Egor Ushakov
MamT$^4$: Multi-view Attention Networks for Mammography Cancer Classification
Nov 03, 2024



Abstract:In this study, we introduce a novel method, called MamT$^4$, which is used for simultaneous analysis of four mammography images. A decision is made based on one image of a breast, with attention also devoted to three additional images: another view of the same breast and two images of the other breast. This approach enables the algorithm to closely replicate the practice of a radiologist who reviews the entire set of mammograms for a patient. Furthermore, this paper emphasizes the preprocessing of images, specifically proposing a cropping model (U-Net based on ResNet-34) to help the method remove image artifacts and focus on the breast region. To the best of our knowledge, this study is the first to achieve a ROC-AUC of 84.0 $\pm$ 1.7 and an F1 score of 56.0 $\pm$ 1.3 on an independent test dataset of Vietnam digital mammography (VinDr-Mammo), which is preprocessed with the cropping model.
EndoNet: model for automatic calculation of H-score on histological slides
Aug 22, 2023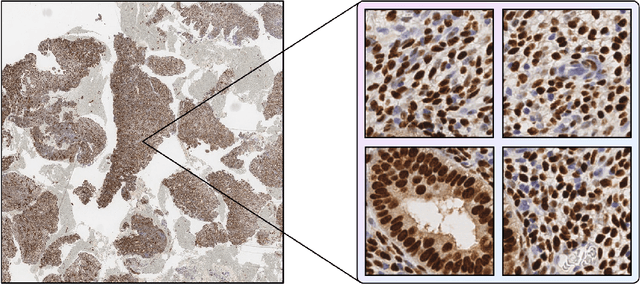
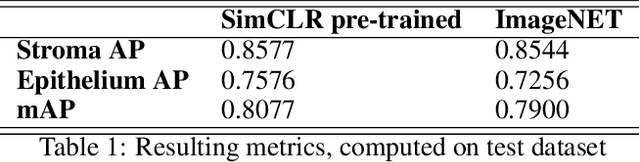
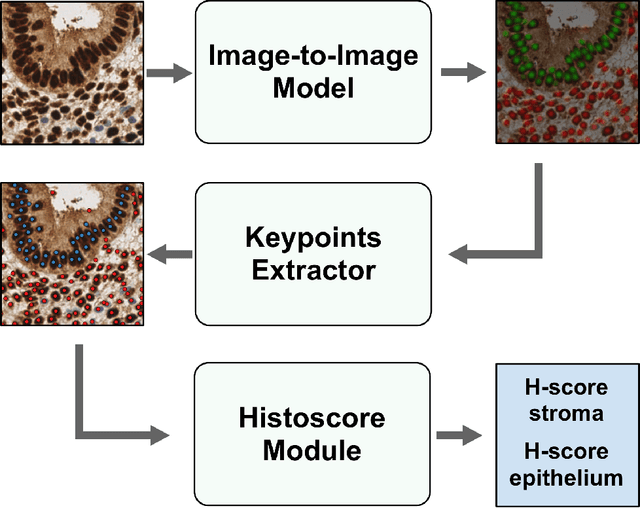
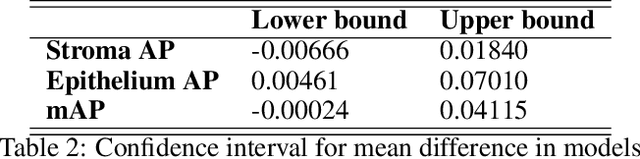
Abstract:H-score is a semi-quantitative method used to assess the presence and distribution of proteins in tissue samples by combining the intensity of staining and percentage of stained nuclei. It is widely used but time-consuming and can be limited in accuracy and precision. Computer-aided methods may help overcome these limitations and improve the efficiency of pathologists' workflows. In this work, we developed a model EndoNet for automatic calculation of H-score on histological slides. Our proposed method uses neural networks and consists of two main parts. The first is a detection model which predicts keypoints of centers of nuclei. The second is a H-score module which calculates the value of the H-score using mean pixel values of predicted keypoints. Our model was trained and validated on 1780 annotated tiles with a shape of 100x100 $\mu m$ and performed 0.77 mAP on a test dataset. Moreover, the model can be adjusted to a specific specialist or whole laboratory to reproduce the manner of calculating the H-score. Thus, EndoNet is effective and robust in the analysis of histology slides, which can improve and significantly accelerate the work of pathologists.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge