David Choffnes
Northeastern University
SunBlock: Cloudless Protection for IoT Systems
Jan 25, 2024
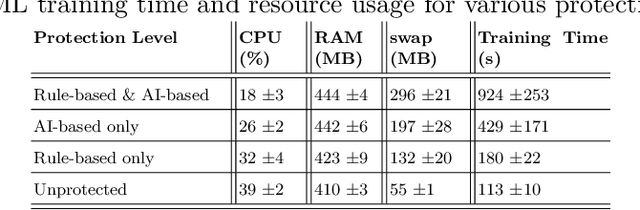

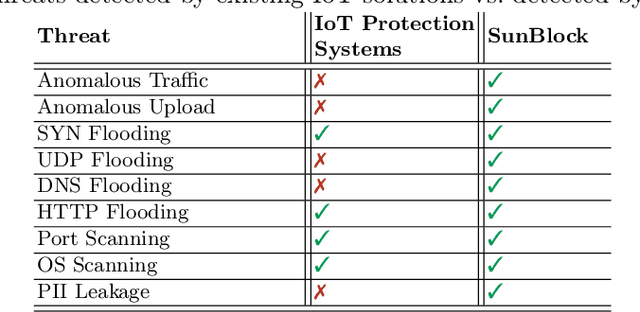
Abstract:With an increasing number of Internet of Things (IoT) devices present in homes, there is a rise in the number of potential information leakage channels and their associated security threats and privacy risks. Despite a long history of attacks on IoT devices in unprotected home networks, the problem of accurate, rapid detection and prevention of such attacks remains open. Many existing IoT protection solutions are cloud-based, sometimes ineffective, and might share consumer data with unknown third parties. This paper investigates the potential for effective IoT threat detection locally, on a home router, using AI tools combined with classic rule-based traffic-filtering algorithms. Our results show that with a slight rise of router hardware resources caused by machine learning and traffic filtering logic, a typical home router instrumented with our solution is able to effectively detect risks and protect a typical home IoT network, equaling or outperforming existing popular solutions, without any effects on benign IoT functionality, and without relying on cloud services and third parties.
Passport: Enabling Accurate Country-Level Router Geolocation using Inaccurate Sources
May 12, 2019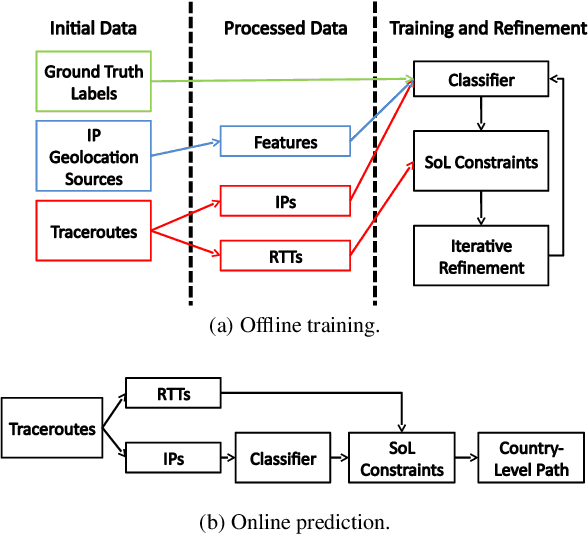

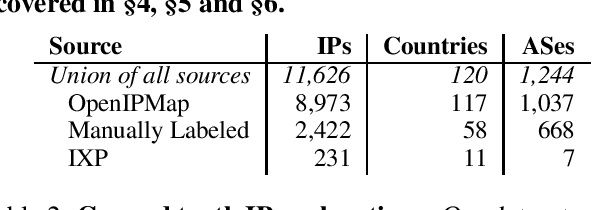
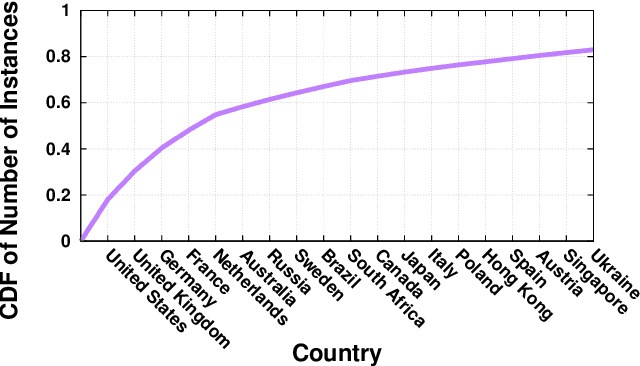
Abstract:When does Internet traffic cross international borders? This question has major geopolitical, legal and social implications and is surprisingly difficult to answer. A critical stumbling block is a dearth of tools that accurately map routers traversed by Internet traffic to the countries in which they are located. This paper presents Passport: a new approach for efficient, accurate country-level router geolocation and a system that implements it. Passport provides location predictions with limited active measurements, using machine learning to combine information from IP geolocation databases, router hostnames, whois records, and ping measurements. We show that Passport substantially outperforms existing techniques, and identify cases where paths traverse countries with implications for security, privacy, and performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge