TMS-Crossbars with Tactile Sensing
Paper and Code
Nov 14, 2021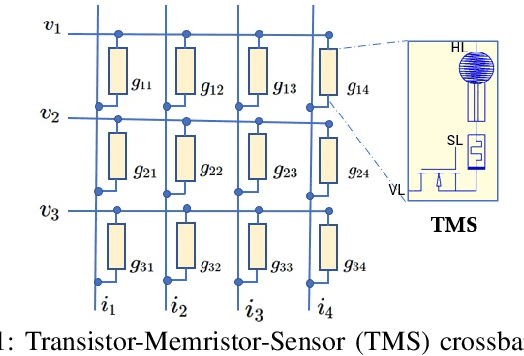
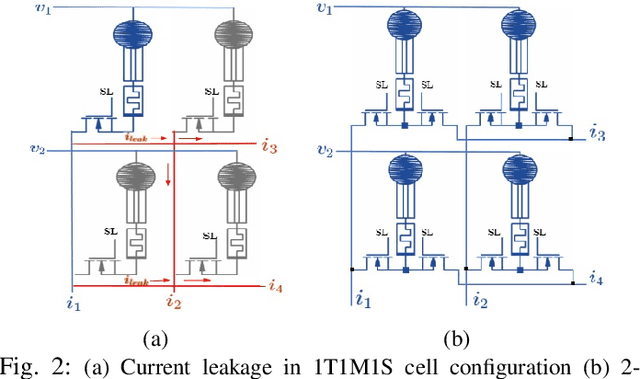
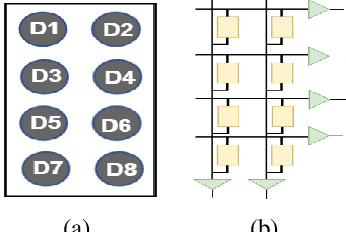
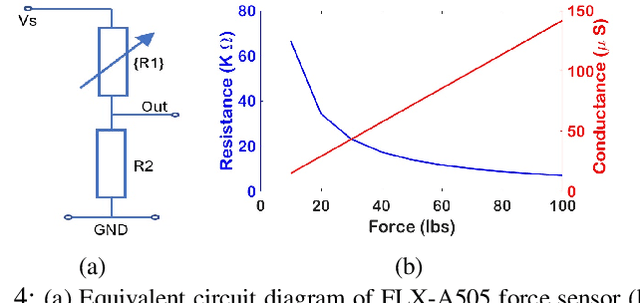
The first stage of tactile sensing is data acquisition using tactile sensors and the sensed data is transmitted to the central unit for neuromorphic computing. The memristive crossbars were proposed to use as synapses in neuromorphic computing but device intelligence at the sensor level are not investigated in literature. We propose the concept of Transistor Memristor Sensor (TMS)-crossbar by including sensor to memristor crossbar array configuration in the input layer of the neural network architecture. 2 possible cell configurations of TMS crossbar arrays: 1 Transistor 1 Memristor 1 Sensor (1T1M1S) and 2 Transistor 1 Memristor 1 Sensor (2T1M1S) are presented. We verified the proposed TMS-crossbar in the practical design of analog neural networks based Braille character recognition system. The proposed design is verified with SPICE simulations using circuit equivalent of FLX-A501 force sensor, TiO$_2$ memristors and low power 22nm high-k CMOS transistors. The proposed analog neuromorphic computing system presents a scalable solution and is possible to encode 125 symbols with good accuracy in comparison with other Braille character recognition systems in the literature. The benefits of analog implementation of the TMS crossbar arrays is substantiated with results of accuracy, area and power requirements in comparison with the binary counterparts.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge