Caroline Lyon
Computer Science Department, University of Hertfordshire, UK
Using Single Layer Networks for Discrete, Sequential Data: An Example from Natural Language Processing
Sep 23, 1997
Abstract:A natural language parser which has been successfully implemented is described. This is a hybrid system, in which neural networks operate within a rule based framework. It can be accessed via telnet for users to try on their own text. (For details, contact the author.) Tested on technical manuals, the parser finds the subject and head of the subject in over 90% of declarative sentences. The neural processing components belong to the class of Generalized Single Layer Networks (GSLN). In general, supervised, feed-forward networks need more than one layer to process data. However, in some cases data can be pre-processed with a non-linear transformation, and then presented in a linearly separable form for subsequent processing by a single layer net. Such networks offer advantages of functional transparency and operational speed. For our parser, the initial stage of processing maps linguistic data onto a higher order representation, which can then be analysed by a single layer network. This transformation is supported by information theoretic analysis.
* 28 pages, 9 figures, Latex format, uses epsfig, .styfile included
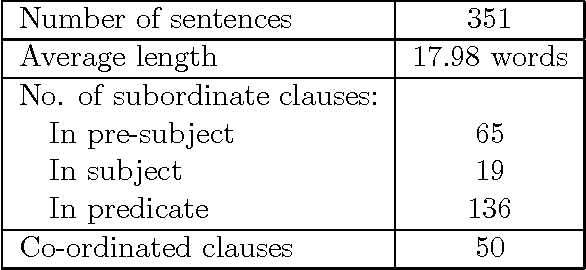
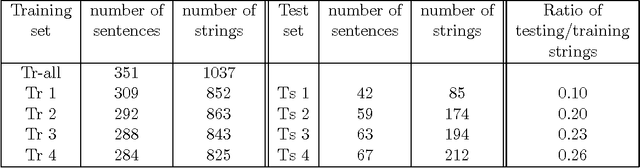
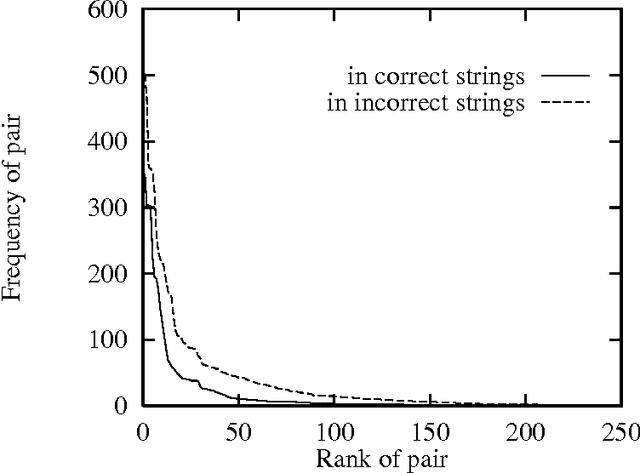
Evaluating Parsing Schemes with Entropy Indicators
Sep 22, 1997Abstract:This paper introduces an objective metric for evaluating a parsing scheme. It is based on Shannon's original work with letter sequences, which can be extended to part-of-speech tag sequences. It is shown that this regular language is an inadequate model for natural language, but a representation is used that models language slightly higher in the Chomsky hierarchy. We show how the entropy of parsed and unparsed sentences can be measured. If the entropy of the parsed sentence is lower, this indicates that some of the structure of the language has been captured. We apply this entropy indicator to support one particular parsing scheme that effects a top down segmentation. This approach could be used to decompose the parsing task into computationally more tractable subtasks. It also lends itself to the extraction of predicate/argument structure.
* 7 pages. LaTeX format, epsfig used, .sty file included
A fast partial parse of natural language sentences using a connectionist method
Mar 22, 1995Abstract:The pattern matching capabilities of neural networks can be used to locate syntactic constituents of natural language. This paper describes a fully automated hybrid system, using neural nets operating within a grammatic framework. It addresses the representation of language for connectionist processing, and describes methods of constraining the problem size. The function of the network is briefly explained, and results are given.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge