Eduardo C. Nunes
Anomalous Sound Detection with Machine Learning: A Systematic Review
Feb 15, 2021



Abstract:Anomalous sound detection (ASD) is the task of identifying whether the sound emitted from an object is normal or anomalous. In some cases, early detection of this anomaly can prevent several problems. This article presents a Systematic Review (SR) about studies related to Anamolous Sound Detection using Machine Learning (ML) techniques. This SR was conducted through a selection of 31 (accepted studies) studies published in journals and conferences between 2010 and 2020. The state of the art was addressed, collecting data sets, methods for extracting features in audio, ML models, and evaluation methods used for ASD. The results showed that the ToyADMOS, MIMII, and Mivia datasets, the Mel-frequency cepstral coefficients (MFCC) method for extracting features, the Autoencoder (AE) and Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) models of ML, the AUC and F1-score evaluation methods were most cited.
Deep Dense and Convolutional Autoencoders for Unsupervised Anomaly Detection in Machine Condition Sounds
Jun 19, 2020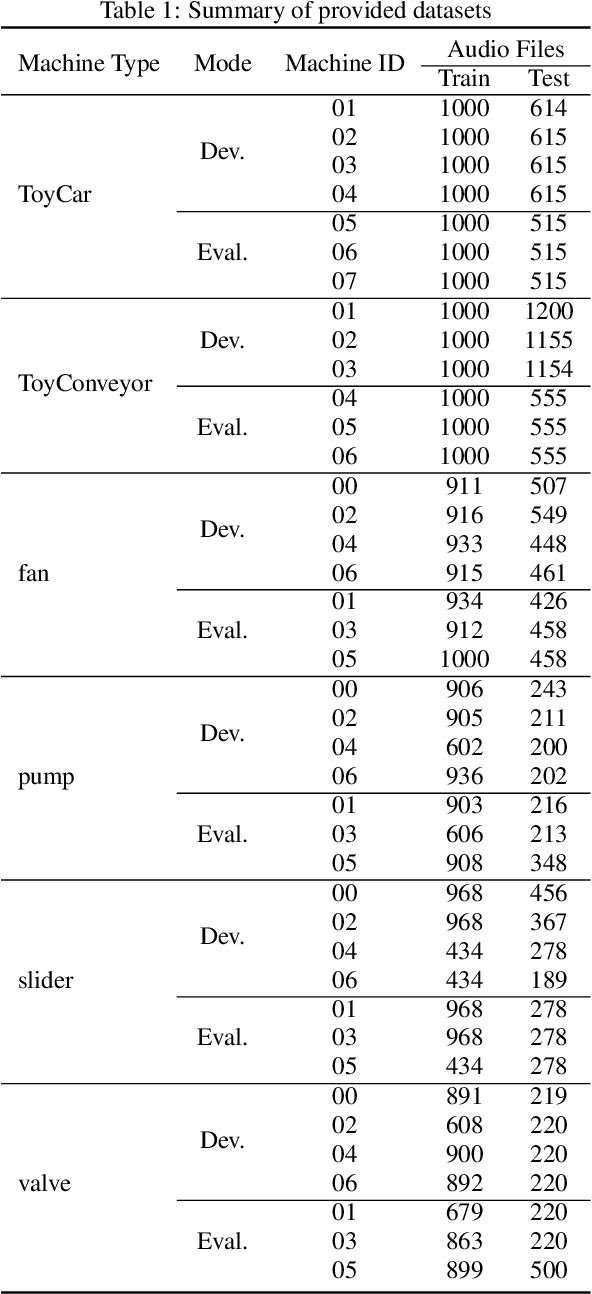
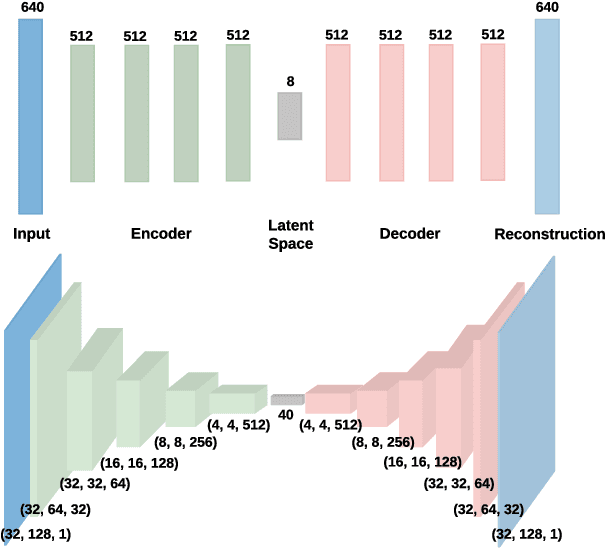
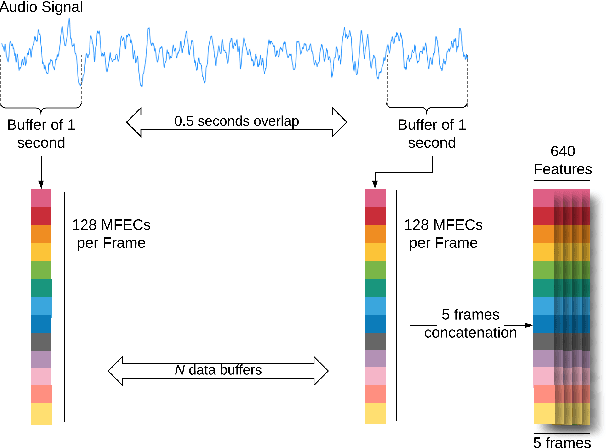
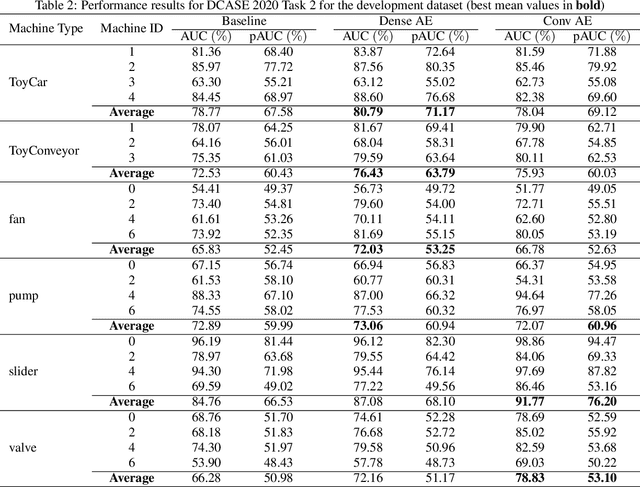
Abstract:This technical report describes two methods that were developed for Task 2 of the DCASE 2020 challenge. The challenge involves an unsupervised learning to detect anomalous sounds, thus only normal machine working condition samples are available during the training process. The two methods involve deep autoencoders, based on dense and convolutional architectures that use melspectogram processed sound features. Experiments were held, using the six machine type datasets of the challenge. Overall, competitive results were achieved by the proposed dense and convolutional AE, outperforming the baseline challenge method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge