A. Maaref
Enhancing AmBC Systems with Deep Learning for Joint Channel Estimation and Signal Detection
Nov 15, 2023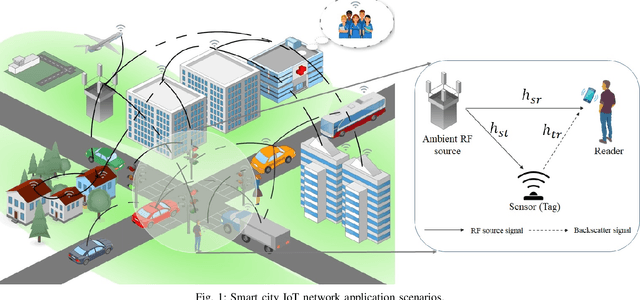
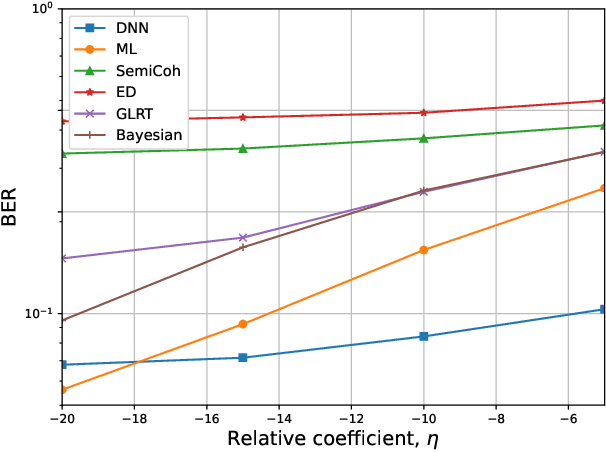
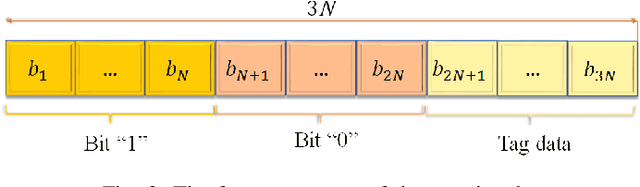
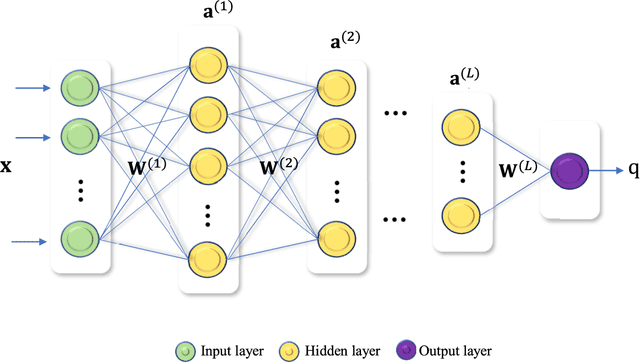
Abstract:The era of ubiquitous, affordable wireless connectivity has opened doors to countless practical applications. In this context, ambient backscatter communication (AmBC) stands out, utilizing passive tags to establish connections with readers by harnessing reflected ambient radio frequency (RF) signals. However, conventional data detectors face limitations due to their inadequate knowledge of channel and RF-source parameters. To address this challenge, we propose an innovative approach using a deep neural network (DNN) for channel state estimation (CSI) and signal detection within AmBC systems. Unlike traditional methods that separate CSI estimation and data detection, our approach leverages a DNN to implicitly estimate CSI and simultaneously detect data. The DNN model, trained offline using simulated data derived from channel statistics, excels in online data recovery, ensuring robust performance in practical scenarios. Comprehensive evaluations validate the superiority of our proposed DNN method over traditional detectors, particularly in terms of bit error rate (BER). In high signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) conditions, our method exhibits an impressive approximately 20% improvement in BER performance compared to the maximum likelihood (ML) approach. These results underscore the effectiveness of our developed approach for AmBC channel estimation and signal detection. In summary, our method outperforms traditional detectors, bolstering the reliability and efficiency of AmBC systems, even in challenging channel conditions.
Improved Signal Detection for Ambient Backscatter Communications
Jun 22, 2023Abstract:In ambient backscatter communication (AmBC) systems, passive tags connect to a reader by reflecting an ambient radio frequency (RF) signal. However, the reader may not know the channel states and RF source parameters and can experience interference. The traditional energy detector (TED) appears to be an ideal solution. However, it performs poorly under these conditions. To address this, we propose two new detectors: (1) A joint correlation-energy detector (JCED) based on the first-order correlation of the received samples and (2) An improved energy detector (IED) based on the p-th norm of the received signal vector. We compare the performance of the IED and TED under generalized noise modeled using the McLeish distribution and derive a general analytical formula for the area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves. Based on our results, both detectors outperform TED. For example, the probability of detection with a false alarm rate of 1% for JCED and IED is 14% and 5% higher, respectively, compared to TED. These gains are even higher using the direct interference cancellation (DIC) technique, with increases of 16% and 7%, respectively. Overall, our proposed detectors offer better performance than the TED, making them useful tools for improving AmBC system performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge