When Physical Unclonable Function Meets Biometrics
Paper and Code
Dec 14, 2020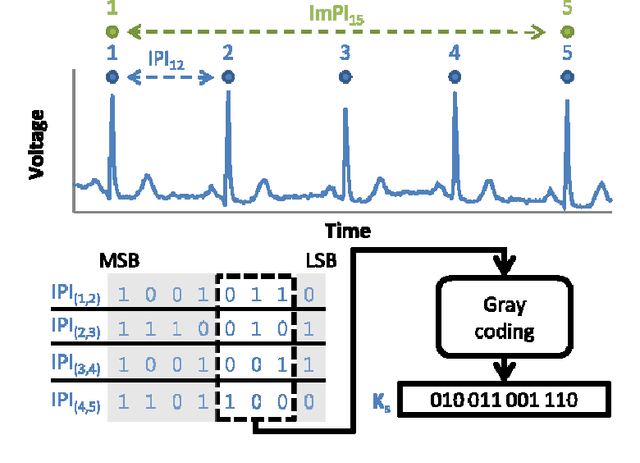
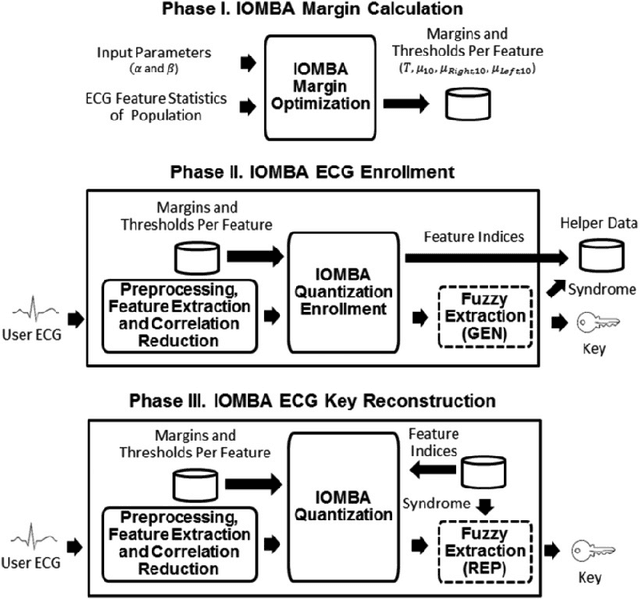
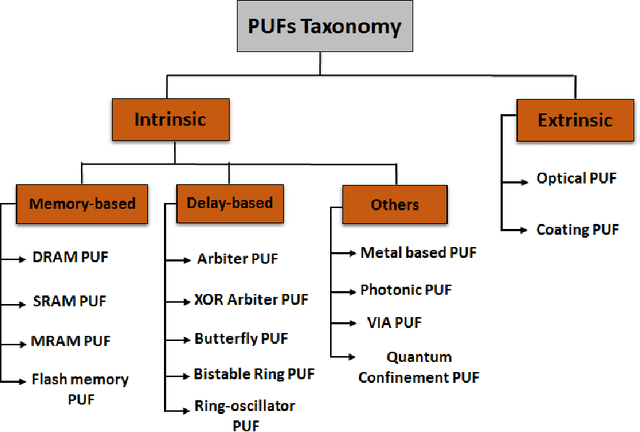
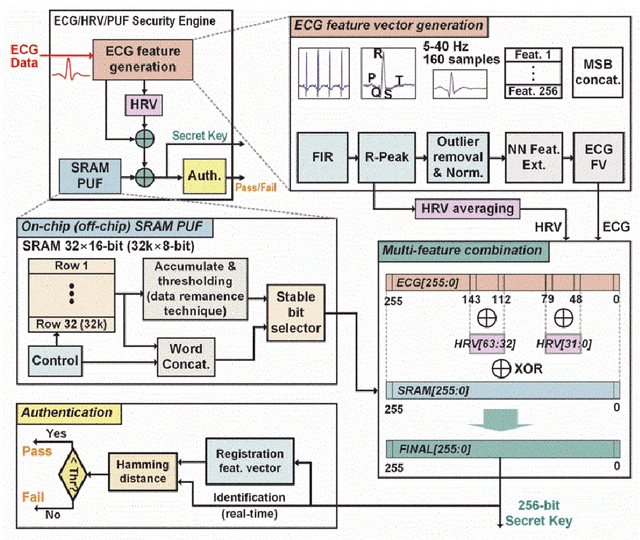
As the Covid-19 pandemic grips the world, healthcare systems are being reshaped, where the e-health concepts become more likely to be accepted. Wearable devices often carry sensitive information from users which are exposed to security and privacy risks. Moreover, users have always had the concern of being counterfeited between the fabrication process and vendors' storage. Hence, not only securing personal data is becoming a crucial obligation, but also device verification is another challenge. To address biometrics authentication and physically unclonable functions (PUFs) need to be put in place to mitigate the security and privacy of the users. Among biometrics modalities, Electrocardiogram (ECG) based biometric has become popular as it can authenticate patients and monitor the patient's vital signs. However, researchers have recently started to study the vulnerabilities of the ECG biometric systems and tried to address the issues of spoofing. Moreover, most of the wearable is enabled with CPU and memories. Thus, volatile memory-based (NVM) PUF can be easily placed in the device to avoid counterfeit. However, many research challenged the unclonability characteristics of PUFs. Thus, a careful study on these attacks should be sufficient to address the need. In this paper, our aim is to provide a comprehensive study on the state-of-the-art developments papers based on biometrics enabled hardware security.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge