Dylan Peifer
Learning a performance metric of Buchberger's algorithm
Jun 07, 2021



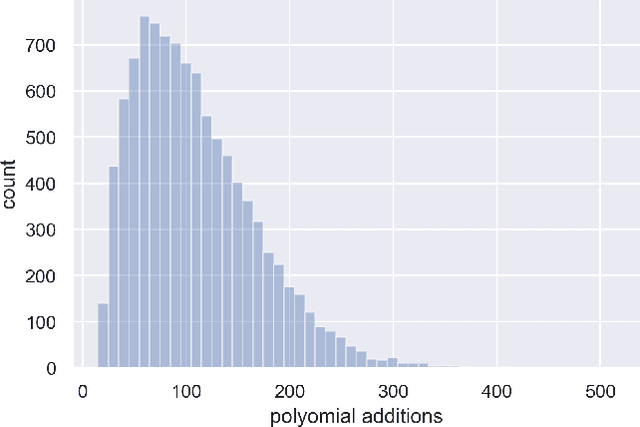
Abstract:What can be (machine) learned about the complexity of Buchberger's algorithm? Given a system of polynomials, Buchberger's algorithm computes a Gr\"obner basis of the ideal these polynomials generate using an iterative procedure based on multivariate long division. The runtime of each step of the algorithm is typically dominated by a series of polynomial additions, and the total number of these additions is a hardware independent performance metric that is often used to evaluate and optimize various implementation choices. In this work we attempt to predict, using just the starting input, the number of polynomial additions that take place during one run of Buchberger's algorithm. Good predictions are useful for quickly estimating difficulty and understanding what features make Gr\"obner basis computation hard. Our features and methods could also be used for value models in the reinforcement learning approach to optimize Buchberger's algorithm introduced in [Peifer, Stillman, and Halpern-Leistner, 2020]. We show that a multiple linear regression model built from a set of easy-to-compute ideal generator statistics can predict the number of polynomial additions somewhat well, better than an uninformed model, and better than regression models built on some intuitive commutative algebra invariants that are more difficult to compute. We also train a simple recursive neural network that outperforms these linear models. Our work serves as a proof of concept, demonstrating that predicting the number of polynomial additions in Buchberger's algorithm is a feasible problem from the point of view of machine learning.
Learning selection strategies in Buchberger's algorithm
May 05, 2020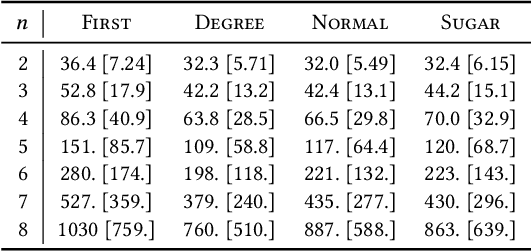
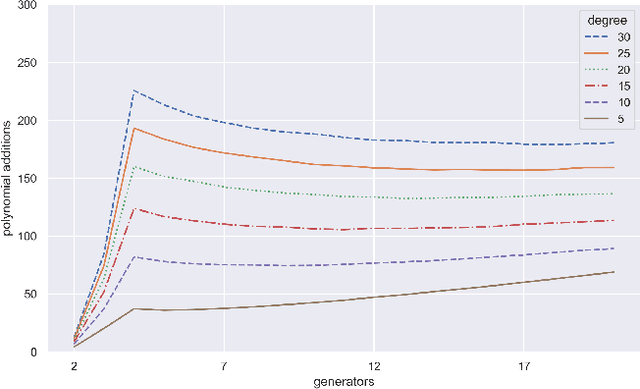
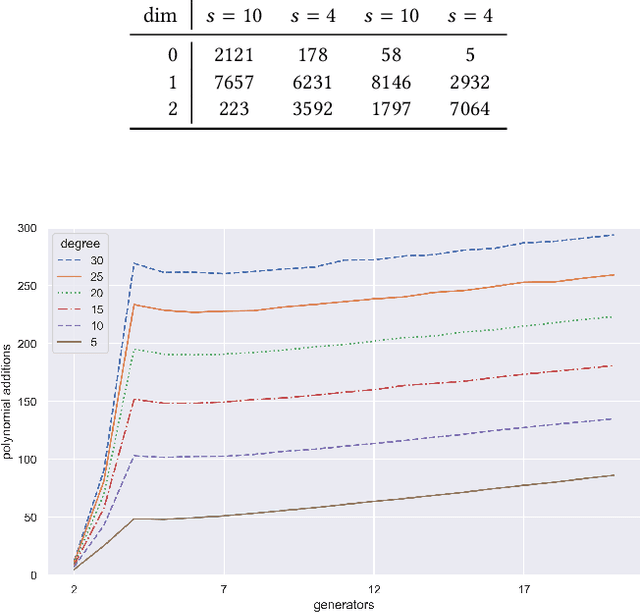
Abstract:Studying the set of exact solutions of a system of polynomial equations largely depends on a single iterative algorithm, known as Buchberger's algorithm. Optimized versions of this algorithm are crucial for many computer algebra systems (e.g., Mathematica, Maple, Sage). We introduce a new approach to Buchberger's algorithm that uses reinforcement learning agents to perform S-pair selection, a key step in the algorithm. We then study how the difficulty of the problem depends on the choices of domain and distribution of polynomials, about which little is known. Finally, we train a policy model using proximal policy optimization (PPO) to learn S-pair selection strategies for random systems of binomial equations. In certain domains, the trained model outperforms state-of-the-art selection heuristics both in number of iterations of the algorithm and total number of polynomial additions performed. These results provide a proof-of-concept that recent developments in machine learning have the potential to improve performance of algorithms in symbolic computation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge