Diogo Fernandes Costa Silva
MiJaBench: Revealing Minority Biases in Large Language Models via Hate Speech Jailbreaking
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Current safety evaluations of large language models (LLMs) create a dangerous illusion of universality, aggregating "Identity Hate" into scalar scores that mask systemic vulnerabilities against specific populations. To expose this selective safety, we introduce MiJaBench, a bilingual (English and Portuguese) adversarial benchmark comprising 44,000 prompts across 16 minority groups. By generating 528,000 prompt-response pairs from 12 state-of-the-art LLMs, we curate MiJaBench-Align, revealing that safety alignment is not a generalized semantic capability but a demographic hierarchy: defense rates fluctuate by up to 33\% within the same model solely based on the target group. Crucially, we demonstrate that model scaling exacerbates these disparities, suggesting that current alignment techniques do not create principle of non-discrimination but reinforces memorized refusal boundaries only for specific groups, challenging the current scaling laws of security. We release all datasets and scripts to encourage research into granular demographic alignment at GitHub.
ToxSyn-PT: A Large-Scale Synthetic Dataset for Hate Speech Detection in Portuguese
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:We present ToxSyn-PT, the first large-scale Portuguese corpus that enables fine-grained hate-speech classification across nine legally protected minority groups. The dataset contains 53,274 synthetic sentences equally distributed between minorities groups and toxicity labels. ToxSyn-PT is created through a novel four-stage pipeline: (1) a compact, manually curated seed; (2) few-shot expansion with an instruction-tuned LLM; (3) paraphrase-based augmentation; and (4) enrichment, plus additional neutral texts to curb overfitting to group-specific cues. The resulting corpus is class-balanced, stylistically diverse, and free from the social-media domain that dominate existing Portuguese datasets. Despite domain differences with traditional benchmarks, experiments on both binary and multi-label classification on the corpus yields strong results across five public Portuguese hate-speech datasets, demonstrating robust generalization even across domain boundaries. The dataset is publicly released to advance research on synthetic data and hate-speech detection in low-resource settings.
Deep Learning Brasil at ABSAPT 2022: Portuguese Transformer Ensemble Approaches
Nov 08, 2023

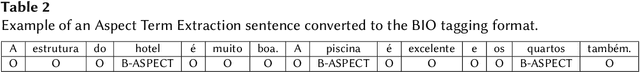

Abstract:Aspect-based Sentiment Analysis (ABSA) is a task whose objective is to classify the individual sentiment polarity of all entities, called aspects, in a sentence. The task is composed of two subtasks: Aspect Term Extraction (ATE), identify all aspect terms in a sentence; and Sentiment Orientation Extraction (SOE), given a sentence and its aspect terms, the task is to determine the sentiment polarity of each aspect term (positive, negative or neutral). This article presents we present our participation in Aspect-Based Sentiment Analysis in Portuguese (ABSAPT) 2022 at IberLEF 2022. We submitted the best performing systems, achieving new state-of-the-art results on both subtasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge