Cole Pearson
Named Entity Recognition in Unstructured Medical Text Documents
Oct 15, 2021
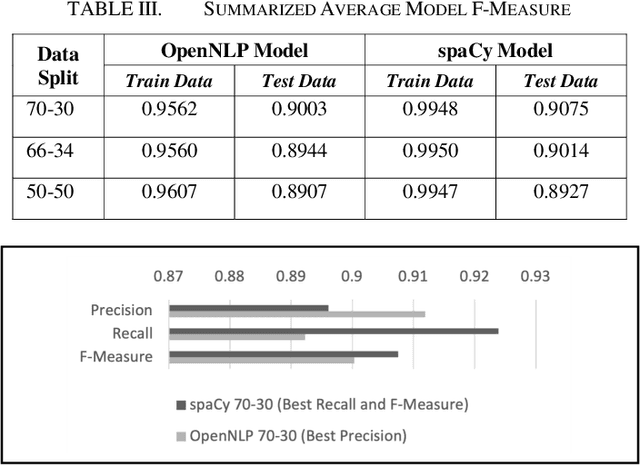
Abstract:Physicians provide expert opinion to legal courts on the medical state of patients, including determining if a patient is likely to have permanent or non-permanent injuries or ailments. An independent medical examination (IME) report summarizes a physicians medical opinion about a patients health status based on the physicians expertise. IME reports contain private and sensitive information (Personally Identifiable Information or PII) that needs to be removed or randomly encoded before further research work can be conducted. In our study the IME is an orthopedic surgeon from a private practice in the United States. The goal of this research is to perform named entity recognition (NER) to identify and subsequently remove/encode PII information from IME reports prepared by the physician. We apply the NER toolkits of OpenNLP and spaCy, two freely available natural language processing platforms, and compare their precision, recall, and f-measure performance at identifying five categories of PII across trials of randomly selected IME reports using each models common default parameters. We find that both platforms achieve high performance (f-measure > 0.9) at de-identification and that a spaCy model trained with a 70-30 train-test data split is most performant.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge