Ana Roxin
LIB
Knowledge-based Drug Samples' Comparison
Jul 05, 2024

Abstract:Drug sample comparison is a process used by the French National police to identify drug distribution networks. The current approach is based on manual comparison done by forensic experts. In this article, we present our approach to acquire, formalise, and specify expert knowledge to improve the current process. For modelling the underlying knowledge we use an ontology coupled with logical rules. The different steps of our approach are designed to be reused in other application domains. The results obtained are explainable making them usable by experts in different fields.
Towards French Smart Building Code: Compliance Checking Based on Semantic Rules
Oct 01, 2019

Abstract:Manually checking models for compliance against building regulation is a time-consuming task for architects and construction engineers. There is thus a need for algorithms that process information from construction projects and report non-compliant elements. Still automated code-compliance checking raises several obstacles. Building regulations are usually published as human readable texts and their content is often ambiguous or incomplete. Also, the vocabulary used for expressing such regulations is very different from the vocabularies used to express Building Information Models (BIM). Furthermore, the high level of details associated to BIM-contained geometries induces complex calculations. Finally, the level of complexity of the IFC standard also hinders the automation of IFC processing tasks. Model chart, formal rules and pre-processors approach allows translating construction regulations into semantic queries. We further demonstrate the usefulness of this approach through several use cases. We argue our approach is a step forward in bridging the gap between regulation texts and automated checking algorithms. Finally with the recent building ontology BOT recommended by the W3C Linked Building Data Community Group, we identify perspectives for standardizing and extending our approach.
IfcWoD, Semantically Adapting IFC Model Relations into OWL Properties
Nov 12, 2015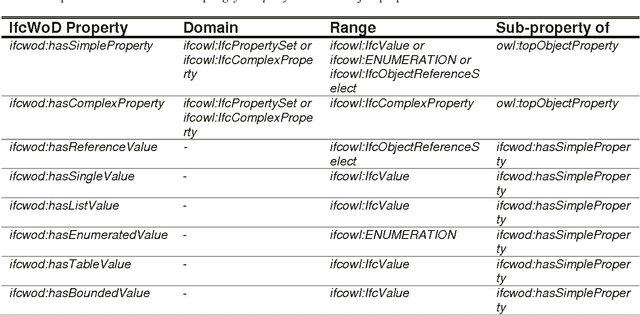
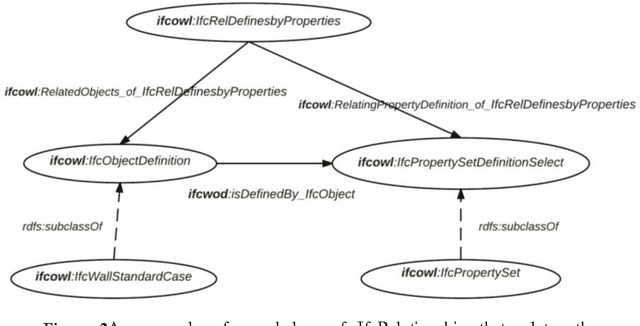
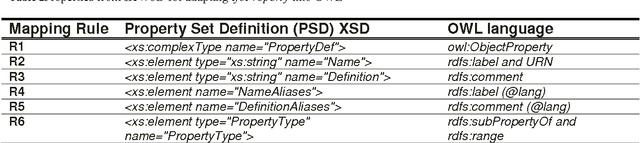

Abstract:In the context of Building Information Modelling, ontologies have been identified as interesting in achieving information interoperability. Regarding the construction and facility management domains, several IFC (Industry Foundation Classes) based ontologies have been developed, such as IfcOWL. In the context of ontology modelling, the constraint of optimizing the size of IFC STEP-based files can be leveraged. In this paper, we propose an adaptation of the IFC model into OWL which leverages from all modelling constraints required by the object-oriented structure of IFC schema. Therefore, we do not only present a syntactic but also a semantic adaptation of the IFC model. Our model takes into consideration the meaning of entities, relationships, properties and attributes defined by the IFC standard. Our approach presents several advantages compared to other initiatives such as the optimization of query execution time. Every advantage is defended by means of practical examples and benchmarks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge