Using Belief Theory to Diagnose Control Knowledge Quality. Application to cartographic generalisation
Paper and Code
Apr 23, 2012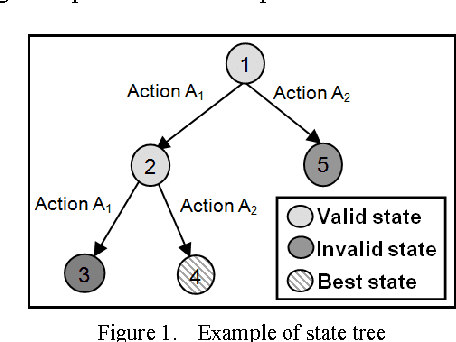
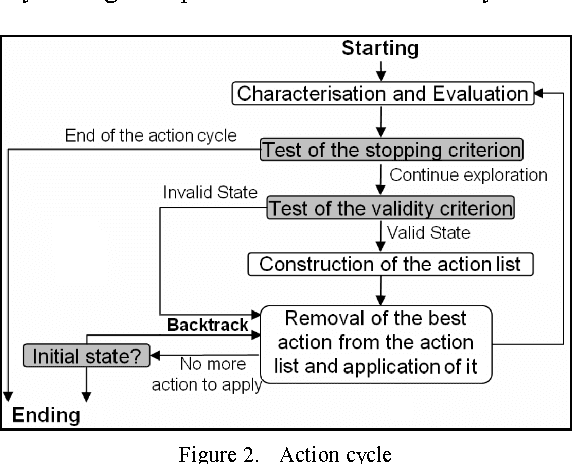
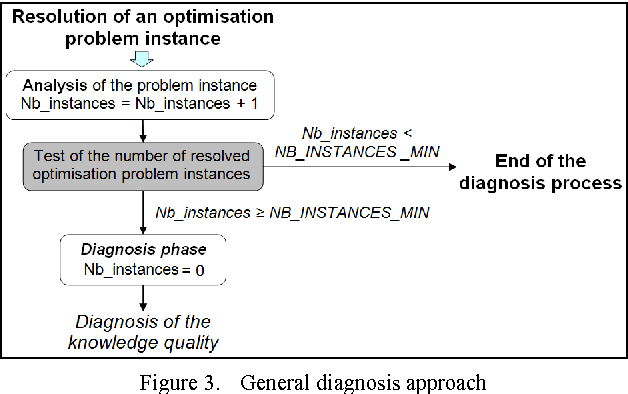
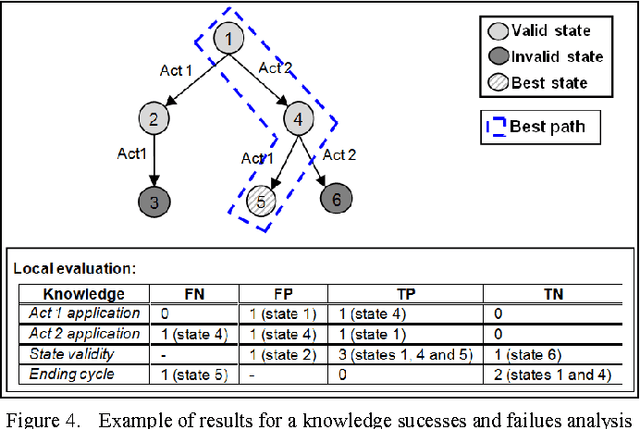
Both humans and artificial systems frequently use trial and error methods to problem solving. In order to be effective, this type of strategy implies having high quality control knowledge to guide the quest for the optimal solution. Unfortunately, this control knowledge is rarely perfect. Moreover, in artificial systems-as in humans-self-evaluation of one's own knowledge is often difficult. Yet, this self-evaluation can be very useful to manage knowledge and to determine when to revise it. The objective of our work is to propose an automated approach to evaluate the quality of control knowledge in artificial systems based on a specific trial and error strategy, namely the informed tree search strategy. Our revision approach consists in analysing the system's execution logs, and in using the belief theory to evaluate the global quality of the knowledge. We present a real-world industrial application in the form of an experiment using this approach in the domain of cartographic generalisation. Thus far, the results of using our approach have been encouraging.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge