Variational Information Bottleneck Model for Accurate Indoor Position Recognition
Paper and Code
Jan 26, 2021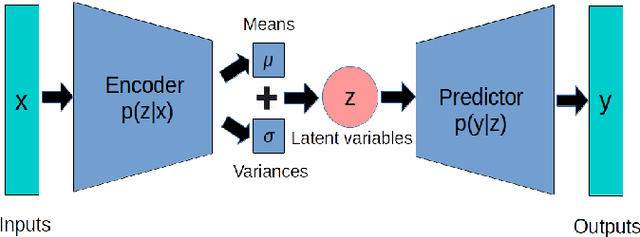
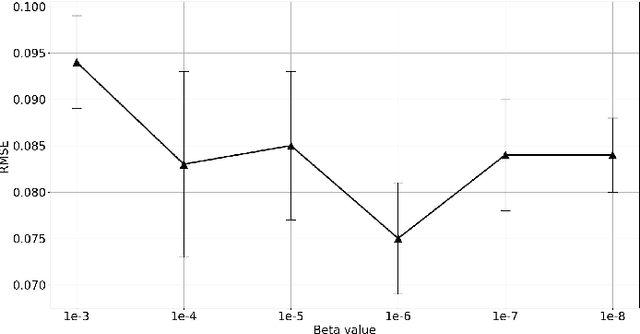
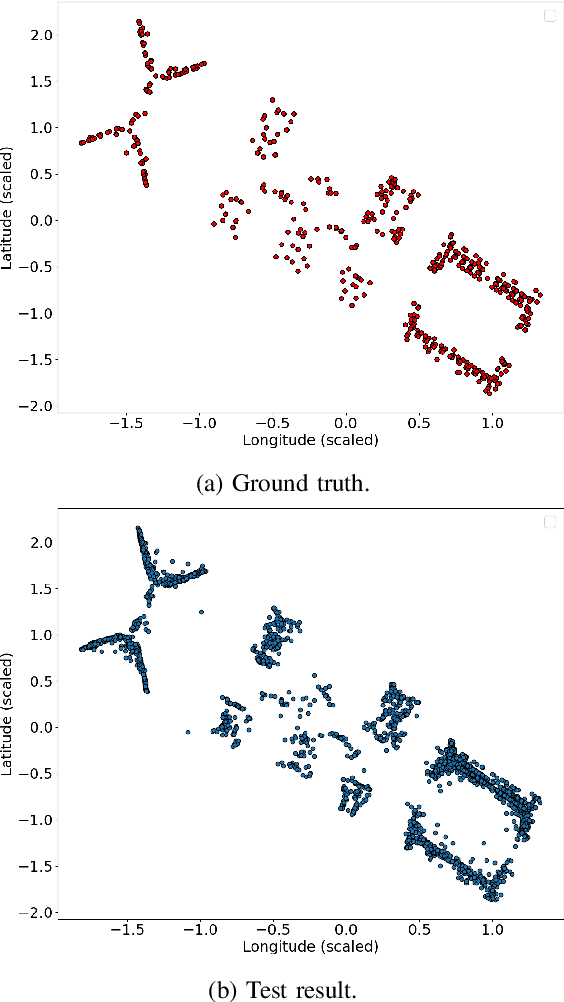
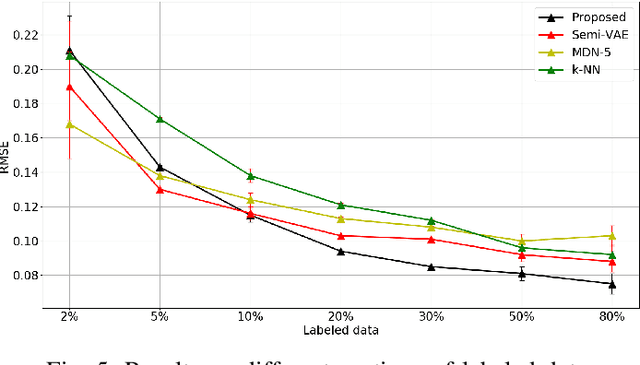
Recognizing user location with WiFi fingerprints is a popular approach for accurate indoor positioning problems. In this work, our goal is to interpret WiFi fingerprints into actual user locations. However, WiFi fingerprint data can be very high dimensional in some cases, we need to find a good representation of the input data for the learning task first. Otherwise, using neural networks will suffer from severe overfitting. In this work, we solve this issue by combining the Information Bottleneck method and Variational Inference. Based on these two approaches, we propose a Variational Information Bottleneck model for accurate indoor positioning. The proposed model consists of an encoder structure and a predictor structure. The encoder is to find a good representation in the input data for the learning task. The predictor is to use the latent representation to predict the final output. To enhance the generalization of our model, we also adopt the Dropout technique for each hidden layer of the decoder. We conduct the validation experiments on a real-world dataset. We also compare the proposed model to other existing methods so as to quantify the performances of our method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge