Elisabetta Valiante
A Statistical Analysis for Per-Instance Evaluation of Stochastic Optimizers: How Many Repeats Are Enough?
Mar 20, 2025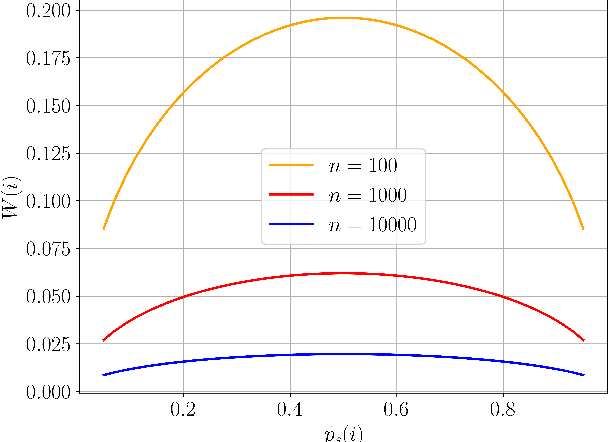
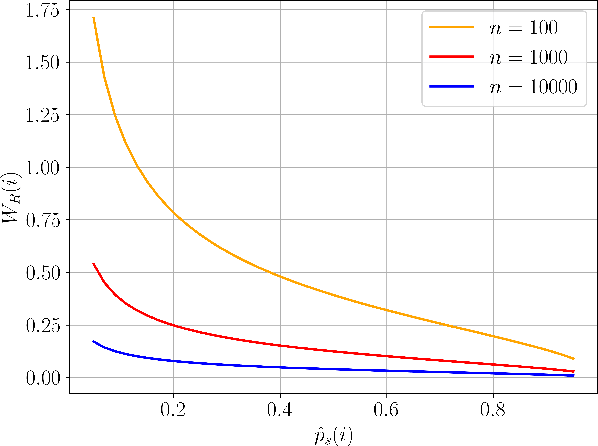
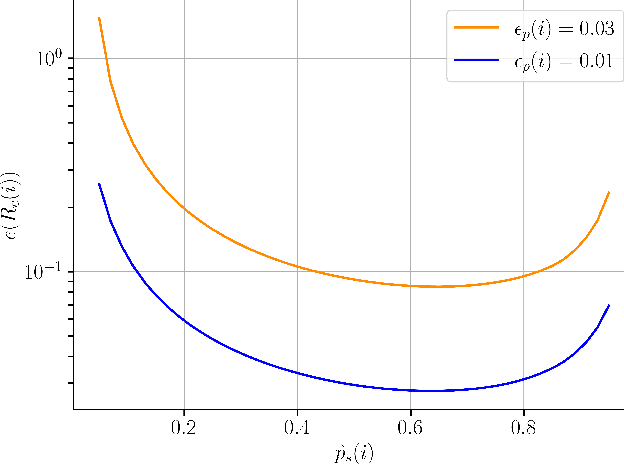
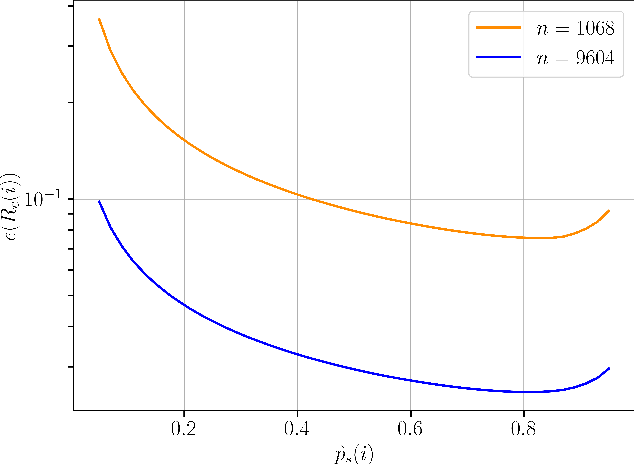
Abstract:A key trait of stochastic optimizers is that multiple runs of the same optimizer in attempting to solve the same problem can produce different results. As a result, their performance is evaluated over several repeats, or runs, on the problem. However, the accuracy of the estimated performance metrics depends on the number of runs and should be studied using statistical tools. We present a statistical analysis of the common metrics, and develop guidelines for experiment design to measure the optimizer's performance using these metrics to a high level of confidence and accuracy. To this end, we first discuss the confidence interval of the metrics and how they are related to the number of runs of an experiment. We then derive a lower bound on the number of repeats in order to guarantee achieving a given accuracy in the metrics. Using this bound, we propose an algorithm to adaptively adjust the number of repeats needed to ensure the accuracy of the evaluated metric. Our simulation results demonstrate the utility of our analysis and how it allows us to conduct reliable benchmarking as well as hyperparameter tuning and prevent us from drawing premature conclusions regarding the performance of stochastic optimizers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge