State Estimation for Human Motion and Humanoid Locomotion
Paper and Code
Jun 08, 2022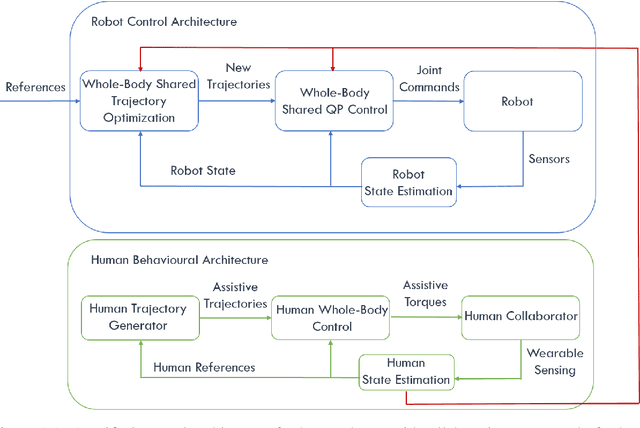
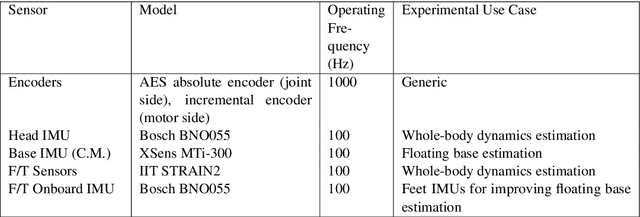
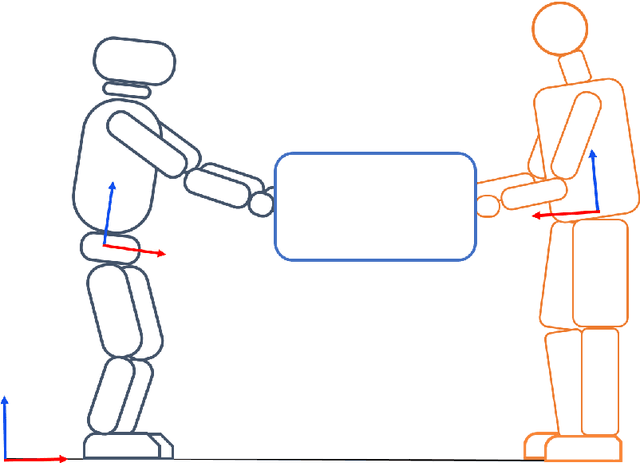

The future where the industrial shop-floors witness humans and robots working in unison and the domestic households becoming a shared space for both these agents is not very far. The scientific community has been accelerating towards that future by extending their research efforts in human-robot interaction towards human-robot collaboration. It is possible that the anthropomorphic nature of the humanoid robots could deem the most suitable for such collaborations in semi-structured, human-centered environments. Wearable sensing technologies for human agents and efficient human-aware control strategies for the humanoid robot will be key in achieving a seamless human-humanoid collaboration. This is where reliable state estimation strategies become crucial in making sense of the information coming from multiple distributed sensors attached to the human and those on the robot to augment the feedback controllers designed for the humanoid robot to aid their human counterparts. In this context, this thesis investigates the theory of Lie groups for designing state estimation techniques aimed towards humanoid locomotion and human motion estimation. [continued]
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge