Badri Vellambi
Intelligence and Unambitiousness Using Algorithmic Information Theory
May 13, 2021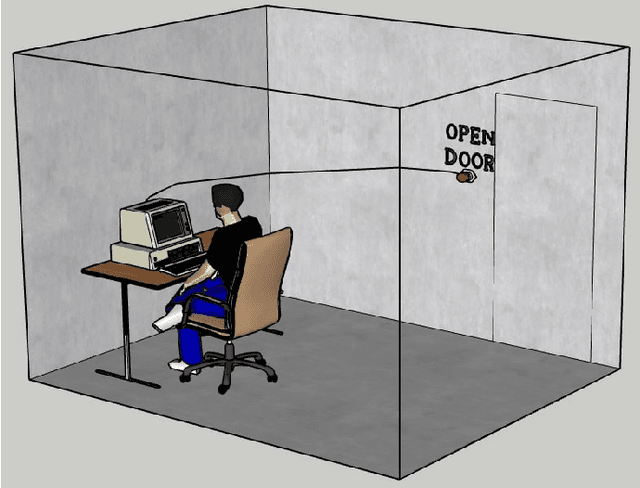
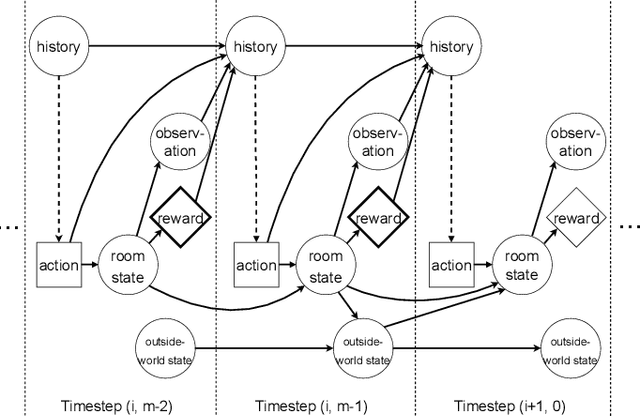
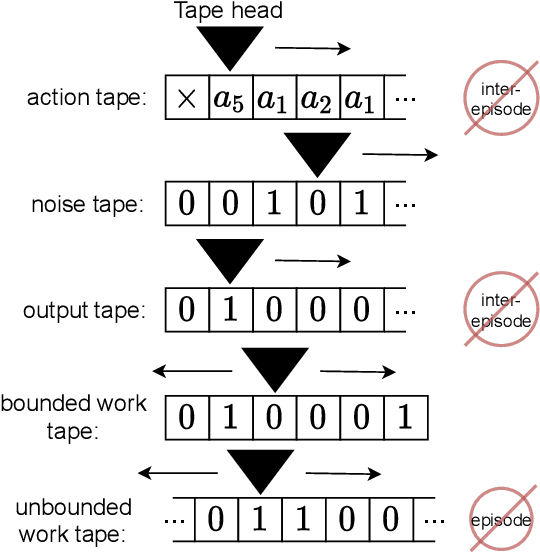
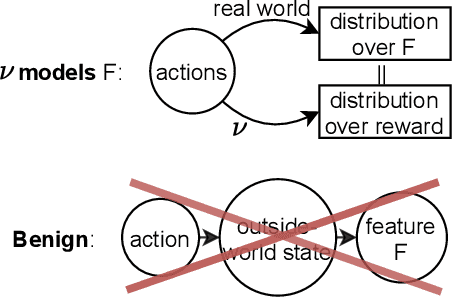
Abstract:Algorithmic Information Theory has inspired intractable constructions of general intelligence (AGI), and undiscovered tractable approximations are likely feasible. Reinforcement Learning (RL), the dominant paradigm by which an agent might learn to solve arbitrary solvable problems, gives an agent a dangerous incentive: to gain arbitrary "power" in order to intervene in the provision of their own reward. We review the arguments that generally intelligent algorithmic-information-theoretic reinforcement learners such as Hutter's (2005) AIXI would seek arbitrary power, including over us. Then, using an information-theoretic exploration schedule, and a setup inspired by causal influence theory, we present a variant of AIXI which learns to not seek arbitrary power; we call it "unambitious". We show that our agent learns to accrue reward at least as well as a human mentor, while relying on that mentor with diminishing probability. And given a formal assumption that we probe empirically, we show that eventually, the agent's world-model incorporates the following true fact: intervening in the "outside world" will have no effect on reward acquisition; hence, it has no incentive to shape the outside world.
* 13 pages, 6 figures, 5-page appendix. arXiv admin note: text overlap with arXiv:1905.12186
Asymptotically Unambitious Artificial General Intelligence
May 29, 2019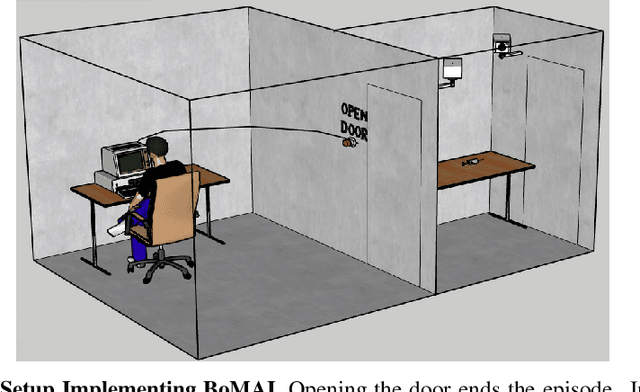
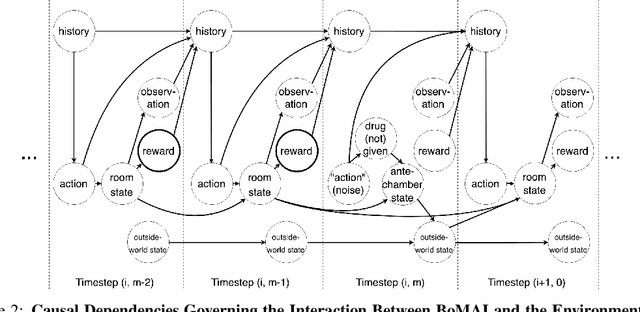
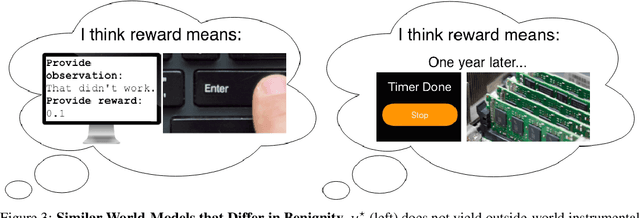
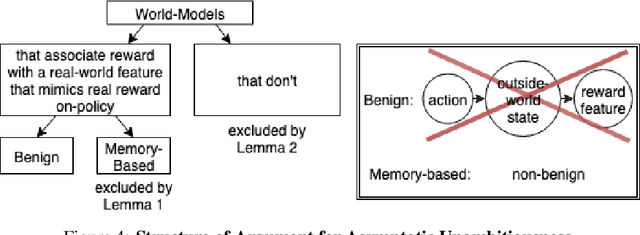
Abstract:General intelligence, the ability to solve arbitrary solvable problems, is supposed by many to be artificially constructible. Narrow intelligence, the ability to solve a given particularly difficult problem, has seen impressive recent development. Notable examples include self-driving cars, Go engines, image classifiers, and translators. Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) presents dangers that narrow intelligence does not: if something smarter than us across every domain were indifferent to our concerns, it would be an existential threat to humanity, just as we threaten many species despite no ill will. Even the theory of how to maintain the alignment of an AGI's goals with our own has proven highly elusive. We present the first algorithm we are aware of for asymptotically unambitious AGI, where "unambitiousness" includes not seeking arbitrary power. Thus, we identify an exception to the Instrumental Convergence Thesis, which is roughly that by default, an AGI would seek power, including over us.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge