Unsupervised learning with GLRM feature selection reveals novel traumatic brain injury phenotypes
Paper and Code
Nov 30, 2018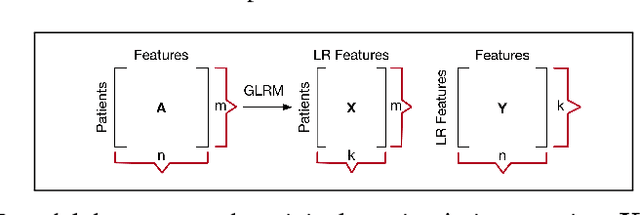
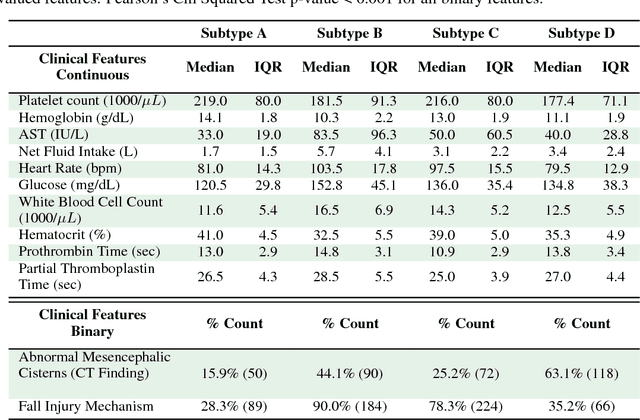
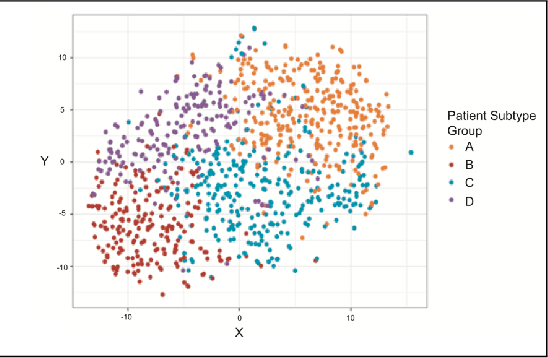
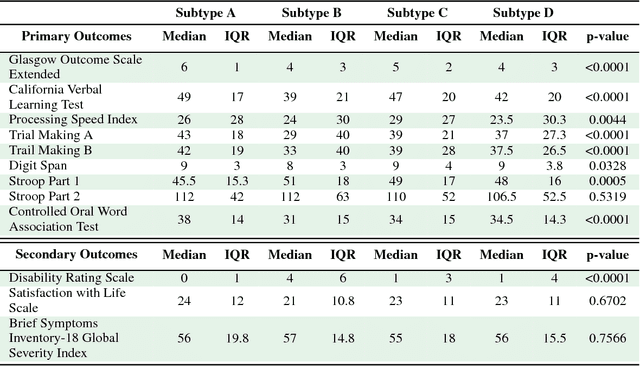
Baseline injury categorization is important to traumatic brain injury (TBI) research and treatment. Current categorization is dominated by symptom-based scores that insufficiently capture injury heterogeneity. In this work, we apply unsupervised clustering to identify novel TBI phenotypes. Our approach uses a generalized low-rank model (GLRM) model for feature selection in a procedure analogous to wrapper methods. The resulting clusters reveal four novel TBI phenotypes with distinct feature profiles and that correlate to 90-day functional and cognitive status.
* Machine Learning for Health (ML4H) Workshop at NeurIPS 2018
arXiv:1811.07216
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge