Tomographic Reconstruction and Regularisation with Search Space Expansion and Total Variation
Paper and Code
Jun 03, 2024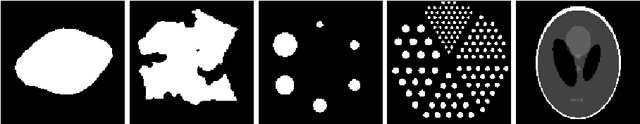
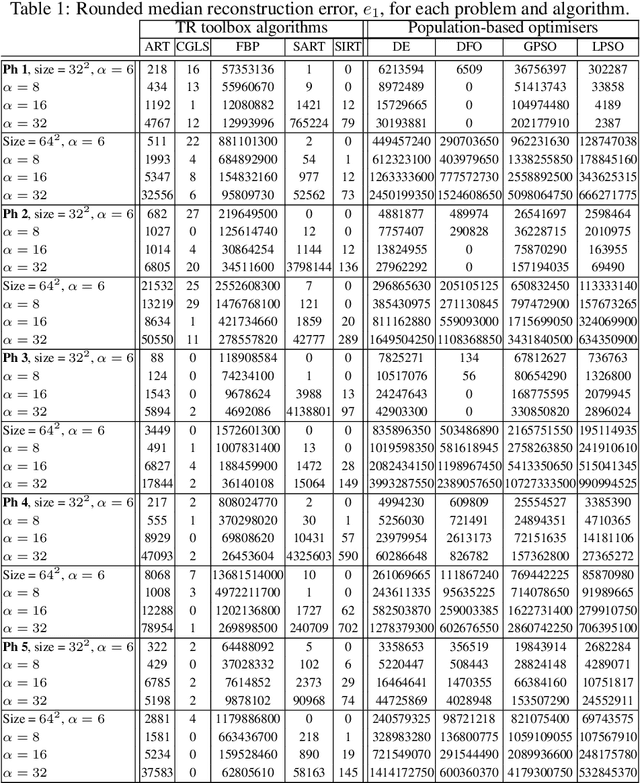
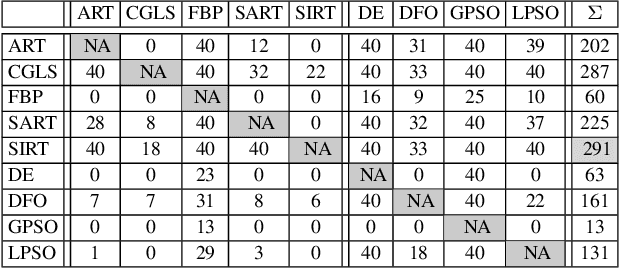
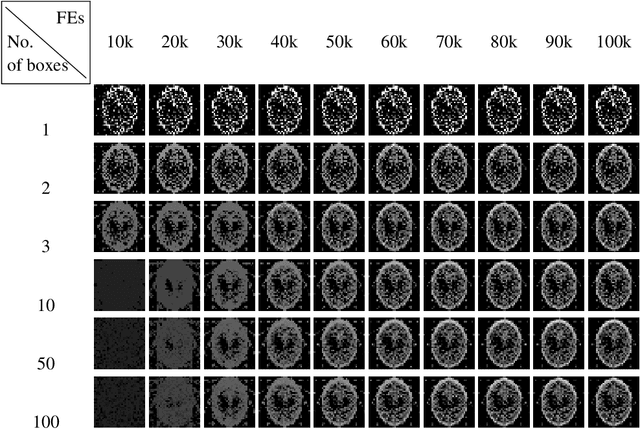
The use of ray projections to reconstruct images is a common technique in medical imaging. Dealing with incomplete data is particularly important when a patient is vulnerable to potentially damaging radiation or is unable to cope with the long scanning time. This paper utilises the reformulation of the problem into an optimisation tasks, followed by using a swarm-based reconstruction from highly undersampled data where particles move in image space in an attempt to minimise the reconstruction error. The process is prone to noise and, in addition to the recently introduced search space expansion technique, a further smoothing process, total variation regularisation, is adapted and investigated. The proposed method is shown to produce lower reproduction errors compared to standard tomographic reconstruction toolbox algorithms as well as one of the leading high-dimensional optimisers on the clinically important Shepp-Logan phantom.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge