Adam Coscia
LLM Prompt Evaluation for Educational Applications
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:As large language models (LLMs) become increasingly common in educational applications, there is a growing need for evidence-based methods to design and evaluate LLM prompts that produce personalized and pedagogically aligned out-puts. This study presents a generalizable, systematic approach for evaluating prompts, demonstrated through an analysis of LLM-generated follow-up questions in a structured dialogue activity. Six prompt templates were designed and tested. The templates incorporated established prompt engineering patterns, with each prompt emphasizing distinct pedagogical strategies. The prompt templates were compared through a tournament-style evaluation framework that can be adapted for other educational applications. The tournament employed the Glicko2 rating system with eight judges evaluating question pairs across three dimensions: format, dialogue support, and appropriateness for learners. Data was sourced from 120 authentic user interactions across three distinct educational deployments. Results showed that a single prompt related to strategic reading out-performed other templates with win probabilities ranging from 81% to 100% in pairwise comparisons. This prompt combined persona and context manager pat-terns and was designed to support metacognitive learning strategies such as self-directed learning. The methodology showcases how educational technology re- searchers can systematically evaluate and improve prompt designs, moving beyond ad-hoc prompt engineering toward evidence-based prompt development for educational applications.
OnGoal: Tracking and Visualizing Conversational Goals in Multi-Turn Dialogue with Large Language Models
Aug 28, 2025
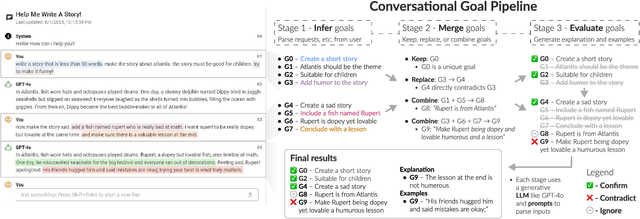

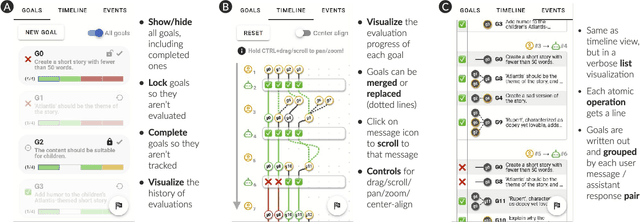
Abstract:As multi-turn dialogues with large language models (LLMs) grow longer and more complex, how can users better evaluate and review progress on their conversational goals? We present OnGoal, an LLM chat interface that helps users better manage goal progress. OnGoal provides real-time feedback on goal alignment through LLM-assisted evaluation, explanations for evaluation results with examples, and overviews of goal progression over time, enabling users to navigate complex dialogues more effectively. Through a study with 20 participants on a writing task, we evaluate OnGoal against a baseline chat interface without goal tracking. Using OnGoal, participants spent less time and effort to achieve their goals while exploring new prompting strategies to overcome miscommunication, suggesting tracking and visualizing goals can enhance engagement and resilience in LLM dialogues. Our findings inspired design implications for future LLM chat interfaces that improve goal communication, reduce cognitive load, enhance interactivity, and enable feedback to improve LLM performance.
KnowledgeVIS: Interpreting Language Models by Comparing Fill-in-the-Blank Prompts
Mar 07, 2024



Abstract:Recent growth in the popularity of large language models has led to their increased usage for summarizing, predicting, and generating text, making it vital to help researchers and engineers understand how and why they work. We present KnowledgeVis, a human-in-the-loop visual analytics system for interpreting language models using fill-in-the-blank sentences as prompts. By comparing predictions between sentences, KnowledgeVis reveals learned associations that intuitively connect what language models learn during training to natural language tasks downstream, helping users create and test multiple prompt variations, analyze predicted words using a novel semantic clustering technique, and discover insights using interactive visualizations. Collectively, these visualizations help users identify the likelihood and uniqueness of individual predictions, compare sets of predictions between prompts, and summarize patterns and relationships between predictions across all prompts. We demonstrate the capabilities of KnowledgeVis with feedback from six NLP experts as well as three different use cases: (1) probing biomedical knowledge in two domain-adapted models; and (2) evaluating harmful identity stereotypes and (3) discovering facts and relationships between three general-purpose models.
iScore: Visual Analytics for Interpreting How Language Models Automatically Score Summaries
Mar 07, 2024Abstract:The recent explosion in popularity of large language models (LLMs) has inspired learning engineers to incorporate them into adaptive educational tools that automatically score summary writing. Understanding and evaluating LLMs is vital before deploying them in critical learning environments, yet their unprecedented size and expanding number of parameters inhibits transparency and impedes trust when they underperform. Through a collaborative user-centered design process with several learning engineers building and deploying summary scoring LLMs, we characterized fundamental design challenges and goals around interpreting their models, including aggregating large text inputs, tracking score provenance, and scaling LLM interpretability methods. To address their concerns, we developed iScore, an interactive visual analytics tool for learning engineers to upload, score, and compare multiple summaries simultaneously. Tightly integrated views allow users to iteratively revise the language in summaries, track changes in the resulting LLM scores, and visualize model weights at multiple levels of abstraction. To validate our approach, we deployed iScore with three learning engineers over the course of a month. We present a case study where interacting with iScore led a learning engineer to improve their LLM's score accuracy by three percentage points. Finally, we conducted qualitative interviews with the learning engineers that revealed how iScore enabled them to understand, evaluate, and build trust in their LLMs during deployment.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge