Armando Vergara-Martel
Prediction of stent under-expansion in calcified coronary arteries using machine-learning on intravascular optical coherence tomography
May 16, 2022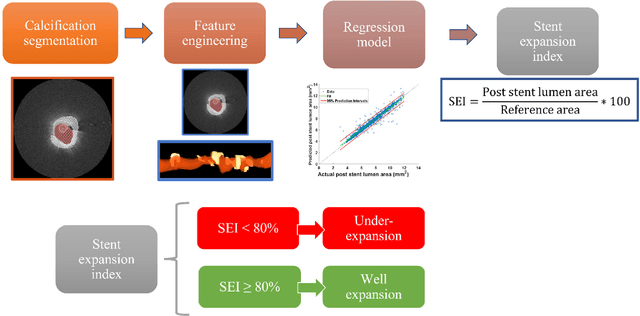
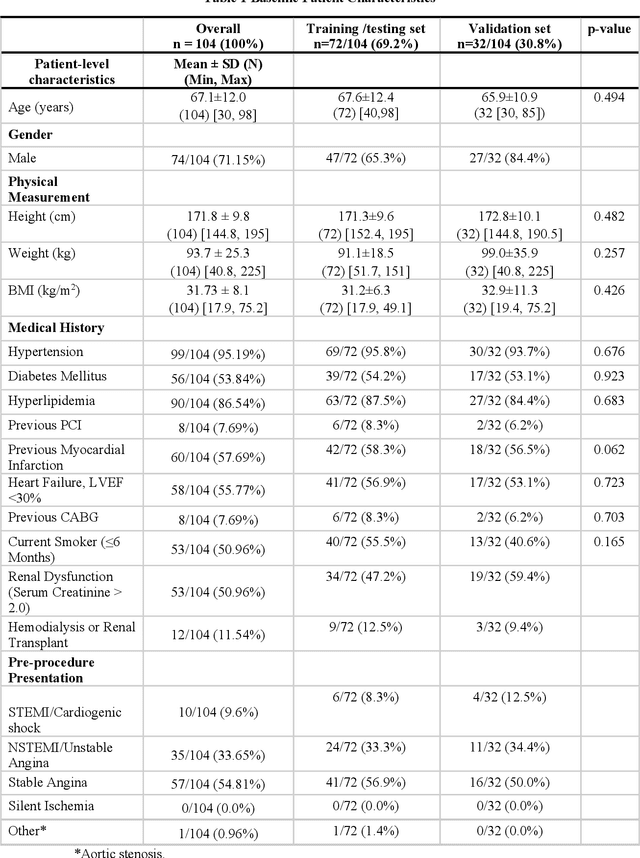
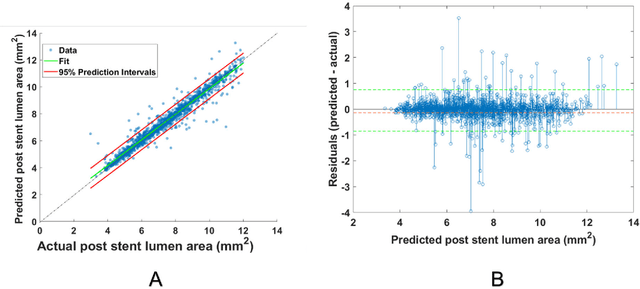
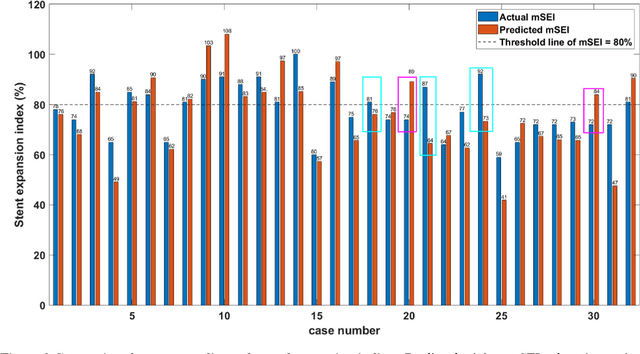
Abstract:BACKGROUND Careful evaluation of the risk of stent under-expansions before the intervention will aid treatment planning, including the application of a pre-stent plaque modification strategy. OBJECTIVES It remains challenging to achieve a proper stent expansion in the presence of severely calcified coronary lesions. Building on our work in deep learning segmentation, we created an automated machine learning approach that uses lesion attributes to predict stent under-expansion from pre-stent images, suggesting the need for plaque modification. METHODS Pre- and post-stent intravascular optical coherence tomography image data were obtained from 110 coronary lesions. Lumen and calcifications in pre-stent images were segmented using deep learning, and numerous features per lesion were extracted. We analyzed stent expansion along the lesion, enabling frame, segmental, and whole-lesion analyses. We trained regression models to predict the poststent lumen area and then to compute the stent expansion index (SEI). Stents with an SEI < or >/= 80% were classified as "under-expanded" and "well-expanded," respectively. RESULTS Best performance (root-mean-square-error = 0.04+/-0.02 mm2, r = 0.94+/-0.04, p < 0.0001) was achieved when we used features from both the lumen and calcification to train a Gaussian regression model for a segmental analysis over a segment length of 31 frames. Under-expansion classification results (AUC=0.85+/-0.02) were significantly improved over other approaches. CONCLUSIONS We used calcifications and lumen features to identify lesions at risk of stent under-expansion. Results suggest that the use of pre-stent images can inform physicians of the need to apply plaque modification approaches.
OCTOPUS -- optical coherence tomography plaque and stent analysis software
Apr 21, 2022



Abstract:Compared with other imaging modalities, intravascular optical coherence tomography (IVOCT) has significant advantages for guiding percutaneous coronary interventions. To aid IVOCT research studies, we developed the Optical Coherence TOmography PlaqUe and Stent (OCTOPUS) analysis software. To automate image analysis results, the software includes several important algorithmic steps: pre-processing, deep learning plaque segmentation, machine learning identification of stent struts, and registration of pullbacks. Interactive visualization and manual editing of segmentations were included in the software. Quantifications include stent deployment characteristics (e.g., stent strut malapposition), strut level analysis, calcium angle, and calcium thickness measurements. Interactive visualizations include (x,y) anatomical, en face, and longitudinal views with optional overlays. Underlying plaque segmentation algorithm yielded excellent pixel-wise results (86.2% sensitivity and 0.781 F1 score). Using OCTOPUS on 34 new pullbacks, we determined that following automated segmentation, only 13% and 23% of frames needed any manual touch up for detailed lumen and calcification labeling, respectively. Only up to 3.8% of plaque pixels were modified, leading to an average editing time of only 7.5 seconds/frame, an approximately 80% reduction compared to manual analysis. Regarding stent analysis, sensitivity and precision were both greater than 90%, and each strut was successfully classified as either covered or uncovered with high sensitivity (94%) and specificity (90%). We introduced and evaluated the clinical application of a highly automated software package, OCTOPUS, for quantitative plaque and stent analysis in IVOCT images. The software is currently used as an offline tool for research purposes; however, the software's embedded algorithms may also be useful for real-time treatment planning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge