Stochastic Geometry Based Modelling and Analysis of Uplink Cooperative Satellite-Aerial-Terrestrial Networks for Nomadic Communications with Weak Satellite Coverage
Paper and Code
Aug 27, 2024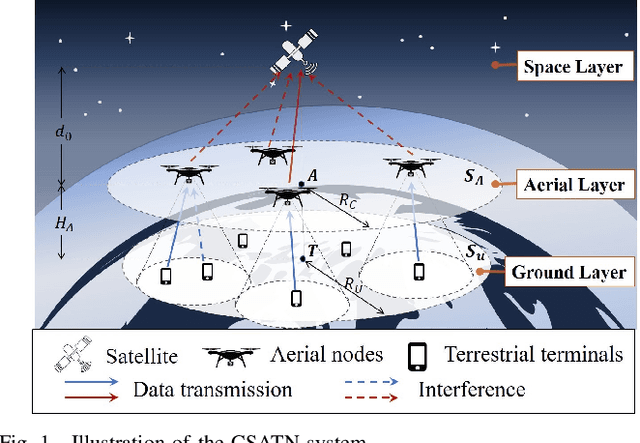
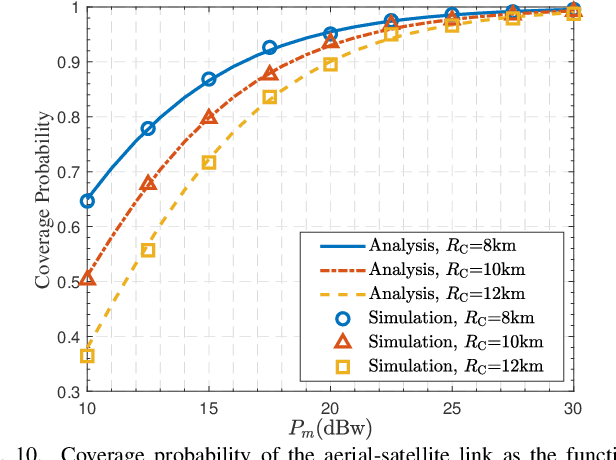
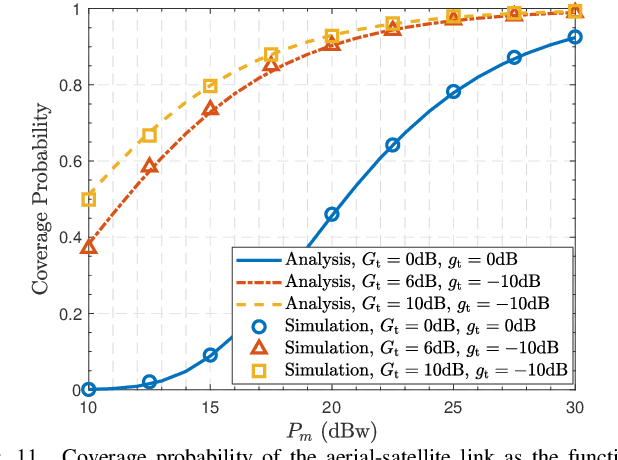
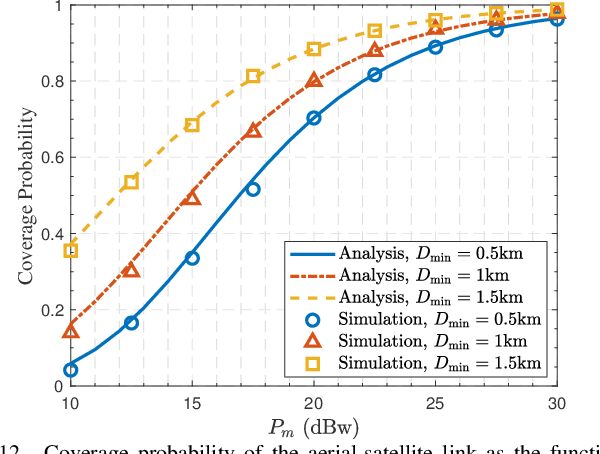
Cooperative satellite-aerial-terrestrial networks (CSATNs), where unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) are utilized as nomadic aerial relays (A), are highly valuable for many important applications, such as post-disaster urban reconstruction. In this scenario, direct communication between terrestrial terminals (T) and satellites (S) is often unavailable due to poor propagation conditions for satellite signals, and users tend to congregate in regions of finite size. There is a current dearth in the open literature regarding the uplink performance analysis of CSATN operating under the above constraints, and the few contributions on the uplink model terrestrial terminals by a Poisson point process (PPP) relying on the unrealistic assumption of an infinite area. This paper aims to fill the above research gap. First, we propose a stochastic geometry based innovative model to characterize the impact of the finite-size distribution region of terrestrial terminals in the CSATN by jointly using a binomial point process (BPP) and a type-II Mat{\'e}rn hard-core point process (MHCPP). Then, we analyze the relationship between the spatial distribution of the coverage areas of aerial nodes and the finite-size distribution region of terrestrial terminals, thereby deriving the distance distribution of the T-A links. Furthermore, we consider the stochastic nature of the spatial distributions of terrestrial terminals and UAVs, and conduct a thorough analysis of the coverage probability and average ergodic rate of the T-A links under Nakagami fading and the A-S links under shadowed-Rician fading. Finally, the accuracy of our theoretical derivations are confirmed by Monte Carlo simulations. Our research offers fundamental insights into the system-level performance optimization for the realistic CSATNs involving nomadic aerial relays and terrestrial terminals confined in a finite-size region.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge