Using Recurrent Neural Networks to Optimize Dynamical Decoupling for Quantum Memory
Paper and Code
Sep 17, 2016
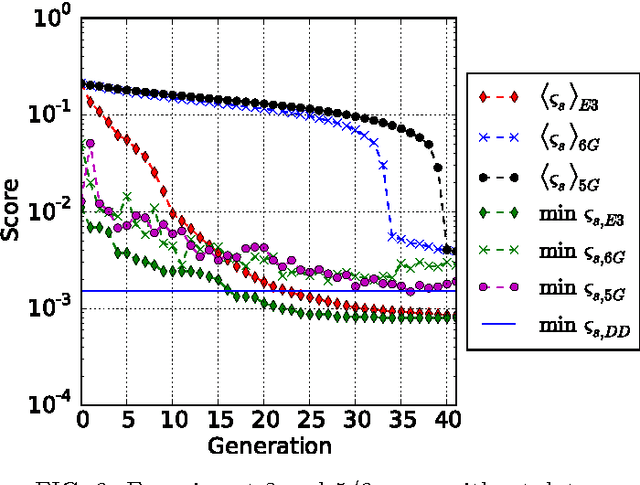


We utilize machine learning models which are based on recurrent neural networks to optimize dynamical decoupling (DD) sequences. DD is a relatively simple technique for suppressing the errors in quantum memory for certain noise models. In numerical simulations, we show that with minimum use of prior knowledge and starting from random sequences, the models are able to improve over time and eventually output DD-sequences with performance better than that of the well known DD-families. Furthermore, our algorithm is easy to implement in experiments to find solutions tailored to the specific hardware, as it treats the figure of merit as a black box.
* Phys. Rev. A 95, 012335 (2017) * 18 pages, comments are welcome
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge