D. M. Asadujjaman
Detection and Classification of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Utilizing Deep Transfer Learning
Jan 24, 2025Abstract:A mutation in the DNA of a single cell that compromises its function initiates leukemia,leading to the overproduction of immature white blood cells that encroach upon the space required for the generation of healthy blood cells.Leukemia is treatable if identified in its initial stages. However,its diagnosis is both arduous and time consuming. This study proposes a novel approach for diagnosing leukemia across four stages Benign,Early,Pre,and Pro using deep learning techniques.We employed two Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) models as MobileNetV2 with an altered head and a custom model. The custom model consists of multiple convolutional layers,each paired with corresponding max pooling layers.We utilized MobileNetV2 with ImageNet weights,adjusting the head to integrate the final results.The dataset used is the publicly available "Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) Image Dataset", and we applied the Synthetic Minority Oversampling Technique (SMOTE) to augment and balance the training dataset.The custom model achieved an accuracy of 98.6%, while MobileNetV2 attained a superior accuracy of 99.69%. The pretrained model showed promising results,indicating an increased likelihood of real-world application.
Skin Disease Detection and Classification of Actinic Keratosis and Psoriasis Utilizing Deep Transfer Learning
Jan 23, 2025



Abstract:Skin diseases can arise from infections, allergies, genetic factors, autoimmune disorders, hormonal imbalances, or environmental triggers such as sun damage and pollution. Some skin diseases, such as Actinic Keratosis and Psoriasis, can be fatal if not treated in time. Early identification is crucial, but the diagnostic methods for these conditions are often expensive and not widely accessible. In this study, we propose a novel and efficient method for diagnosing skin diseases using deep learning techniques. This approach employs a modified VGG16 Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) model. The model includes several convolutional layers and utilizes ImageNet weights with modified top layers. The top layer is updated with fully connected layers and a final softmax activation layer to classify skin diseases. The dataset used, titled "Skin Disease Dataset," is publicly available. While the VGG16 architecture does not include data augmentation by default, preprocessing techniques such as rotation, shifting, and zooming were applied to augment the data prior to model training. The proposed methodology achieved 90.67% accuracy using the modified VGG16 model, demonstrating its reliability in classifying skin diseases. The promising results highlight the potential of this approach for real-world applications.
Early Detection and Classification of Breast Cancer Using Deep Learning Techniques
Jan 21, 2025
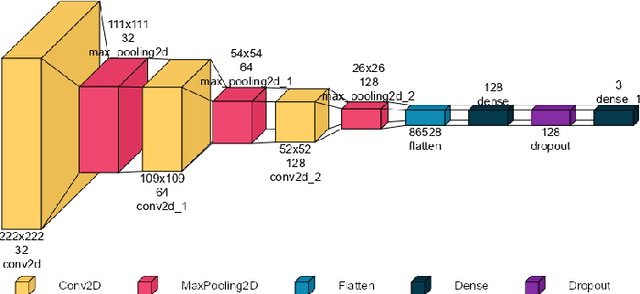


Abstract:Breast cancer is one of the deadliest cancers causing about massive number of patients to die annually all over the world according to the WHO. It is a kind of cancer that develops when the tissues of the breast grow rapidly and unboundly. This fatality rate can be prevented if the cancer is detected before it gets malignant. Using automation for early-age detection of breast cancer, Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies can be implemented for the best outcome. In this study, we are using the Breast Cancer Image Classification dataset collected from the Kaggle depository, which comprises 9248 Breast Ultrasound Images and is classified into three categories: Benign, Malignant, and Normal which refers to non-cancerous, cancerous, and normal images.This research introduces three pretrained model featuring custom classifiers that includes ResNet50, MobileNet, and VGG16, along with a custom CNN model utilizing the ReLU activation function.The models ResNet50, MobileNet, VGG16, and a custom CNN recorded accuracies of 98.41%, 97.91%, 98.19%, and 92.94% on the dataset, correspondingly, with ResNet50 achieving the highest accuracy of 98.41%.This model, with its deep and powerful architecture, is particularly successful in detecting aberrant cells as well as cancerous or non-cancerous tumors. These accuracies show that the Machine Learning methods are more compatible for the classification and early detection of breast cancer.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge