Elena Lodi
Opinions within Media, Power and Gossip
Feb 11, 2011
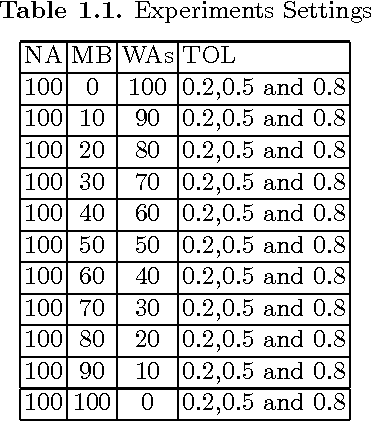

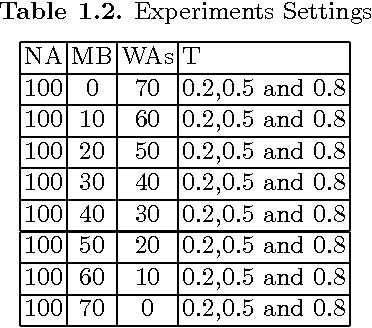
Abstract:Despite the increasing diffusion of the Internet technology, TV remains the principal medium of communication. People's perceptions, knowledge, beliefs and opinions about matter of facts get (in)formed through the information reported on by the mass-media. However, a single source of information (and consensus) could be a potential cause of anomalies in the structure and evolution of a society. Hence, as the information available (and the way it is reported) is fundamental for our perceptions and opinions, the definition of conditions allowing for a good information to be disseminated is a pressing challenge. In this paper starting from a report on the last Italian political campaign in 2008, we derive a socio-cognitive computational model of opinion dynamics where agents get informed by different sources of information. Then, a what-if analysis, performed trough simulations on the model's parameters space, is shown. In particular, the scenario implemented includes three main streams of information acquisition, differing in both the contents and the perceived reliability of the messages spread. Agents' internal opinion is updated either by accessing one of the information sources, namely media and experts, or by exchanging information with one another. They are also endowed with cognitive mechanisms to accept, reject or partially consider the acquired information.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge