Dibakar Sen
Progressive Ideation using an Agentic AI Framework for Human-AI Co-Creation
Jan 01, 2026Abstract:The generation of truly novel and diverse ideas is important for contemporary engineering design, yet it remains a significant cognitive challenge for novice designers. Current 'single-spurt' AI systems exacerbate this challenge by producing a high volume of semantically clustered ideas. We propose MIDAS (Meta-cognitive Ideation through Distributed Agentic AI System), a novel framework that replaces the single-AI paradigm with a distributed 'team' of specialized AI agents designed to emulate the human meta-cognitive ideation workflow. This agentic system progressively refines ideas and assesses each one for both global novelty (against existing solutions) and local novelty (against previously generated ideas). MIDAS, therefore, demonstrates a viable and progressive paradigm for true human-AI co-creation, elevating the human designer from a passive filterer to a participatory, active, collaborative partner.
Attention is also needed for form design
Aug 27, 2025Abstract:Conventional product design is a cognitively demanding process, limited by its time-consuming nature, reliance on subjective expertise, and the opaque translation of inspiration into tangible concepts. This research introduces a novel, attention-aware framework that integrates two synergistic systems: EUPHORIA, an immersive Virtual Reality environment using eye-tracking to implicitly capture a designer's aesthetic preferences, and RETINA, an agentic AI pipeline that translates these implicit preferences into concrete design outputs. The foundational principles were validated in a two-part study. An initial study correlated user's implicit attention with explicit preference and the next one correlated mood to attention. A comparative study where 4 designers solved challenging design problems using 4 distinct workflows, from a manual process to an end-to-end automated pipeline, showed the integrated EUPHORIA-RETINA workflow was over 4 times more time-efficient than the conventional method. A panel of 50 design experts evaluated the 16 final renderings. Designs generated by the fully automated system consistently received the highest Worthiness (calculated by an inverse Plackett-Luce model based on gradient descent optimization) and Design Effectiveness scores, indicating superior quality across 8 criteria: novelty, visual appeal, emotional resonance, clarity of purpose, distinctiveness of silhouette, implied materiality, proportional balance, & adherence to the brief. This research presents a validated paradigm shift from traditional Computer-Assisted Design (CAD) to a collaborative model of Designer-Assisting Computers (DAC). By automating logistical and skill-dependent generative tasks, the proposed framework elevates the designer's role to that of a creative director, synergizing human intuition with the generative power of agentic AI to produce higher-quality designs more efficiently.
A Novel Mathematical Framework for Objective Evaluation of Ideas using a Conversational AI (CAI) System
Sep 11, 2024
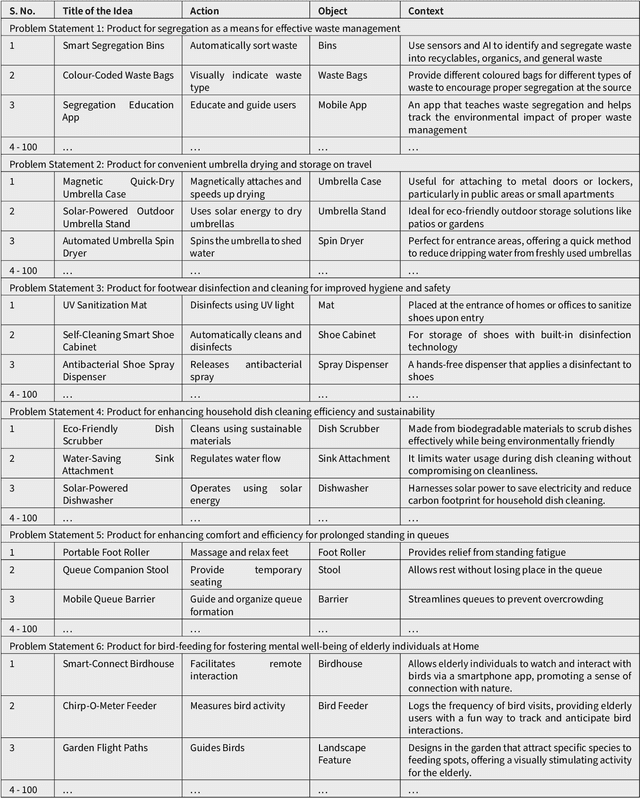

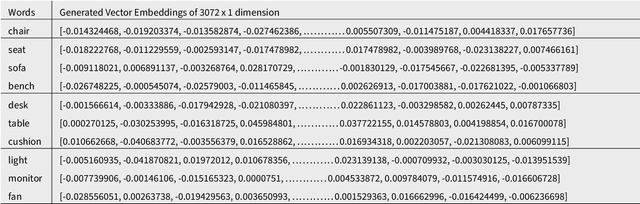
Abstract:The demand for innovation in product design necessitates a prolific ideation phase. Conversational AI (CAI) systems that use Large Language Models (LLMs) such as GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) have been shown to be fruitful in augmenting human creativity, providing numerous novel and diverse ideas. Despite the success in ideation quantity, the qualitative assessment of these ideas remains challenging and traditionally reliant on expert human evaluation. This method suffers from limitations such as human judgment errors, bias, and oversight. Addressing this gap, our study introduces a comprehensive mathematical framework for automated analysis to objectively evaluate the plethora of ideas generated by CAI systems and/or humans. This framework is particularly advantageous for novice designers who lack experience in selecting promising ideas. By converting the ideas into higher dimensional vectors and quantitatively measuring the diversity between them using tools such as UMAP, DBSCAN and PCA, the proposed method provides a reliable and objective way of selecting the most promising ideas, thereby enhancing the efficiency of the ideation phase.
A Novel Idea Generation Tool using a Structured Conversational AI (CAI) System
Sep 09, 2024Abstract:This paper presents a novel conversational AI-enabled active ideation interface as a creative idea-generation tool to assist novice designers in mitigating the initial latency and ideation bottlenecks that are commonly observed. It is a dynamic, interactive, and contextually responsive approach, actively involving a large language model (LLM) from the domain of natural language processing (NLP) in artificial intelligence (AI) to produce multiple statements of potential ideas for different design problems. Integrating such AI models with ideation creates what we refer to as an Active Ideation scenario, which helps foster continuous dialogue-based interaction, context-sensitive conversation, and prolific idea generation. A pilot study was conducted with thirty novice designers to generate ideas for given problems using traditional methods and the new CAI-based interface. The key parameters of fluency, novelty, and variety were used to compare the outcomes qualitatively by a panel of experts. The findings demonstrated the effectiveness of the proposed tool for generating prolific, diverse and novel ideas. The interface was enhanced by incorporating a prompt-engineered structured dialogue style for each ideation stage to make it uniform and more convenient for the designers. The resulting responses of such a structured CAI interface were found to be more succinct and aligned towards the subsequent design stage, namely conceptualization. The paper thus established the rich potential of using Generative AI (Gen-AI) for the early ill-structured phase of the creative product design process.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge