Two Use Cases of Machine Learning for SDN-Enabled IP/Optical Networks: Traffic Matrix Prediction and Optical Path Performance Prediction
Paper and Code
Jun 12, 2018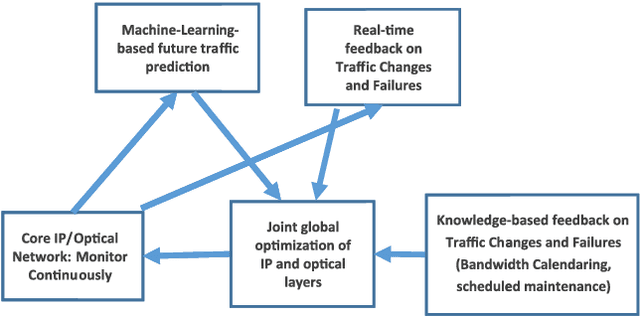
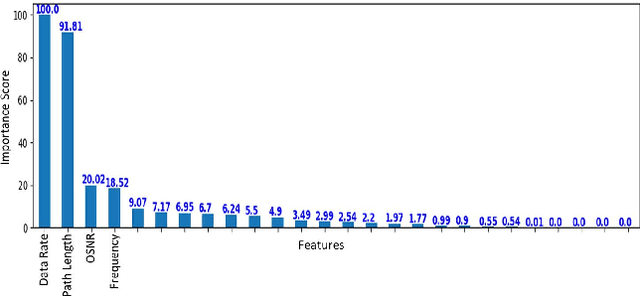
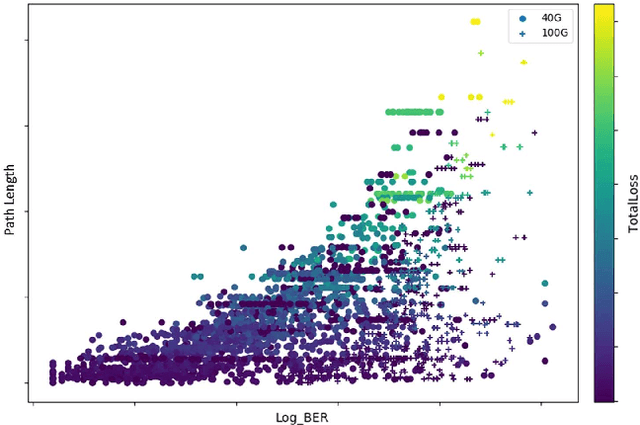
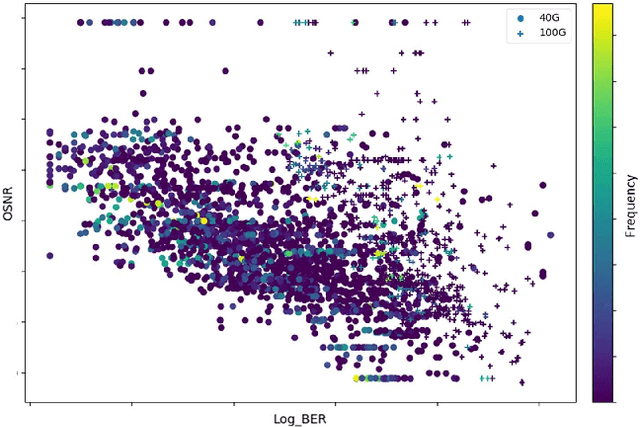
We describe two applications of machine learning in the context of IP/Optical networks. The first one allows agile management of resources at a core IP/Optical network by using machine learning for short-term and long-term prediction of traffic flows and joint global optimization of IP and optical layers using colorless/directionless (CD) flexible ROADMs. Multilayer coordination allows for significant cost savings, flexible new services to meet dynamic capacity needs, and improved robustness by being able to proactively adapt to new traffic patterns and network conditions. The second application is important as we migrate our metro networks to Open ROADM networks, to allow physical routing without the need for detailed knowledge of optical parameters. We discuss a proof-of-concept study, where detailed performance data for wavelengths on a current flexible ROADM network is used for machine learning to predict the optical performance of each wavelength. Both applications can be efficiently implemented by using a SDN (Software Defined Network) controller.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge