Claudine Brucks
Symbolic Computing with Incremental Mindmaps to Manage and Mine Data Streams - Some Applications
Feb 18, 2009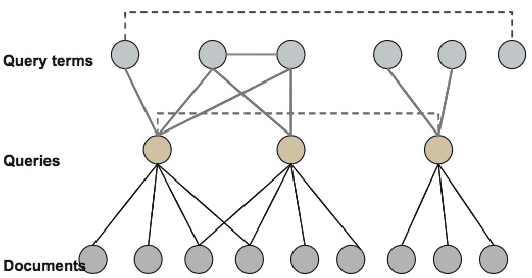
Abstract:In our understanding, a mind-map is an adaptive engine that basically works incrementally on the fundament of existing transactional streams. Generally, mind-maps consist of symbolic cells that are connected with each other and that become either stronger or weaker depending on the transactional stream. Based on the underlying biologic principle, these symbolic cells and their connections as well may adaptively survive or die, forming different cell agglomerates of arbitrary size. In this work, we intend to prove mind-maps' eligibility following diverse application scenarios, for example being an underlying management system to represent normal and abnormal traffic behaviour in computer networks, supporting the detection of the user behaviour within search engines, or being a hidden communication layer for natural language interaction.
* 4 pages; 4 figures
Assembling Actor-based Mind-Maps from Text Stream
Oct 25, 2008



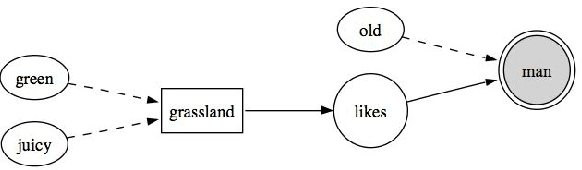
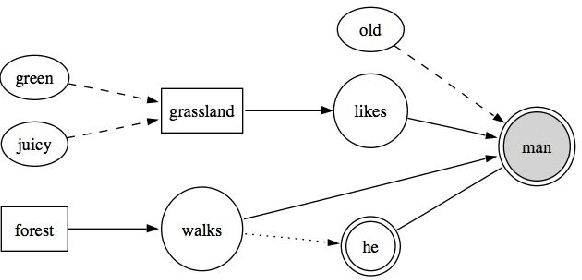
Abstract:For human beings, the processing of text streams of unknown size leads generally to problems because e.g. noise must be selected out, information be tested for its relevance or redundancy, and linguistic phenomenon like ambiguity or the resolution of pronouns be advanced. Putting this into simulation by using an artificial mind-map is a challenge, which offers the gate for a wide field of applications like automatic text summarization or punctual retrieval. In this work we present a framework that is a first step towards an automatic intellect. It aims at assembling a mind-map based on incoming text streams and on a subject-verb-object strategy, having the verb as an interconnection between the adjacent nouns. The mind-map's performance is enriched by a pronoun resolution engine that bases on the work of D. Klein, and C. D. Manning.
* 12 pages, 8 Figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge