Özgün Ersoy
Compressive Sensing Imaging Using Caustic Lens Mask Generated by Periodic Perturbation in a Ripple Tank
May 01, 2024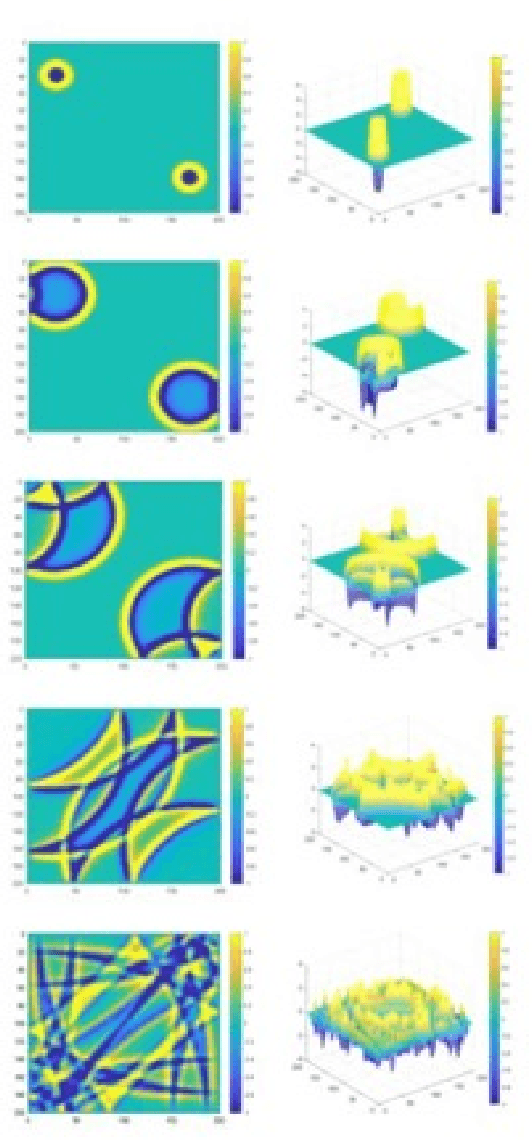

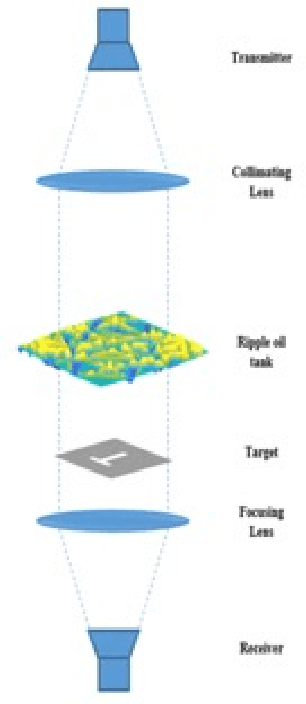
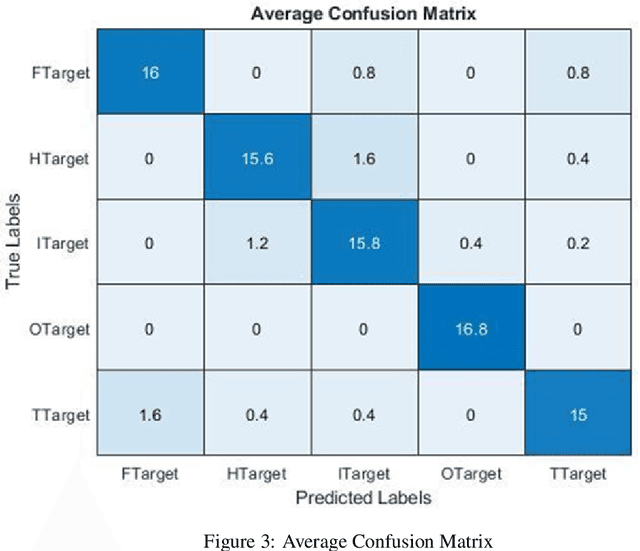
Abstract:Terahertz imaging shows significant potential across diverse fields, yet the cost-effectiveness of multi-pixel imaging equipment remains an obstacle for many researchers. To tackle this issue, the utilization of single-pixel imaging arises as a lower-cost option, however, the data collection process necessary for reconstructing images is time-consuming. Compressive Sensing offers a promising solution by enabling image generation with fewer measurements than required by Nyquist's theorem, yet long processing times remain an issue, especially for large-sized images. Our proposed solution to this issue involves using caustic lens effect induced by perturbations in a ripple tank as a sampling mask. The dynamic characteristics of the ripple tank introduce randomness into the sampling process, thereby reducing measurement time through exploitation of the inherent sparsity of THz band signals. In this study, a Convolutional Neural Network was used to conduct target classification, based on the distinctive signal patterns obtained via the caustic lens mask. The suggested classifier obtained a 95.16 % accuracy rate in differentiating targets resembling Latin letters.
UAV-based Maritime Communications: Relaying to Enhance the Link Quality
Apr 17, 2023Abstract:Providing a stable connectivity in maritime communications is of utmost importance to unleash the full potential of smart ports. Nonetheless, due to the crowded nature of harbor environments, it is likely that some ships are shadowed by others, resulting in reduced received power that subsequently diminishes their data rates-even threatens basic connectivity requirements. Given that UAVs have been regarded as an integral part of future generations of wireless communication networks, they can be employed in maritime communications as well. In this paper, we investigate the use of UAV-mounted relays in order to help mitigate the reduced data rates of blocked links in maritime communications. Various communication architectures are considered based on the positioning mechanism of the UAV; in this regard, fixed, k-means algorithm-based, and landing spot-based positioning approaches are examined. On the other hand, since UAVs are predominantly battery-operated, the energy consumption performances of these approaches are also measured. Results reveal that the landing spot-based UAV relay positioning approach finds the best trade-off between the data rate and energy consumption.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge