SOMPS-Net : Attention based social graph framework for early detection of fake health news
Paper and Code
Nov 22, 2021
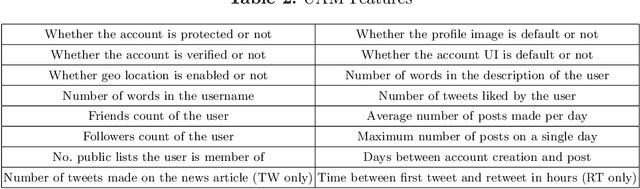

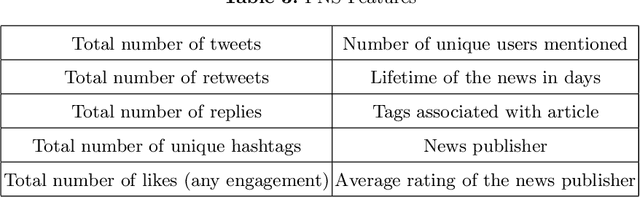
Fake news is fabricated information that is presented as genuine, with intention to deceive the reader. Recently, the magnitude of people relying on social media for news consumption has increased significantly. Owing to this rapid increase, the adverse effects of misinformation affect a wider audience. On account of the increased vulnerability of people to such deceptive fake news, a reliable technique to detect misinformation at its early stages is imperative. Hence, the authors propose a novel graph-based framework SOcial graph with Multi-head attention and Publisher information and news Statistics Network (SOMPS-Net) comprising of two components - Social Interaction Graph (SIG) and Publisher and News Statistics (PNS). The posited model is experimented on the HealthStory dataset and generalizes across diverse medical topics including Cancer, Alzheimer's, Obstetrics, and Nutrition. SOMPS-Net significantly outperformed other state-of-the-art graph-based models experimented on HealthStory by 17.1%. Further, experiments on early detection demonstrated that SOMPS-Net predicted fake news articles with 79% certainty within just 8 hours of its broadcast. Thus the contributions of this work lay down the foundation for capturing fake health news across multiple medical topics at its early stages.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge