Transmitter Selection for Secrecy in a Frequency Selective Fading Channel with Unreliable Backhaul
Paper and Code
Feb 17, 2021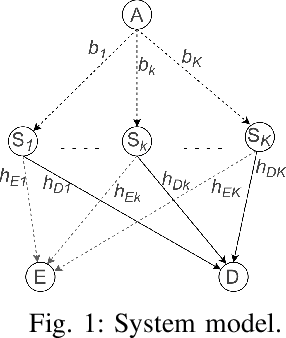
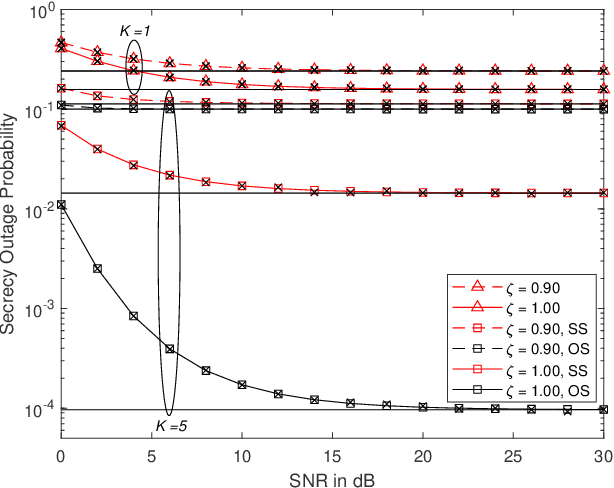
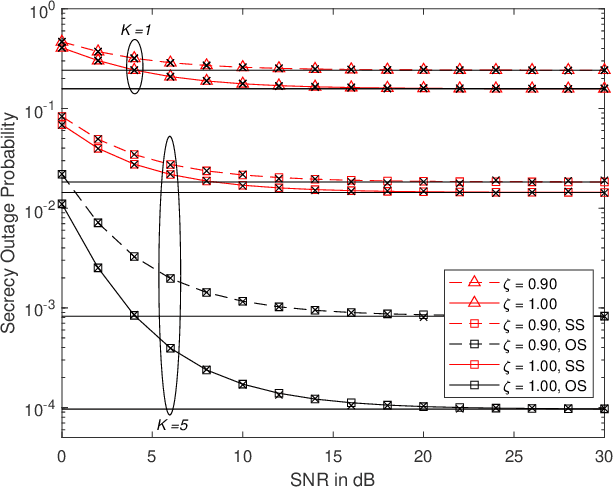
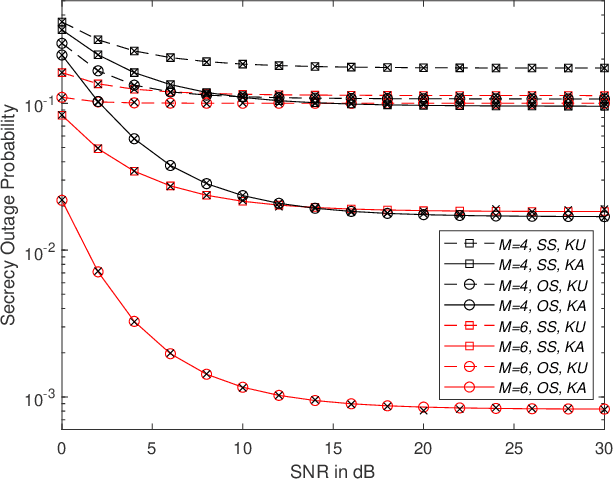
In this paper, a communication network using single carrier with cyclic prefix modulation over frequency selective channels is considered, where an access point provides connectivity to a legitimate destination through multiple transmitters with unreliable backhaul links in the presence of an eavesdropper. A sub-optimal and an optimal transmitter selection scheme are proposed to improve the secrecy of the system, depending on whether the active backhaul channel knowledge is available a priori or not. The secrecy outage probability (SOP) and its asymptotic limit are presented in closed-form. This provides some insights regarding how knowledge of the active backhaul links affects the secrecy performance of the network. Our results show that the optimal transmitter selection scheme obtains a larger benefit than the sub-optimal scheme from the knowledge of the active backhaul links, resulting in a significantly improved system performance; however, the sub-optimal transmitter selection scheme can reduce the complexity and feedback overhead.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge