Donghyeon Han
FlashMoE: Reducing SSD I/O Bottlenecks via ML-Based Cache Replacement for Mixture-of-Experts Inference on Edge Devices
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Recently, Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) models have gained attention for efficiently scaling large language models. Although these models are extremely large, their sparse activation enables inference to be performed by accessing only a fraction of the model at a time. This property opens the possibility of on-device inference of MoE, which was previously considered infeasible for such large models. Consequently, various systems have been proposed to leverage this sparsity and enable efficient MoE inference for edge devices. However, previous MoE inference systems like Fiddler[8] or DAOP[13] rely on DRAM-based offloading and are not suitable for memory constrained on-device environments. As recent MoE models grow to hundreds of gigabytes, RAM-offloading solutions become impractical. To address this, we propose FlashMoE, a system that offloads inactive experts to SSD, enabling efficient MoE inference under limited RAM. FlashMoE incorporates a lightweight ML-based caching strategy that adaptively combines recency and frequency signals to maximize expert reuse, significantly reducing storage I/O. In addition, we built a user-grade desktop platform to demonstrate the practicality of FlashMoE. On this real hardware setup, FlashMoE improves cache hit rate by up to 51% over well-known offloading policies such as LRU and LFU, and achieves up to 2.6x speedup compared to existing MoE inference systems.
Extension of Direct Feedback Alignment to Convolutional and Recurrent Neural Network for Bio-plausible Deep Learning
Jun 23, 2020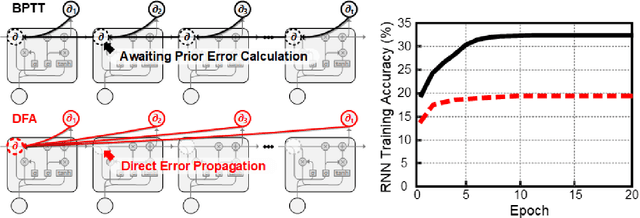
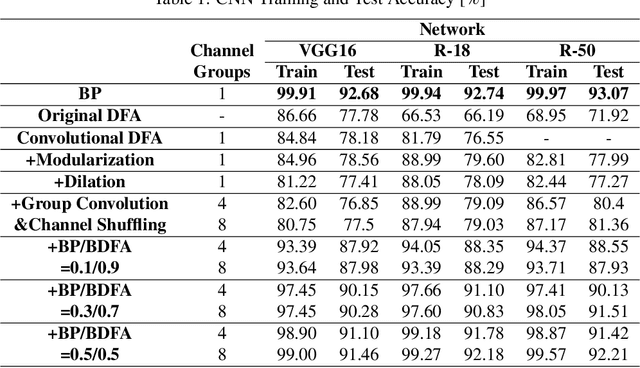
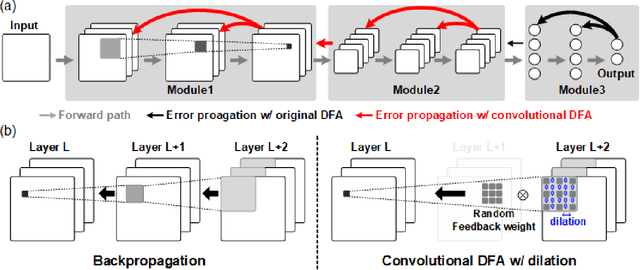
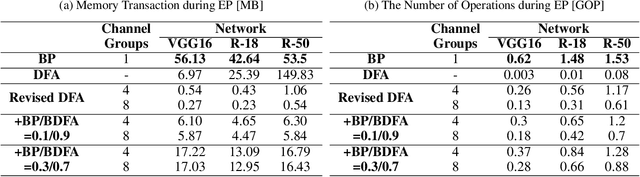
Abstract:Throughout this paper, we focus on the improvement of the direct feedback alignment (DFA) algorithm and extend the usage of the DFA to convolutional and recurrent neural networks (CNNs and RNNs). Even though the DFA algorithm is biologically plausible and has a potential of high-speed training, it has not been considered as the substitute for back-propagation (BP) due to the low accuracy in the CNN and RNN training. In this work, we propose a new DFA algorithm for BP-level accurate CNN and RNN training. Firstly, we divide the network into several modules and apply the DFA algorithm within the module. Second, the DFA with the sparse backward weight is applied. It comes with a form of dilated convolution in the CNN case, and in a form of sparse matrix multiplication in the RNN case. Additionally, the error propagation method of CNN becomes simpler through the group convolution. Finally, hybrid DFA increases the accuracy of the CNN and RNN training to the BP-level while taking advantage of the parallelism and hardware efficiency of the DFA algorithm.
Efficient Convolutional Neural Network Training with Direct Feedback Alignment
Jan 06, 2019



Abstract:There were many algorithms to substitute the back-propagation (BP) in the deep neural network (DNN) training. However, they could not become popular because their training accuracy and the computational efficiency were worse than BP. One of them was direct feedback alignment (DFA), but it showed low training performance especially for the convolutional neural network (CNN). In this paper, we overcome the limitation of the DFA algorithm by combining with the conventional BP during the CNN training. To improve the training stability, we also suggest the feedback weight initialization method by analyzing the patterns of the fixed random matrices in the DFA. Finally, we propose the new training algorithm, binary direct feedback alignment (BDFA) to minimize the computational cost while maintaining the training accuracy compared with the DFA. In our experiments, we use the CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100 dataset to simulate the CNN learning from the scratch and apply the BDFA to the online learning based object tracking application to examine the training in the small dataset environment. Our proposed algorithms show better performance than conventional BP in both two different training tasks especially when the dataset is small.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge