Systematic Unsupervised Recycled Field-Programmable Gate Array Detection
Paper and Code
Apr 05, 2022


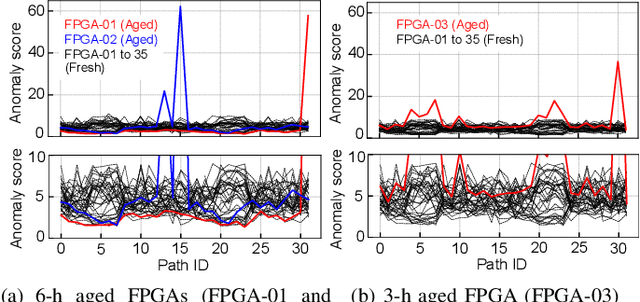
With the expansion of the semiconductor supply chain, the use of recycled field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs) has become a serious concern. Several methods for detecting recycled FPGAs by analyzing the ring oscillator (RO) frequencies have been proposed; however, most assume the known fresh FPGAs (KFFs) as the training data in machine-learning-based classification. In this study, we propose a novel recycled FPGA detection method based on an unsupervised anomaly detection scheme when there are few or no KFFs available. As the RO frequencies in the neighboring logic blocks on an FPGA are similar because of systematic process variation, our method compares the RO frequencies and does not require KFFs. The proposed method efficiently identifies recycled FPGAs through outlier detection using direct density ratio estimation. Experiments using Xilinx Artix-7 FPGAs demonstrate that the proposed method successfully distinguishes recycled FPGAs from 35 fresh FPGAs. In contrast, a conventional recycled FPGA detection method results in certain misclassification.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge