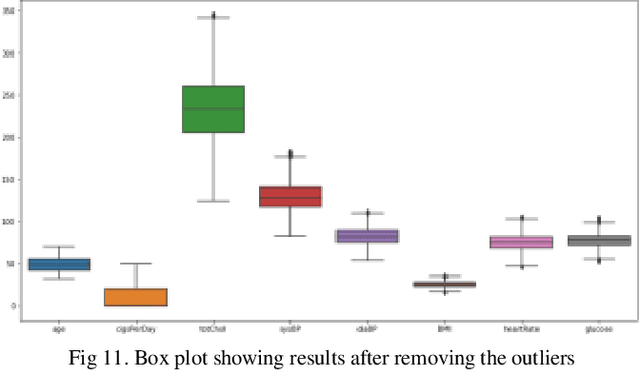
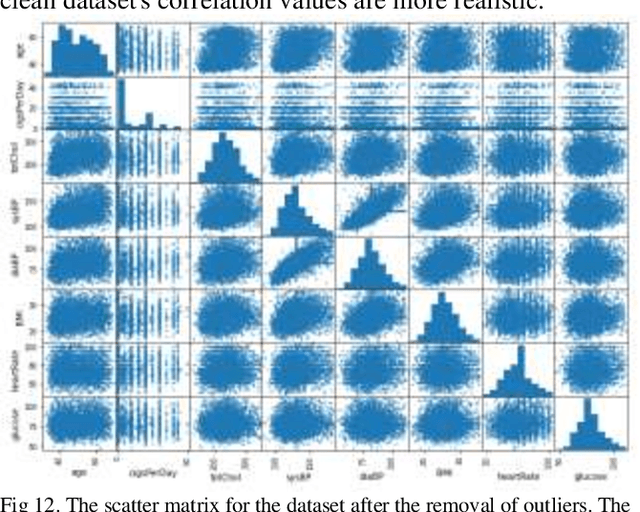
Abstract:Coronary heart disease, which is a form of cardiovascular disease (CVD), is the leading cause of death worldwide. The odds of survival are good if it is found or diagnosed early. The current report discusses a comparative approach to the classification of coronary heart disease datasets using machine learning (ML) algorithms. The current study created and tested several machine-learning-based classification models. The dataset was subjected to Smote to handle unbalanced classes and feature selection technique in order to assess the impact on two distinct performance metrics. The results show that logistic regression produced the highest performance score on the original dataset compared to the other algorithms employed. In conclusion, this study suggests that LR on a well-processed and standardized dataset can predict coronary heart disease with greater accuracy than the other algorithms.
Developing a Machine Learning Algorithm-Based Classification Models for the Detection of High-Energy Gamma Particles
Nov 18, 2021


Abstract:Cherenkov gamma telescope observes high energy gamma rays, taking advantage of the radiation emitted by charged particles produced inside the electromagnetic showers initiated by the gammas, and developing in the atmosphere. The detector records and allows for the reconstruction of the shower parameters. The reconstruction of the parameter values was achieved using a Monte Carlo simulation algorithm called CORSIKA. The present study developed multiple machine-learning-based classification models and evaluated their performance. Different data transformation and feature extraction techniques were applied to the dataset to assess the impact on two separate performance metrics. The results of the proposed application reveal that the different data transformations did not significantly impact (p = 0.3165) the performance of the models. A pairwise comparison indicates that the performance from each transformed data was not significantly different from the performance of the raw data. Additionally, the SVM algorithm produced the highest performance score on the standardized dataset. In conclusion, this study suggests that high-energy gamma particles can be predicted with sufficient accuracy using SVM on a standardized dataset than the other algorithms with the various data transformations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge