Buket D. Barkana
Deep Convolutional Neural Network for Age Estimation based on VGG-Face Model
Sep 06, 2017



Abstract:Automatic age estimation from real-world and unconstrained face images is rapidly gaining importance. In our proposed work, a deep CNN model that was trained on a database for face recognition task is used to estimate the age information on the Adience database. This paper has three significant contributions in this field. (1) This work proves that a CNN model, which was trained for face recognition task, can be utilized for age estimation to improve performance; (2) Over fitting problem can be overcome by employing a pretrained CNN on a large database for face recognition task; (3) Not only the number of training images and the number subjects in a training database effect the performance of the age estimation model, but also the pre-training task of the employed CNN determines the performance of the model.
Skincure: An Innovative Smart Phone-Based Application To Assist In Melanoma Early Detection And Prevention
Jan 06, 2015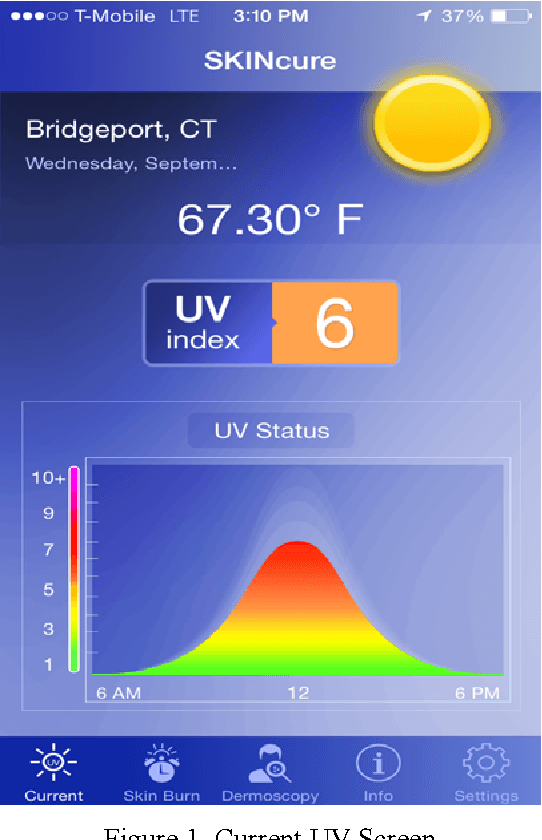
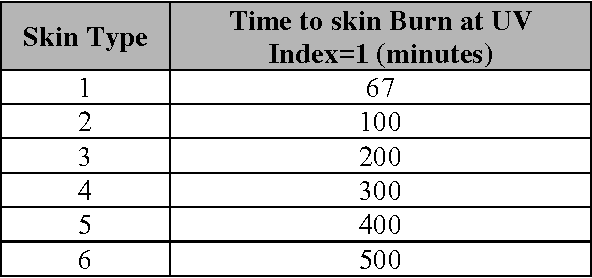
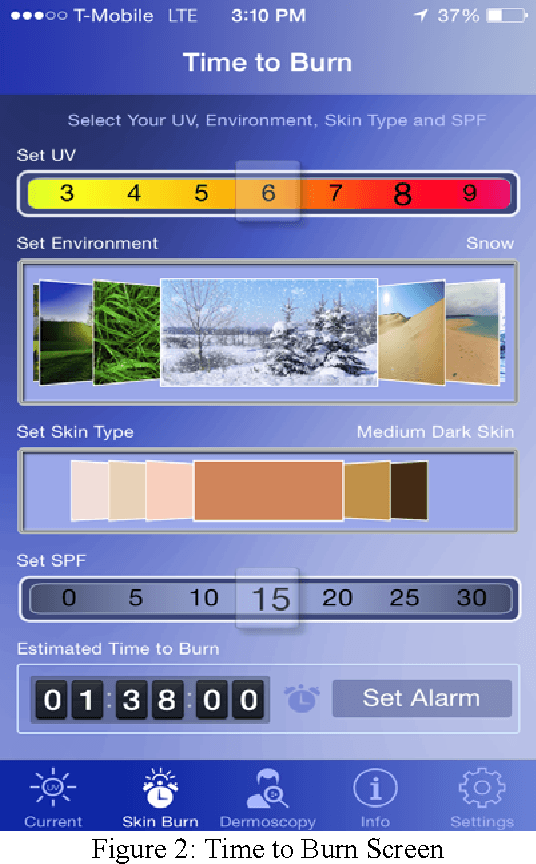
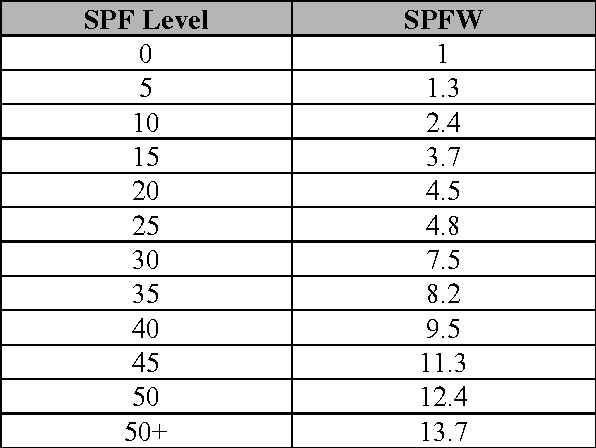
Abstract:Melanoma spreads through metastasis, and therefore it has been proven to be very fatal. Statistical evidence has revealed that the majority of deaths resulting from skin cancer are as a result of melanoma. Further investigations have shown that the survival rates in patients depend on the stage of the infection; early detection and intervention of melanoma implicates higher chances of cure. Clinical diagnosis and prognosis of melanoma is challenging since the processes are prone to misdiagnosis and inaccuracies due to doctors subjectivity. This paper proposes an innovative and fully functional smart-phone based application to assist in melanoma early detection and prevention. The application has two major components; the first component is a real-time alert to help users prevent skin burn caused by sunlight; a novel equation to compute the time for skin to burn is thereby introduced. The second component is an automated image analysis module which contains image acquisition, hair detection and exclusion, lesion segmentation, feature extraction, and classification. The proposed system exploits PH2 Dermoscopy image database from Pedro Hispano Hospital for development and testing purposes. The image database contains a total of 200 dermoscopy images of lesions, including normal, atypical, and melanoma cases. The experimental results show that the proposed system is efficient, achieving classification of the normal, atypical and melanoma images with accuracy of 96.3%, 95.7% and 97.5%, respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge