A. Queiroz
Intelligibility Enhancement of Acoustic Noisy Speech for Autism Spectrum Disorder Condition
Jan 22, 2024



Abstract:This work introduces a time domain personalized method (pGTFF0) to achieve intelligibility improvement of noisy speech for Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) situation. For this proposal, harmonic features estimated from speech frames are considered as center frequencies of Gammatone auditory filterbanks. A gain factor is further applied to the output of the filtered samples. The key goal is the emulation of an external noise filtering tailored for individuals with ASD. A perceptual listening test demonstrates that ASD volunteers attained lower intelligibility rates than Neurotypical (NT). The proposed solution is compared to three competing approaches considering four acoustic noises at different signal-to-noise ratios. Two objective measures (ESTOI and PESQ) are also adopted for evaluation. The experimental results show that the personalized solution outperformed the competing approaches in terms of intelligibility and quality improvement.
Harmonic Detection from Noisy Speech with Auditory Frame Gain for Intelligibility Enhancement
Jan 22, 2024



Abstract:This paper introduces a novel (HDAG - Harmonic Detection for Auditory Gain) method for speech intelligibility enhancement in noisy scenarios. In the proposed scheme, a series of selective Gammachirp filters are adopted to emphasize the harmonic components of speech reducing the masking effects of acoustic noises. The fundamental frequency are estimated by the HHT-Amp technique. Harmonic patterns estimated with low accuracy are detected and adjusted according the FSFFE low/high pitch separation. The central frequencies of the filterbank are defined considering the third octave subbands which are best suited to cover the regions most relevant to intelligibility. Before signal reconstruction, the gammachirp filtered components are amplified by gain factors regulated by FSFFE classification. The proposed HDAG solution and three baseline techniques are examined considering six background noises with four signal-to-noise ratios. Three objective measures are adopted for the evaluation of speech intelligibility and quality. Several experiments are conducted to demonstrate that the proposed scheme achieves better speech intelligibility improvement when compared to the competing approaches. A perceptual listening test is further considered and corroborates with the objective results.
Noisy Speech Based Temporal Decomposition to Improve Fundamental Frequency Estimation
Dec 18, 2021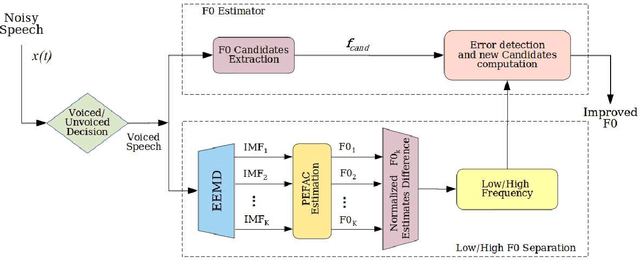
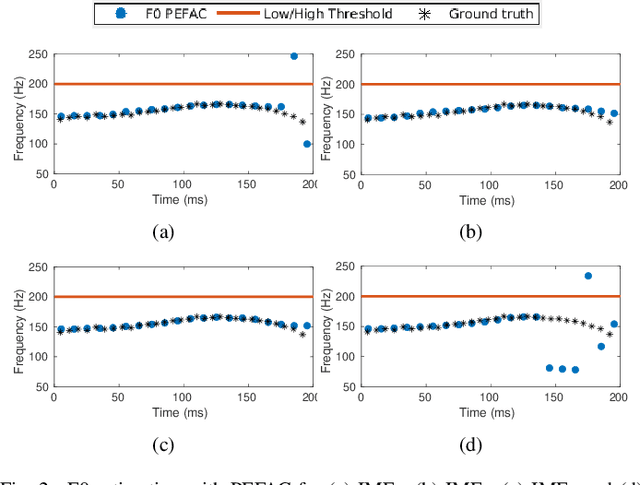
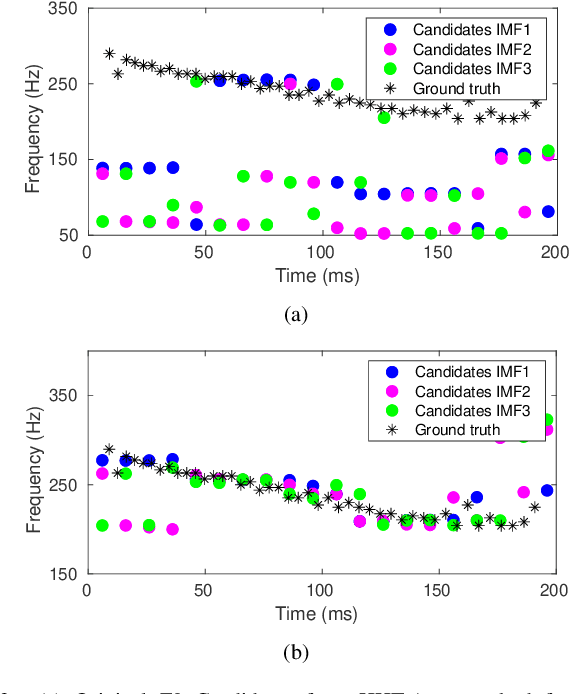
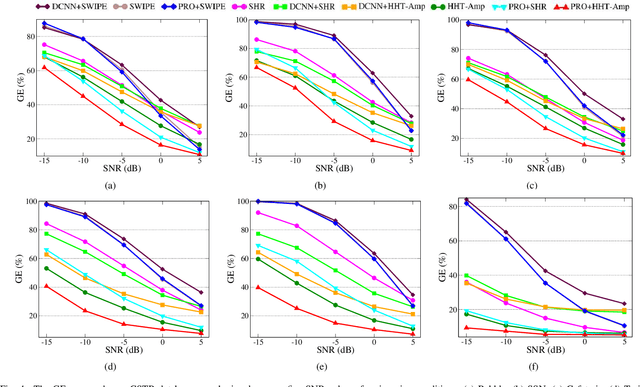
Abstract:This paper introduces a novel method to separate noisy speech into low or high frequency frames, in order to improve fundamental frequency (F0) estimation accuracy. In this proposal, the target signal is analyzed by means of the ensemble empirical mode decomposition. Next, the pitch information is extracted from the first decomposition modes. This feature indicates the frequency region where the F0 of speech should be located, thus separating the frames into low-frequency (LF) or high-frequency (HF). The separation is applied to correct candidates extracted from a conventional fundamental frequency detection method, and hence improving the accuracy of F0 estimate. The proposed method is evaluated in experiments with CSTR and TIMIT databases, considering six acoustic noises under various signal-to-noise ratios. A pitch enhancement algorithm is adopted as baseline in the evaluation analysis considering three conventional estimators. Results show that the proposed method outperforms the competing strategies, in terms of low/high frequency separation accuracy. Moreover, the performance metrics of the F0 estimation techniques show that the novel solution is able to better improve F0 detection accuracy when compared to competitive approaches under different noisy conditions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge